Atomic Structure Problem Set PROBLEM SET #3: ATOMIC
... all isotopes of hydrogen? 1. proton 2. neutron 3. electron 4. positron ...
... all isotopes of hydrogen? 1. proton 2. neutron 3. electron 4. positron ...
E:\My Documents\sch3u\unit 1\atomic structure history.wpd
... Radioactivity also had been discovered by this time. Ernst Rutherford conducted exhaustive studies of radioactivity. He found that there were three types of radiation given off by radioactive material: alpha particles: heavy particles with a positive charge. beta particles: light particles with a ne ...
... Radioactivity also had been discovered by this time. Ernst Rutherford conducted exhaustive studies of radioactivity. He found that there were three types of radiation given off by radioactive material: alpha particles: heavy particles with a positive charge. beta particles: light particles with a ne ...
Elements and Compounds Chapter 3
... Negative ions were explained by assuming that extra electrons can be added to atoms. ...
... Negative ions were explained by assuming that extra electrons can be added to atoms. ...
Atomic Mass
... Negative ions were explained by assuming that extra electrons can be added to atoms. ...
... Negative ions were explained by assuming that extra electrons can be added to atoms. ...
Historical Development of the Periodic Table
... increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the gaps he had left. ...
... increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the gaps he had left. ...
Historical Development of the Periodic Table Periodic Table of the
... increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the gaps he had left. ...
... increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the gaps he had left. ...
Chemistry –Worksheet: Atomic structure
... 21. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom of tungsten-184 which has an atomic number of 74? # of neutrons:_________________ 22. Which of the following combinations of particles represents an ion of net charge -1 and of mass number 82? (A) 46 neutrons, 35 protons, 36 electrons (C) 46 neutro ...
... 21. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom of tungsten-184 which has an atomic number of 74? # of neutrons:_________________ 22. Which of the following combinations of particles represents an ion of net charge -1 and of mass number 82? (A) 46 neutrons, 35 protons, 36 electrons (C) 46 neutro ...
Atoms PPT
... • Neutrons = atomic mass – atomic number • Atomic symbols – First letter is ALWAYS upper case – Second letter is ALWAYS lower case • Example: Identify the Number of Protons, Neutrons and Electrons in Oxygen Oxygen element 8 with mass 16 ...
... • Neutrons = atomic mass – atomic number • Atomic symbols – First letter is ALWAYS upper case – Second letter is ALWAYS lower case • Example: Identify the Number of Protons, Neutrons and Electrons in Oxygen Oxygen element 8 with mass 16 ...
File
... general, they are shiny and good conductors of heat and electricity. They also have higher densities and melting points than groups 1 & 2. (1 or 2 outer level electrons) Lanthanides & Actinides: These are also transition metals that were taken out and placed at the bottom of the table so the table w ...
... general, they are shiny and good conductors of heat and electricity. They also have higher densities and melting points than groups 1 & 2. (1 or 2 outer level electrons) Lanthanides & Actinides: These are also transition metals that were taken out and placed at the bottom of the table so the table w ...
Build An Atom - ChemConnections
... b. Whether an atom is neutral or an ion (cation or anion) and its respective charge. c. Orbits versus clouds. d. The total mass of an atom or ion. e. The mass relationship of isotopes and their rela ...
... b. Whether an atom is neutral or an ion (cation or anion) and its respective charge. c. Orbits versus clouds. d. The total mass of an atom or ion. e. The mass relationship of isotopes and their rela ...
6.1.1.A AtomicStructurex
... What does all this have to do with Electricity? The number of valence electrons in an atom will determine if an element will allow electricity to flow. The ability of an atom to draw electrons to itself (away from its neighbors) is called Electronegativity. ...
... What does all this have to do with Electricity? The number of valence electrons in an atom will determine if an element will allow electricity to flow. The ability of an atom to draw electrons to itself (away from its neighbors) is called Electronegativity. ...
Section 2: “The Structure of Atoms
... hold a maximum of 2 electrons. Each “p” orbital is shaped like a bar bell. There are 3 different types that can each hold 2 electrons. The “p” orbital, therefore, can hold up to 6 electrons. “d” and “f” orbitals are more complex. There are 5 types of “d” orbitals and 7 types of “f” orbitals each tha ...
... hold a maximum of 2 electrons. Each “p” orbital is shaped like a bar bell. There are 3 different types that can each hold 2 electrons. The “p” orbital, therefore, can hold up to 6 electrons. “d” and “f” orbitals are more complex. There are 5 types of “d” orbitals and 7 types of “f” orbitals each tha ...
