Lecture 1 - ComLabGames
... Under what conditions does your best response depend on the choices of the other players? ...
... Under what conditions does your best response depend on the choices of the other players? ...
6.1 Discrete vs Continuous Random Variables
... bet, a player places his chips on the intersection of four numbered squares on the roulette table. If one of these numbers comes up on the wheel and the player bet $1, the player gets his $1 back plus $8 more. Otherwise, the casino keeps the original $1 bet. If X=net gain from a single $1 corner bet ...
... bet, a player places his chips on the intersection of four numbered squares on the roulette table. If one of these numbers comes up on the wheel and the player bet $1, the player gets his $1 back plus $8 more. Otherwise, the casino keeps the original $1 bet. If X=net gain from a single $1 corner bet ...
Computer Games - CSE, IIT Bombay
... β is current lowest for α’s from that move For next possible node, while finding β, if some α ...
... β is current lowest for α’s from that move For next possible node, while finding β, if some α ...
Evolutionary game theory
... that all individuals can share there is always selection pressure to take more than a fair share, often resulting in the overuse and demise of the common good (Hardin 1968). As a final example of this point consider the Prisoner’s Dilemma game (e.g. Axelrod & Hamilton 1981). This game is played betw ...
... that all individuals can share there is always selection pressure to take more than a fair share, often resulting in the overuse and demise of the common good (Hardin 1968). As a final example of this point consider the Prisoner’s Dilemma game (e.g. Axelrod & Hamilton 1981). This game is played betw ...
NOTES ON NASH EQUILIBRIUM 1. 2 × 2 games, pure
... Both Ruth and Charlie deciding to testify is a Nash equilibrium: • Charlie testifying, Ruth finds herself better off by testifying (-10) than by not testifying (-15); • Ruth testifying, Charlie finds himself better off by testifying (-10) than by not testifying (-15). Note that Ruth and Charlie woul ...
... Both Ruth and Charlie deciding to testify is a Nash equilibrium: • Charlie testifying, Ruth finds herself better off by testifying (-10) than by not testifying (-15); • Ruth testifying, Charlie finds himself better off by testifying (-10) than by not testifying (-15). Note that Ruth and Charlie woul ...
Computing the Optimal Strategy to Commit to
... as long as one can credibly show that one cannot change the code later, the code serves as a commitment device. This holds true for recreational tournaments among agents (e.g., poker tournaments, RoboSoccer), and for industrial applications such as sensor webs. Finally, there is also an implicit lea ...
... as long as one can credibly show that one cannot change the code later, the code serves as a commitment device. This holds true for recreational tournaments among agents (e.g., poker tournaments, RoboSoccer), and for industrial applications such as sensor webs. Finally, there is also an implicit lea ...
Homogeneous Product Oligopoly
... Result - PSNE: p = MC = ATC (number of firms doesn't matter; ≥ 2) Bertrand Paradox - huge monopoly/duopoly discontinuity; go from monopoly output to perfect competition (p = MC) by going from 1 firm to 2 firms; Hamilton said people who call it a paradox "don't understand the Bertrand model" How Gene ...
... Result - PSNE: p = MC = ATC (number of firms doesn't matter; ≥ 2) Bertrand Paradox - huge monopoly/duopoly discontinuity; go from monopoly output to perfect competition (p = MC) by going from 1 firm to 2 firms; Hamilton said people who call it a paradox "don't understand the Bertrand model" How Gene ...
Computing Stackelberg Strategies in Stochastic
... turns out that if we allow for the type of signaling discussed in the previous section, then QPACE can be modified to compute an optimal strategy for a Stackelberg leader in a stochastic game. By running both algorithms on randomly generated games, we obtain some insight into how valuable the abilit ...
... turns out that if we allow for the type of signaling discussed in the previous section, then QPACE can be modified to compute an optimal strategy for a Stackelberg leader in a stochastic game. By running both algorithms on randomly generated games, we obtain some insight into how valuable the abilit ...
GAMES THEORY: MARKET BEHAVIOUR CURSO: TERCERO
... others. In turn, our payoff (compensation, well-being) is often affected by the choices made by others. In simpler terms, people often operate in situations of strategic interaction. Game Theory is the discipline that studies strategic interaction. We will present the concepts required to analyze di ...
