Ch 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... - Atoms of an element all have same Z, but can have different A. - Isotopes are atoms of an element with same Z, but different A’s. (An atom with a particular number of neutrons is called a nuclide.) - The atomic weight on the periodic table is the weighted average of all isotopes. It is the sum of ...
... - Atoms of an element all have same Z, but can have different A. - Isotopes are atoms of an element with same Z, but different A’s. (An atom with a particular number of neutrons is called a nuclide.) - The atomic weight on the periodic table is the weighted average of all isotopes. It is the sum of ...
File
... Electrons constantly orbit around the nucleus. Protons have a positive charge. The number of protons that an atom has is its atomic number. Neutrons do not have a charge, therefore they are said to be neutral. Electrons have a negative charge. The number of electrons that a normal (or stable) atom h ...
... Electrons constantly orbit around the nucleus. Protons have a positive charge. The number of protons that an atom has is its atomic number. Neutrons do not have a charge, therefore they are said to be neutral. Electrons have a negative charge. The number of electrons that a normal (or stable) atom h ...
Atomic masses are weighted averages.
... What we know now of Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms are not indivisible – they are made of subatomic particles 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element ...
... What we know now of Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms are not indivisible – they are made of subatomic particles 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element ...
Subatomic Particles - Parkway C-2
... So different numbers of…. Neutrons! How many neutrons does each have? How would we figure that out? Mass Number - Atomic Number = Number of neutrons ...
... So different numbers of…. Neutrons! How many neutrons does each have? How would we figure that out? Mass Number - Atomic Number = Number of neutrons ...
The Periodic Table of the Elements
... element is determined by its periodic table group (vertical column) in which the element is categorized. FOR THE “A” GROUPS ONLY, the number of the group identifies how many valence electrons are contained within the elements listed under that particular column. ...
... element is determined by its periodic table group (vertical column) in which the element is categorized. FOR THE “A” GROUPS ONLY, the number of the group identifies how many valence electrons are contained within the elements listed under that particular column. ...
Chapter Three: Atoms and Atomic Masses
... We symbolize this ion as Al3+. Note that losing electrons is indicated with +, and gaining electrons is indicated with -. ...
... We symbolize this ion as Al3+. Note that losing electrons is indicated with +, and gaining electrons is indicated with -. ...
Atomic Theory
... • Electrons in the outermost energy level are called VALENCE ELECTRONS. • Valence electrons determine how an atom will act in a chemical reaction. • Atoms with equal numbers of valence electrons have similar properties. ...
... • Electrons in the outermost energy level are called VALENCE ELECTRONS. • Valence electrons determine how an atom will act in a chemical reaction. • Atoms with equal numbers of valence electrons have similar properties. ...
Elements and Compounds
... because they do not have consistent properties. Elements are represented on the Periodic Table of Elements with one or two letter chemical symbols, such as O for oxygen or Si for silicon. Compounds consists of atoms of different kinds of elements that are bound together. Compounds can be broken down ...
... because they do not have consistent properties. Elements are represented on the Periodic Table of Elements with one or two letter chemical symbols, such as O for oxygen or Si for silicon. Compounds consists of atoms of different kinds of elements that are bound together. Compounds can be broken down ...
Average Atomic Mass
... 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. (atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical and physical properties of that element.) 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in siz ...
... 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. (atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical and physical properties of that element.) 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in siz ...
Chemistry Unit 2: Atomic Structure Unit Assignment #1 1. State the
... 13. Write the nuclear symbol for deuterium (H-2): a. Identify the atomic number b. Identify the mass number 14. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in Co–59. 15. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an atom of Ac–221? 16. How many electrons, neutrons, and protons are ...
... 13. Write the nuclear symbol for deuterium (H-2): a. Identify the atomic number b. Identify the mass number 14. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in Co–59. 15. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an atom of Ac–221? 16. How many electrons, neutrons, and protons are ...
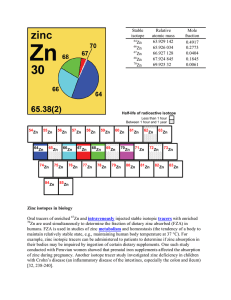
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that element in the sample. The symbol of the atomic weight of element E is A r(E), and the symbol of the atomic weight of an atom (isotope) of element E having mass number A is Ar( AE). Because relative atomic masses ar ...
... mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that element in the sample. The symbol of the atomic weight of element E is A r(E), and the symbol of the atomic weight of an atom (isotope) of element E having mass number A is Ar( AE). Because relative atomic masses ar ...
Topic 7. 1 Atomic Structure
... Concluded that neutral particles must aslo exist in nucleus. Bombarded a beryllium target with alpha particles Alpha particles are helium nucleus Discovered that , carbon was produced with another particle. **** Write reaction on board**** Concluded this particle had almost identical mas ...
... Concluded that neutral particles must aslo exist in nucleus. Bombarded a beryllium target with alpha particles Alpha particles are helium nucleus Discovered that , carbon was produced with another particle. **** Write reaction on board**** Concluded this particle had almost identical mas ...
