3.2-3.3 Honors Notes - teacherstroh
... Niels Bohr: 1885-1962 Niels Bohr was a Danish physicist. He proposed a model of the atom that is similar to the model of the solar system. The electrons go around the nucleus like planets orbit around the sun. All electrons have their energy levels – a certain distance from the nucleus. Each energy ...
... Niels Bohr: 1885-1962 Niels Bohr was a Danish physicist. He proposed a model of the atom that is similar to the model of the solar system. The electrons go around the nucleus like planets orbit around the sun. All electrons have their energy levels – a certain distance from the nucleus. Each energy ...
Electrons and the Atom PPT
... a shell contains the maximum number of electrons, it is said to be filled. Electrons in the outer shell of an atom are known as valence electrons and the shell is the valence shell. The valence electrons are the only electrons involved in forming chemical bonds ...
... a shell contains the maximum number of electrons, it is said to be filled. Electrons in the outer shell of an atom are known as valence electrons and the shell is the valence shell. The valence electrons are the only electrons involved in forming chemical bonds ...
Variation in Properties of Group II Compounds
... II elements and their compounds are illustrated. Variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds include both physical and chemical properties. Variation in Physical Properties of the Elements Variation in Atomic and Ionic radii There is a general increase in atomic and ionic radii ...
... II elements and their compounds are illustrated. Variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds include both physical and chemical properties. Variation in Physical Properties of the Elements Variation in Atomic and Ionic radii There is a general increase in atomic and ionic radii ...
key
... Placed in table above using blue electrons. We predict it to be a colorless gas with low electrical conductivity and high electrical reactivity. c) Are there any elements that have not yet been discovered? If so, what would their properties be? This table has room for four more elements. The element ...
... Placed in table above using blue electrons. We predict it to be a colorless gas with low electrical conductivity and high electrical reactivity. c) Are there any elements that have not yet been discovered? If so, what would their properties be? This table has room for four more elements. The element ...
mystery elements
... After looking at a summary of John Dalton’s 1808 Atomic Theory, which 2 statements are not true? (Continue reading ‘Modern Atomic Theory’ if you’re not sure) ...
... After looking at a summary of John Dalton’s 1808 Atomic Theory, which 2 statements are not true? (Continue reading ‘Modern Atomic Theory’ if you’re not sure) ...
Physical Properties
... Problems with Newland’s Law of Octaves 1) It was not valid for elements that had atomic masses higher than Ca. 2) When more elements were discovered (Noble gases) they could not be accommodated in his table. However, the modern periodic table does draw from the concept of periods of eight. ...
... Problems with Newland’s Law of Octaves 1) It was not valid for elements that had atomic masses higher than Ca. 2) When more elements were discovered (Noble gases) they could not be accommodated in his table. However, the modern periodic table does draw from the concept of periods of eight. ...
Atoms
... Over time, scientist began to realize that every different atom makes a different element. For example atoms of a certain kind make up carbon and atoms of another kind make up hydrogen. The number of protons in an atom determines what element it will be. A long time ago people learned that it is imp ...
... Over time, scientist began to realize that every different atom makes a different element. For example atoms of a certain kind make up carbon and atoms of another kind make up hydrogen. The number of protons in an atom determines what element it will be. A long time ago people learned that it is imp ...
Atomic Mass
... It was quite the most incredible event that has ever happened to me in my life. It was almost as incredible as if you fired a 15-inch shell at a piece of tissue paper and it came back and hit you. On consideration, I realized that this scattering backward must be the result of a single collision, a ...
... It was quite the most incredible event that has ever happened to me in my life. It was almost as incredible as if you fired a 15-inch shell at a piece of tissue paper and it came back and hit you. On consideration, I realized that this scattering backward must be the result of a single collision, a ...
Atoms - SD308.org
... He never developed a theory because he did not have experimental support nor did he explain chemical behavior. It took 2000 years after Democritus for the real nature of atoms and events at the atomic level to be established ...
... He never developed a theory because he did not have experimental support nor did he explain chemical behavior. It took 2000 years after Democritus for the real nature of atoms and events at the atomic level to be established ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... Balancing: 1) write out word equation is the problem is a written 2) balance atoms one at a time 3) first balance atoms that are combined into a formula 4) then balance polyatomic ions 5) Balance H atoms and O atoms after all other elements are balanced 6) Check the number for all atoms on both side ...
... Balancing: 1) write out word equation is the problem is a written 2) balance atoms one at a time 3) first balance atoms that are combined into a formula 4) then balance polyatomic ions 5) Balance H atoms and O atoms after all other elements are balanced 6) Check the number for all atoms on both side ...
ATOMS - Greenville Public School District
... F, Cl, Br, I, At very reactive They are very reactive because have 7 valence electrons, this means they are ALMOST full and can combine with many elements. • Nonmetals • Halogen elements combine with metals to form compounds called salts. ...
... F, Cl, Br, I, At very reactive They are very reactive because have 7 valence electrons, this means they are ALMOST full and can combine with many elements. • Nonmetals • Halogen elements combine with metals to form compounds called salts. ...
Ionization energy
... - term comes from noble people, did not associate with anyone other then their kind - characterized by an octet of electrons in the outermost energy level; (happy) - exception of helium - very stable, (unreactive) - colorless, odorless - practical applications: balloons, illumination ...