... others. In turn, our payoff (compensation, well-being) is often affected by the choices made by others. In simpler terms, people often operate in situations of strategic interaction. Game Theory is the discipline that studies strategic interaction. We will present the concepts required to analyze di ...
A note on pre-play communication
... An alternative approach to the study of credible pre-play communication is to use dynamic arguments. Players may use past interactions to arrive at common understanding of messages. This approach is intuitive and leads to useful formal results. Demichelis (2012), Demichelis and Weibull (2008), and S ...
... An alternative approach to the study of credible pre-play communication is to use dynamic arguments. Players may use past interactions to arrive at common understanding of messages. This approach is intuitive and leads to useful formal results. Demichelis (2012), Demichelis and Weibull (2008), and S ...
Lecture notes - MIT OpenCourseWare
... to Alice’s strategy: under this strategy he gets 2, which is the highest he can get in this game. One can, however, discredit the latter Nash equilibrium because it relies on an sequentially irrational move at the node after Alice goes to Opera. This node does not happen according to Alice’s strateg ...
... to Alice’s strategy: under this strategy he gets 2, which is the highest he can get in this game. One can, however, discredit the latter Nash equilibrium because it relies on an sequentially irrational move at the node after Alice goes to Opera. This node does not happen according to Alice’s strateg ...
Agent-Based Modeling of Coporate Takeover
... of synergy gains impounded in the tender price (0.50 in the simulations) and in the limit, as the number of shareholders increases to infinity fraction of shares tendered must converge to the fraction sought (50% + 1 share in the simulations). ...
... of synergy gains impounded in the tender price (0.50 in the simulations) and in the limit, as the number of shareholders increases to infinity fraction of shares tendered must converge to the fraction sought (50% + 1 share in the simulations). ...
Cartels and collusion in oligopoly • Single-period non
... Subgame-Perfect Equilibrium 1 • Game: model of interaction between a group of players (prisoners, firms, people) • Each player (or firm) attempts to maximize its own payoffs • Multi-period game most conveniently represented by a game tree. Nodes are junctures of game tree, at which a player moves. ...
... Subgame-Perfect Equilibrium 1 • Game: model of interaction between a group of players (prisoners, firms, people) • Each player (or firm) attempts to maximize its own payoffs • Multi-period game most conveniently represented by a game tree. Nodes are junctures of game tree, at which a player moves. ...
updated version for the 2015 Superbowl
... Definition: A combination of strategies is a Nash (non-cooperative) equilibrium if each player’s strategy is best, given the strategies chosen by the other players. The Nash equilibrium is a “mutual best response” in the sense that each player is correctly assessing the strategies of all other playe ...
... Definition: A combination of strategies is a Nash (non-cooperative) equilibrium if each player’s strategy is best, given the strategies chosen by the other players. The Nash equilibrium is a “mutual best response” in the sense that each player is correctly assessing the strategies of all other playe ...
Karl Sigmund Review
... rationality are as far removed from the everyday use of that word as modern theology’s concepts of divinity are from the average layperson’s idea of the Good Lord). Psychologists, for instance, analyze decisions in terms of (often unconscious) cues and heuristics, and are not likely to switch to th ...
... rationality are as far removed from the everyday use of that word as modern theology’s concepts of divinity are from the average layperson’s idea of the Good Lord). Psychologists, for instance, analyze decisions in terms of (often unconscious) cues and heuristics, and are not likely to switch to th ...
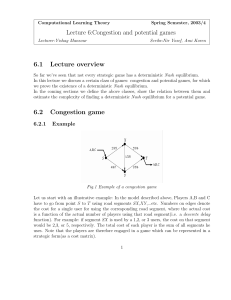
Lecture 6:Congestion and potential games 6.1 Lecture overview 6.2
... Definition A function Φ: A → R is an exact potential for game G if ∀~a∈A ∀ai ,bi ∈Ai Φ(bi , a~−i ) − Φ(ai , a~−i ) = ui (bi , a~−i ) − ui (ai , a~−i ) Definition A function Φ: A → R is a weighted potential for game G if ∀~a∈A ∀ai ,bi ∈Ai Φ(bi , a~−i ) − Φ(ai , a~−i ) = ωi (ui (bi , a~−i ) − ui (ai , ...