Atomic Structure
... What does all this have to do with Electricity? The number of valence electrons in an atom will determine if an element will allow electricity to flow. The ability of an atom to draw electrons to itself (away from its neighbors) is called Electronegativity. ...
... What does all this have to do with Electricity? The number of valence electrons in an atom will determine if an element will allow electricity to flow. The ability of an atom to draw electrons to itself (away from its neighbors) is called Electronegativity. ...
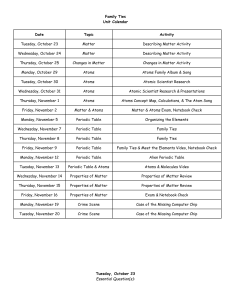
8F Compounds and Mixtures
... but have not reacted with each other. Sea water is a mixture of salts, water and other substances. A mixture is not the same as a compound: 1. The proportions of the substances in a mixture are not fixed. 2. The properties of a mixture are often an “average” of the properties of its ingredients (e.g ...
... but have not reacted with each other. Sea water is a mixture of salts, water and other substances. A mixture is not the same as a compound: 1. The proportions of the substances in a mixture are not fixed. 2. The properties of a mixture are often an “average” of the properties of its ingredients (e.g ...
The History of the Atom - cho
... Chemistry CPS: Project #2: GUIDELINES The History of the Atom: NAMES OF THE SCIENTISTS:__________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Date assigned: ______________________________ Date due: __________________________________ P ...
... Chemistry CPS: Project #2: GUIDELINES The History of the Atom: NAMES OF THE SCIENTISTS:__________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Date assigned: ______________________________ Date due: __________________________________ P ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements
... Now using the mass of Hydrogen and Oxygen to show these results are consistent with the law of definite proportion ...
... Now using the mass of Hydrogen and Oxygen to show these results are consistent with the law of definite proportion ...
Synthesis of elements by helium and oxygen building blocks Bohr
... The hot filament reaches a temperature of less than 2500 degrees Celsius, leading to the inability to create atomic ions of species with a high ionization energy, such as Osmium (Os), and Tungsten (H f -W). It follows from these facts that at 4000 K the orbitals of the elements cannot be formed! Nuc ...
... The hot filament reaches a temperature of less than 2500 degrees Celsius, leading to the inability to create atomic ions of species with a high ionization energy, such as Osmium (Os), and Tungsten (H f -W). It follows from these facts that at 4000 K the orbitals of the elements cannot be formed! Nuc ...
Atomic_structure
... The atomic number tells you how many protons there are in one atom of an element. The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons, which is why the atom has no overall charge. Since the mass of the atom is made up of the neutrons and protons, the number of neutrons in an atom is calculated ...
... The atomic number tells you how many protons there are in one atom of an element. The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons, which is why the atom has no overall charge. Since the mass of the atom is made up of the neutrons and protons, the number of neutrons in an atom is calculated ...
3. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... seem to explain much more experimental observations and the arrangement elements in the periodic table. According to new Wave-mechanical model an electron a hydrogen atom has addition features: 1) Each shell could have sub-shells called s, p, d and f. Listed below is sub-shell description of each sh ...
... seem to explain much more experimental observations and the arrangement elements in the periodic table. According to new Wave-mechanical model an electron a hydrogen atom has addition features: 1) Each shell could have sub-shells called s, p, d and f. Listed below is sub-shell description of each sh ...
1-Three states of matter . A: density, volume and weight B: solid
... 8. Why is the calcium ion (Ca2+) more stable than the calcium atom (Ca)? a. Twenty electrons are more stable than eighteen electrons. b. Eighteen electrons are less stable than twenty electrons. c. The two electrons more than the noble gas configuration is more stable. d. The noble gas configuration ...
... 8. Why is the calcium ion (Ca2+) more stable than the calcium atom (Ca)? a. Twenty electrons are more stable than eighteen electrons. b. Eighteen electrons are less stable than twenty electrons. c. The two electrons more than the noble gas configuration is more stable. d. The noble gas configuration ...
2013 atoms
... isotopes of the element. Because of the discovery of isotopes, scientists hypothesized that atoms contained still a third type of particle that explained these differences in mass. ...
... isotopes of the element. Because of the discovery of isotopes, scientists hypothesized that atoms contained still a third type of particle that explained these differences in mass. ...