Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation FOURTH EDITION by Steven
... – all elements on reactants side also on product side – equal numbers of atoms of each element on reactant side as on product side ...
... – all elements on reactants side also on product side – equal numbers of atoms of each element on reactant side as on product side ...
Atomic Structure
... The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons Neutral oxygen has 8 protons, therefore it has 8 electrons Neutral lead has 82 protons, therefore, it has 82 electrons ...
... The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons Neutral oxygen has 8 protons, therefore it has 8 electrons Neutral lead has 82 protons, therefore, it has 82 electrons ...
Group 2 Elements
... elements down the group •know the reactions of the elements Mg to Ba in Group 2 with oxygen, chlorine and water •understand the formation of characteristic flame colours by Group 1 and 2 compounds in terms of electron transitions •know the flame colours for Groups 1 and 2 compounds •understand exper ...
... elements down the group •know the reactions of the elements Mg to Ba in Group 2 with oxygen, chlorine and water •understand the formation of characteristic flame colours by Group 1 and 2 compounds in terms of electron transitions •know the flame colours for Groups 1 and 2 compounds •understand exper ...
Standard 1:Atomic Structure + Elements, Compounds, Mixtures
... The atomic mass is an average the estimated world supply of that atom. Some atoms have the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons. These are called isotopes Carbon-14 is an isotope of carbon because it has 2 extra neutrons. Isotopes are sometimes radioactive ...
... The atomic mass is an average the estimated world supply of that atom. Some atoms have the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons. These are called isotopes Carbon-14 is an isotope of carbon because it has 2 extra neutrons. Isotopes are sometimes radioactive ...
Early Atomic Theory
... Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. Electrons are dispersed throughout the remainder of the atom (mainly open space). Neutral atoms contain the same number of protons and neutrons to maintain charge balance. ...
... Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. Electrons are dispersed throughout the remainder of the atom (mainly open space). Neutral atoms contain the same number of protons and neutrons to maintain charge balance. ...
Flexbook - What is Matter?
... the substance is an element. Elements cannot be chemically broken down into anything smaller and still retain the properties of the element. For example, an atom of iron can be smashed into electrons, protons, and neutrons, but those pieces would not have the properties of iron. Atoms from two or mo ...
... the substance is an element. Elements cannot be chemically broken down into anything smaller and still retain the properties of the element. For example, an atom of iron can be smashed into electrons, protons, and neutrons, but those pieces would not have the properties of iron. Atoms from two or mo ...
atomic number
... nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. For example, any atom with 6 protons in the nucleus is a Carbon atom. • Elements are arranged in the periodic table by their atomic number. • In a neutral atom, # electrons = #protons. • The symbol for an element is simply its 1, 2, or 3 letter abbrevi ...
... nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. For example, any atom with 6 protons in the nucleus is a Carbon atom. • Elements are arranged in the periodic table by their atomic number. • In a neutral atom, # electrons = #protons. • The symbol for an element is simply its 1, 2, or 3 letter abbrevi ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... of that ELEMENT 3. Democritus’s GREEK term “____________,” which means “not able to be divided,” is the ORIGIN of the word, ___________ *4. Individual ATOMS are so __________ they can only be seen using a scanning tunneling MICROSCOPE (STM), a special type of ELECTRON microscope *a. Due to their ___ ...
... of that ELEMENT 3. Democritus’s GREEK term “____________,” which means “not able to be divided,” is the ORIGIN of the word, ___________ *4. Individual ATOMS are so __________ they can only be seen using a scanning tunneling MICROSCOPE (STM), a special type of ELECTRON microscope *a. Due to their ___ ...
Teacher quality grant - Gulf Coast State College
... can achieve this by sharing electrons in a covalent bond. 2 The nuclei come closer together and the two electrons begin to circle around both of them. The new H2 molecule is very ...
... can achieve this by sharing electrons in a covalent bond. 2 The nuclei come closer together and the two electrons begin to circle around both of them. The new H2 molecule is very ...
Teacher quality grant
... can achieve this by sharing electrons in a covalent bond. 2 The nuclei come closer together and the two electrons begin to circle around both of them. The new H2 molecule is very ...
... can achieve this by sharing electrons in a covalent bond. 2 The nuclei come closer together and the two electrons begin to circle around both of them. The new H2 molecule is very ...