... - term comes from noble people, did not associate with anyone other then their kind - characterized by an octet of electrons in the outermost energy level; (happy) - exception of helium - very stable, (unreactive) - colorless, odorless - practical applications: balloons, illumination ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... 3) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 4) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed into atoms of another element. ...
... 3) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 4) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed into atoms of another element. ...
2010 Physical Science Comprehensive Test REVIEW Ch 0.3 Sig
... 38. Be able to identify the atomic number, mass number, and stable isotopes. Your periodic table will not have a key on it. Such as: What is the atomic number of phosphorus? Such as: What is the mass number of K-41? Such as: K-41 is stable, but K-40 is not 42. Many models have been developed to expl ...
... 38. Be able to identify the atomic number, mass number, and stable isotopes. Your periodic table will not have a key on it. Such as: What is the atomic number of phosphorus? Such as: What is the mass number of K-41? Such as: K-41 is stable, but K-40 is not 42. Many models have been developed to expl ...
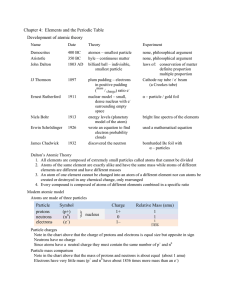
Chapter 4: Elements and the Periodic Table Development of atomic
... Conductivity – most metals are good conductors of heat and electricity Luster – most metals are very shiny or have high metallic luster Magnetic – many metals (but not all) are attracted to magnets Chemical properties of metals Reactivity – metals react by losing electrons to form positive ions Some ...
... Conductivity – most metals are good conductors of heat and electricity Luster – most metals are very shiny or have high metallic luster Magnetic – many metals (but not all) are attracted to magnets Chemical properties of metals Reactivity – metals react by losing electrons to form positive ions Some ...
Column A
... _P,As,Sb,Bi__8. Name of another element in the same family with Nitrogen _Li,Be,B,C,O,F,Ne____9. Name of another element in the same period with Nitrogen ...
... _P,As,Sb,Bi__8. Name of another element in the same family with Nitrogen _Li,Be,B,C,O,F,Ne____9. Name of another element in the same period with Nitrogen ...
Chapter 2 2012
... compound specifies the number of each kind of atom present in a single molecular unit of a compound. • The number of atoms of each element is written as a subscript; when only a one atom of an element is present, the subscript is dropped. • In the case of organic (carbon-containing) compounds, it is ...
... compound specifies the number of each kind of atom present in a single molecular unit of a compound. • The number of atoms of each element is written as a subscript; when only a one atom of an element is present, the subscript is dropped. • In the case of organic (carbon-containing) compounds, it is ...
Atomic Theory Practice Test
... Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 18. The electrons involved in the formation of a chemical bond are called a. dipoles. c. Lewis electrons. b. s electrons. d. valence electrons. ____ 19. In a chemical bond, the link between atoms result ...
... Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 18. The electrons involved in the formation of a chemical bond are called a. dipoles. c. Lewis electrons. b. s electrons. d. valence electrons. ____ 19. In a chemical bond, the link between atoms result ...
Page 1 of 3 Chapter 2 Essential Chemistry CONTENT I. Basic
... 2. Sketch an atom based on the atomic number and show its sub-atomic particles and their charges. Locate valence electrons. 3. Using a table, compare and contrast 3 types of chemical bonds. 4. Using a sketch, compare and contrast non-polar and polar molecules, as well as dissociation of hydrophilic ...
... 2. Sketch an atom based on the atomic number and show its sub-atomic particles and their charges. Locate valence electrons. 3. Using a table, compare and contrast 3 types of chemical bonds. 4. Using a sketch, compare and contrast non-polar and polar molecules, as well as dissociation of hydrophilic ...
Unit 2
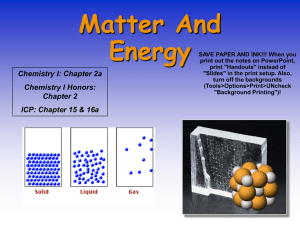
... • Substances keep most of their identities and own properties • Vary in amounts • Can be separated by physical means based on the physical properties of the various parts of the ...
... • Substances keep most of their identities and own properties • Vary in amounts • Can be separated by physical means based on the physical properties of the various parts of the ...
Atomic Structure Notes Blank
... b. Some particles actually bounced back or were greatly deflected. 2. Discovered the ___________________. 3. Concluded that the atom: a. was mostly _____________ through which electrons move b. contained a _______, dense, ______________ charged area (_________) in its center D. James Chadwick – 1932 ...
... b. Some particles actually bounced back or were greatly deflected. 2. Discovered the ___________________. 3. Concluded that the atom: a. was mostly _____________ through which electrons move b. contained a _______, dense, ______________ charged area (_________) in its center D. James Chadwick – 1932 ...
ATOMS / ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES Atom
... Atom-the smallest possible piece of an element Proton-the positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom Neutron-the neutral (no charge) particle found in the nucleus of an atom Electron- the negatively charged particle found on the outside of the nucleus of an atom Nucleus-the dense co ...
... Atom-the smallest possible piece of an element Proton-the positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom Neutron-the neutral (no charge) particle found in the nucleus of an atom Electron- the negatively charged particle found on the outside of the nucleus of an atom Nucleus-the dense co ...