11129_evl_ch1_ste_eleve (3)
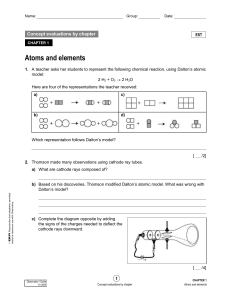
... 7. Six different elements are represented below according to the Rutherford-Bohr atomic model. ...
... 7. Six different elements are represented below according to the Rutherford-Bohr atomic model. ...
Periodic Table for class
... first periodic table, chemists had discovered all three of the missing elements (scandium, gallium, and germanium), and their properties were very close to what Mendeleev had predicted. ...
... first periodic table, chemists had discovered all three of the missing elements (scandium, gallium, and germanium), and their properties were very close to what Mendeleev had predicted. ...
Protons
... Compound: a substance that is composed of atoms of two or more different elements that are chemically combined ( due to chemical reactions) Example: Table salt, or NaCl, is a compound. ...
... Compound: a substance that is composed of atoms of two or more different elements that are chemically combined ( due to chemical reactions) Example: Table salt, or NaCl, is a compound. ...
Definition - kcpe-kcse
... - term comes from noble people, did not associate with anyone other then their kind - characterized by an octet of electrons in the outermost energy level; (happy) - exception of helium - very stable, (unreactive) - colorless, odorless - practical applications: balloons, illumination ...
... - term comes from noble people, did not associate with anyone other then their kind - characterized by an octet of electrons in the outermost energy level; (happy) - exception of helium - very stable, (unreactive) - colorless, odorless - practical applications: balloons, illumination ...
Extension 18.2: Isotopes
... The number of protons does determine which element it is, but the mass number essentially determines its mass (the nucleus’s mass is approximately equal to the mass number times the proton’s mass): M nucleus ≈ A x mproton. So different forms of an element may have different mass. ...
... The number of protons does determine which element it is, but the mass number essentially determines its mass (the nucleus’s mass is approximately equal to the mass number times the proton’s mass): M nucleus ≈ A x mproton. So different forms of an element may have different mass. ...
30.09.2013 1 Chapter 2 Atoms and Molecules Warning!! Chapter
... • Cations with more than one charge (e.g., transition metals) are named using Roman numerals indicating ...
... • Cations with more than one charge (e.g., transition metals) are named using Roman numerals indicating ...
Chapter 3 STUDY GUIDE True/False Indicate whether the statement
... 5. Substances are either elements or mixtures. ...
... 5. Substances are either elements or mixtures. ...
Review for Exam 1
... Determine how many of each ion type is needed for an overall charge of zero. When the cation and anion have different charges, use the ion charges to determine the number of ions of each needed. ...
... Determine how many of each ion type is needed for an overall charge of zero. When the cation and anion have different charges, use the ion charges to determine the number of ions of each needed. ...
Chapter 3 Power Point
... are much more massive than electrons Scientists often refer to the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus as the mass number ...
... are much more massive than electrons Scientists often refer to the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus as the mass number ...
atomic number - Z
... A mole (mol) is the number of particles that is the same as the number of atoms of carbon in 12 g of carbon12. useful for counting small particles • Avogadro’s constant - the number of particles per mole of a substance: 6.022 × 1023 • Moles and grams are related. • molar mass - mass in grams of 1 m ...
... A mole (mol) is the number of particles that is the same as the number of atoms of carbon in 12 g of carbon12. useful for counting small particles • Avogadro’s constant - the number of particles per mole of a substance: 6.022 × 1023 • Moles and grams are related. • molar mass - mass in grams of 1 m ...
Chapter 2
... John Dalton and the Atomic Theory of Matter • 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. • 2. All atoms of a given element are alike and differ from the atoms of any other element. • 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in fixed proportions. • 4 ...
... John Dalton and the Atomic Theory of Matter • 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. • 2. All atoms of a given element are alike and differ from the atoms of any other element. • 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in fixed proportions. • 4 ...
1 - College of Arts and Sciences
... A mass of 4.0 g indicates that the uncertainty is in the first decimal place of the measurement. Thus, the mass might be anything between 3.9 and 4.1 ...
... A mass of 4.0 g indicates that the uncertainty is in the first decimal place of the measurement. Thus, the mass might be anything between 3.9 and 4.1 ...