... Definition A function Φ: A → R is an exact potential for game G if ∀~a∈A ∀ai ,bi ∈Ai Φ(bi , a~−i ) − Φ(ai , a~−i ) = ui (bi , a~−i ) − ui (ai , a~−i ) Definition A function Φ: A → R is a weighted potential for game G if ∀~a∈A ∀ai ,bi ∈Ai Φ(bi , a~−i ) − Φ(ai , a~−i ) = ωi (ui (bi , a~−i ) − ui (ai , ...
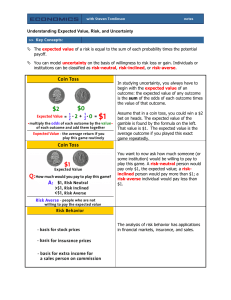
Understanding Expected Value, Risk, and Uncertainty The expected
... You can model uncertainty on the basis of willingness to risk loss or gain. Individuals or institutions can be classified as risk-neutral, risk-inclined, or risk-averse. In studying uncertainty, you always have to begin with the expected value of an outcome: the expected value of any outcome is the ...
... You can model uncertainty on the basis of willingness to risk loss or gain. Individuals or institutions can be classified as risk-neutral, risk-inclined, or risk-averse. In studying uncertainty, you always have to begin with the expected value of an outcome: the expected value of any outcome is the ...
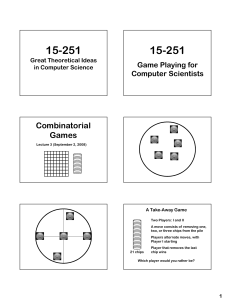
Combinatorial Games
... chomp on (1,1), leaving only an “L” shaped position Then, for any move that Player II takes, Player I can simply mirror it on the flip side of the “L” ...
... chomp on (1,1), leaving only an “L” shaped position Then, for any move that Player II takes, Player I can simply mirror it on the flip side of the “L” ...
A Game Theory Approach to Policy-Making
... into the model.That this is desirable for economic modelling has been compellingly argued by Conlisk (1996) and others (see for example Dawnay and Shah (2005)). For example, legal scholars have begun to stress that bounded rationality must be taken into account when designing policies with punitive ...
... into the model.That this is desirable for economic modelling has been compellingly argued by Conlisk (1996) and others (see for example Dawnay and Shah (2005)). For example, legal scholars have begun to stress that bounded rationality must be taken into account when designing policies with punitive ...
Sprouts - Suffolk Maths
... The line must go from a dot to a dot so that it does not cross another line and so that once the line is draw, no dot has more then three lines coming out of it. The animated game marks these used-up dots with red X's. You might want to circle used-up dots. The new dot goes on the line the player ju ...
... The line must go from a dot to a dot so that it does not cross another line and so that once the line is draw, no dot has more then three lines coming out of it. The animated game marks these used-up dots with red X's. You might want to circle used-up dots. The new dot goes on the line the player ju ...
Lecture 31: Duopoly
... which two players have to choose simultaneously the value of some decision variables, the values of which affect both players. • We introduced the idea of a Nash Equilibrium in which each is optimising given the decision of the other. • Today we will apply that in Duopoly. ...
... which two players have to choose simultaneously the value of some decision variables, the values of which affect both players. • We introduced the idea of a Nash Equilibrium in which each is optimising given the decision of the other. • Today we will apply that in Duopoly. ...
Expected Value
... • We place a $1 chip on 7. If the ball lands in the 7 slot we win $35 (net winnings). If the ball lands on any other number we lose our $1 chip. • What is the expectation of this bet? • To answer this question we need to know the probability of winning and losing. • The probability of winning is 1/3 ...
... • We place a $1 chip on 7. If the ball lands in the 7 slot we win $35 (net winnings). If the ball lands on any other number we lose our $1 chip. • What is the expectation of this bet? • To answer this question we need to know the probability of winning and losing. • The probability of winning is 1/3 ...
RecSports Mixed Ultimate Frisbee Rules
... Rule 1: Players The roster limit is 11. Each team shall consist of seven players on the field, however, a game may begin with as few as five players There must be at least two of each gender on the field to begin the game (3 girls, 2 guys or 3 guys, 2 girls). Substitution Substitutions may o ...
... Rule 1: Players The roster limit is 11. Each team shall consist of seven players on the field, however, a game may begin with as few as five players There must be at least two of each gender on the field to begin the game (3 girls, 2 guys or 3 guys, 2 girls). Substitution Substitutions may o ...