Unit Analysis Matter Classification
... 0.316522 nanometers. Each cube contains two tungsten atoms. Tungsten has a density of 19.300 g/cm3 . 1 mole of tungsten is 183.85 grams. Calculate the number of tungsten atoms in one mole of tungsten. Note: You do not need to know what a mole is to solve the problem! Only problem-solving skills! Use ...
... 0.316522 nanometers. Each cube contains two tungsten atoms. Tungsten has a density of 19.300 g/cm3 . 1 mole of tungsten is 183.85 grams. Calculate the number of tungsten atoms in one mole of tungsten. Note: You do not need to know what a mole is to solve the problem! Only problem-solving skills! Use ...
Ch 3: Atoms
... isotopes of an element – is a number with a decimal – is always the larger number on the periodic table. mass number (A) - sum of the protons and neutrons in a nucleus this number is rounded from atomic mass due to the fact that there are isotopes # neutrons = A - Z example - # of neutrons in Li = 6 ...
... isotopes of an element – is a number with a decimal – is always the larger number on the periodic table. mass number (A) - sum of the protons and neutrons in a nucleus this number is rounded from atomic mass due to the fact that there are isotopes # neutrons = A - Z example - # of neutrons in Li = 6 ...
3.2-3.3 Honors Notes - teacherstroh
... Question to ponder: If atoms are neutral and electrons are negative, what else could scientists infer about the atom? How did Thomson’s experiment reject the idea that atoms are indivisible? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________ ...
... Question to ponder: If atoms are neutral and electrons are negative, what else could scientists infer about the atom? How did Thomson’s experiment reject the idea that atoms are indivisible? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________ ...
Atom
... element are different from those of any other element. Every atom has at least one isotope; one atom’s isotope is NOT identical to another isotope of the same atom. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. T ...
... element are different from those of any other element. Every atom has at least one isotope; one atom’s isotope is NOT identical to another isotope of the same atom. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. T ...
Topic 1 - Periodic Table
... Students should be able to: Determine the atomic number, atomic mass, the number of protons, and the number of electrons of any atom of a particular element using a periodic table. Determine the number of neutrons in an isotope given its mass number. Perform calculations to determine the “weig ...
... Students should be able to: Determine the atomic number, atomic mass, the number of protons, and the number of electrons of any atom of a particular element using a periodic table. Determine the number of neutrons in an isotope given its mass number. Perform calculations to determine the “weig ...
Elements, Atomic Structure, and Atomic Models
... that element – Atoms are neutral, so each proton in an atom (with its positive charge) is balanced by one electron (with a negative charge); thus, atomic number also equals number of ...
... that element – Atoms are neutral, so each proton in an atom (with its positive charge) is balanced by one electron (with a negative charge); thus, atomic number also equals number of ...
Unit 2, Day 25
... is used because the mass of each subatomic particle is too small to measure in grams The mass of each atom is equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. (Electrons are ignored, because their mass is so small that they don’t affect the mass enough) ...
... is used because the mass of each subatomic particle is too small to measure in grams The mass of each atom is equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. (Electrons are ignored, because their mass is so small that they don’t affect the mass enough) ...
1. All matter is made up of
... • They are malleable, ductile, have luster, and are good conductors of heat and electricity 56. Explain some of the properties of ...
... • They are malleable, ductile, have luster, and are good conductors of heat and electricity 56. Explain some of the properties of ...
Chapter 3 STUDY GUIDE True/False Indicate whether the statement
... 24. When someone stirs cocoa powder into hot water or hot milk, the cocoa changes from a ____. a. homogeneous mixture into a compound b. homogeneous mixture into a non-uniform mixture c. compound into a heterogeneous mixture d. heterogeneous mixture into a homogeneous mixture ...
... 24. When someone stirs cocoa powder into hot water or hot milk, the cocoa changes from a ____. a. homogeneous mixture into a compound b. homogeneous mixture into a non-uniform mixture c. compound into a heterogeneous mixture d. heterogeneous mixture into a homogeneous mixture ...
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide (2012-2013)
... The left side of a chemical reaction is made up of reactants / products, the right side is reactants / products. f. Energy Transfer- Forms of energy: ___________________ ____________________ A change that gives off energy is called ________________________________ Example _____________________ ...
... The left side of a chemical reaction is made up of reactants / products, the right side is reactants / products. f. Energy Transfer- Forms of energy: ___________________ ____________________ A change that gives off energy is called ________________________________ Example _____________________ ...
SCIENCE: EIGHTH GRADE CRT FIRST QUARTER
... Which group of elements does not normally form chemical N bonds? Based on the number of valence electrons, which of the L following elements is the most reactive: Li, Be, B, Ne? How many electrons does a nitrogen (N) atom contain? Y How many protons does an argon (Ar) atom contain? How many neutrons ...
... Which group of elements does not normally form chemical N bonds? Based on the number of valence electrons, which of the L following elements is the most reactive: Li, Be, B, Ne? How many electrons does a nitrogen (N) atom contain? Y How many protons does an argon (Ar) atom contain? How many neutrons ...