1 - College of Arts and Sciences
... A mass of 4.0 g indicates that the uncertainty is in the first decimal place of the measurement. Thus, the mass might be anything between 3.9 and 4.1 ...
... A mass of 4.0 g indicates that the uncertainty is in the first decimal place of the measurement. Thus, the mass might be anything between 3.9 and 4.1 ...
Atom Reading Passage and Questions File
... The center of the atom is called the nucleus. Neutrons and protons are located in the atomic nucleus. Electrons are very small particles located outside the nucleus. They orbit the nucleus at fantasist speeds, like the Earth orbits the sun. Each type of subatomic particle has a different electrical ...
... The center of the atom is called the nucleus. Neutrons and protons are located in the atomic nucleus. Electrons are very small particles located outside the nucleus. They orbit the nucleus at fantasist speeds, like the Earth orbits the sun. Each type of subatomic particle has a different electrical ...
Atoms
... National Science Education Standards NSES B1a. Matter is made of minute particles called atoms, and atoms are composed of even smaller components. These components have measurable properties, such as mass and electrical charge. Each atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively char ...
... National Science Education Standards NSES B1a. Matter is made of minute particles called atoms, and atoms are composed of even smaller components. These components have measurable properties, such as mass and electrical charge. Each atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively char ...
Review Notes for Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Test on Friday
... 12. If you want to know the symbols for proton, neutron, and electron, look at TABLE O. Table O shows the symbols, charge and mass for all subatomic particles - the bottom number in front of the symbol is the charge and the top number is the mass in a.m.u. 13. Atomic number - the number on the botto ...
... 12. If you want to know the symbols for proton, neutron, and electron, look at TABLE O. Table O shows the symbols, charge and mass for all subatomic particles - the bottom number in front of the symbol is the charge and the top number is the mass in a.m.u. 13. Atomic number - the number on the botto ...
Class 9 CBSE Test paper Solved Chapter 3: Structure of...
... and electronic configuration is 2,8,2. It can lose 2 electrons to get octet configuration thus its valency is 2. Oxygen has atomic number 8 and its electronic configuration is 2, 6. It can gain 2 electrons to get octet configuration thus its valency is 8-6=2 (iii) The atomic number is equal to numbe ...
... and electronic configuration is 2,8,2. It can lose 2 electrons to get octet configuration thus its valency is 2. Oxygen has atomic number 8 and its electronic configuration is 2, 6. It can gain 2 electrons to get octet configuration thus its valency is 8-6=2 (iii) The atomic number is equal to numbe ...
Covalent Bonds
... indicated by the number of protons added to the number of neutrons • The atomic mass indicates approximately how much matter it contains as compared with another atom • Atomic mass number is denoted by a superscript to the left of the chemical symbol atomic mass ...
... indicated by the number of protons added to the number of neutrons • The atomic mass indicates approximately how much matter it contains as compared with another atom • Atomic mass number is denoted by a superscript to the left of the chemical symbol atomic mass ...
Atomic Theory, and the Periodic Table
... 10. In 1926, Erwin Schrodinger proposed the electron cloud model. These regions of space containing the electrons are called electron clouds. ...
... 10. In 1926, Erwin Schrodinger proposed the electron cloud model. These regions of space containing the electrons are called electron clouds. ...
ATOMS
... Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical ...
... Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical ...
Presentation
... that can be broken down by chemical methods When they are broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the compound. Made of molecules- two or more atoms ...
... that can be broken down by chemical methods When they are broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the compound. Made of molecules- two or more atoms ...
Chapter 10
... • Metals increase in reactivity left and down. • Nonmetals become more reactive up and to the right. • Most reactive metal is? Fr • Most reactive nonmetal is?F ...
... • Metals increase in reactivity left and down. • Nonmetals become more reactive up and to the right. • Most reactive metal is? Fr • Most reactive nonmetal is?F ...
Everything around us is made up of atoms. Atoms are one of the
... Everything around us is made up of atoms. Atoms are one of the smallest units of matter. An atom is too small to see directly through a microscope. The smallest speck that can be seen under an ordinary microscope contains more than ten billion atoms. An atom is more that a million times smaller than ...
... Everything around us is made up of atoms. Atoms are one of the smallest units of matter. An atom is too small to see directly through a microscope. The smallest speck that can be seen under an ordinary microscope contains more than ten billion atoms. An atom is more that a million times smaller than ...