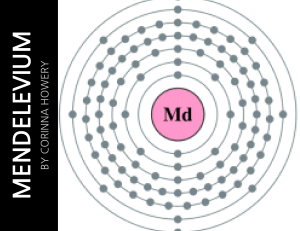
Mendelevium
... table so its atomic number is 101. There are 101 protons/electrons in the nucleus and 157 neutrons. It also has 2 valence electrons. Mendelevium has 7 shells. On the periodic table, mendelevium is in the group actinide and it is radioactive. Mendeleviums state of matter is radioactive. ...
... table so its atomic number is 101. There are 101 protons/electrons in the nucleus and 157 neutrons. It also has 2 valence electrons. Mendelevium has 7 shells. On the periodic table, mendelevium is in the group actinide and it is radioactive. Mendeleviums state of matter is radioactive. ...
e - Humble ISD
... He fired Helium nuclei at a piece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick. He found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit and bounced back. ...
... He fired Helium nuclei at a piece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick. He found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit and bounced back. ...
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... the operations of art and nature, nothing is created; an equal amount of matter exists both before and after the experiment. Upon this principle, the whole art of performing chemical ...
... the operations of art and nature, nothing is created; an equal amount of matter exists both before and after the experiment. Upon this principle, the whole art of performing chemical ...
ATOMS:
... Isotopes : naturally occurring versions of an element that vary in the numbers of neutrons in their nucleus. Isotopes of an element will vary in mass because some have more or fewer neutrons. Isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties since these are determined by the number of pro ...
... Isotopes : naturally occurring versions of an element that vary in the numbers of neutrons in their nucleus. Isotopes of an element will vary in mass because some have more or fewer neutrons. Isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties since these are determined by the number of pro ...
Atomic Systems and Bonding
... thus are not too tightly bound (making it easier to ‘move out’) outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in thei ...
... thus are not too tightly bound (making it easier to ‘move out’) outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in thei ...
The Chemistry of Life
... 3) How can we tell that this atom may be an isotope? a) there are more neutrons than protons b) there are more protons than neutrons c) there are enough neutrons to balance the charge of the protons d) this atom has an overall negative charge ...
... 3) How can we tell that this atom may be an isotope? a) there are more neutrons than protons b) there are more protons than neutrons c) there are enough neutrons to balance the charge of the protons d) this atom has an overall negative charge ...
Atomic Structure LO Teacher
... 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of 2 or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements are joined in a definite, wholenumber ratio, such as 1:1, 2:1, or 3:2. Dalton’s essential ideas are still useful today, but several modifications to his theory have been made… ...
... 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of 2 or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements are joined in a definite, wholenumber ratio, such as 1:1, 2:1, or 3:2. Dalton’s essential ideas are still useful today, but several modifications to his theory have been made… ...
Atomic Structure LO Teacher
... 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of 2 or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements are joined in a definite, wholenumber ratio, such as 1:1, 2:1, or 3:2. Dalton’s essential ideas are still useful today, but several modifications to his theory have been made… ...
... 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of 2 or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements are joined in a definite, wholenumber ratio, such as 1:1, 2:1, or 3:2. Dalton’s essential ideas are still useful today, but several modifications to his theory have been made… ...
3lectouttch
... 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of 2 or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements are joined in a definite, wholenumber ratio, such as 1:1, 2:1, or 3:2. Dalton’s essential ideas are still useful today, but several modifications to his theory have been made… ...
... 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of 2 or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements are joined in a definite, wholenumber ratio, such as 1:1, 2:1, or 3:2. Dalton’s essential ideas are still useful today, but several modifications to his theory have been made… ...
CH4 REVIEW
... particles in order to smash them together. Scientists use these devices to make atoms. How can scientists determine whether the atoms formed are a new element or a new isotope of a known element? ...
... particles in order to smash them together. Scientists use these devices to make atoms. How can scientists determine whether the atoms formed are a new element or a new isotope of a known element? ...
NYS Regents Chemistry
... the bright line spectrum of hydrogen atoms. Each energy level has a specific energy. The further the level is away from the nucleus the greater the energy of the electrons in it. 1. Bright line spectrum: When an electron in an atom gains just the right amount of energy, from an outside source, elect ...
... the bright line spectrum of hydrogen atoms. Each energy level has a specific energy. The further the level is away from the nucleus the greater the energy of the electrons in it. 1. Bright line spectrum: When an electron in an atom gains just the right amount of energy, from an outside source, elect ...