ppt - Discover Earth Science
... Isotopes - forms of an atom of an element that have the same number of protons in the nucleus, but a different number of neutrons. They are different “versions” of the same element. Remember that an atom’s identity is determined by the # of protons, so an isotope is still the same element (atomic # ...
... Isotopes - forms of an atom of an element that have the same number of protons in the nucleus, but a different number of neutrons. They are different “versions” of the same element. Remember that an atom’s identity is determined by the # of protons, so an isotope is still the same element (atomic # ...
Symbols of Elements - Chemistry with Mr. Patmos
... He then arranged columns so that elements with most similar properties were next to each other – First Periodic table Blank spaces left bc/ no known elements with mass and properties that fit ...
... He then arranged columns so that elements with most similar properties were next to each other – First Periodic table Blank spaces left bc/ no known elements with mass and properties that fit ...
Regular Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam
... E) iron, Fe 42) Which of the following is NOT a correct name, symbol combination? A) potassium, P B) gold, Au C) calcium, Ca D) manganese, Mn E) chromium, Cr 43) The names of the elements whose symbols are Si, P, Mn, and S are respectively, A) silicon, phosphorus, magnesium, and sulfur. B) silver, p ...
... E) iron, Fe 42) Which of the following is NOT a correct name, symbol combination? A) potassium, P B) gold, Au C) calcium, Ca D) manganese, Mn E) chromium, Cr 43) The names of the elements whose symbols are Si, P, Mn, and S are respectively, A) silicon, phosphorus, magnesium, and sulfur. B) silver, p ...
3.1 Early History of Atomic Theories
... chemists. In textbooks such as this one, only the success of a few is documented. However, the success of these chemists was often facilitated by both the success and failure of many others. Recall that by the use of deductive logic the Greeks (for example, Democritus) in about 300 B.C. hypothesized ...
... chemists. In textbooks such as this one, only the success of a few is documented. However, the success of these chemists was often facilitated by both the success and failure of many others. Recall that by the use of deductive logic the Greeks (for example, Democritus) in about 300 B.C. hypothesized ...
25 NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY NOTES __ /__ pts
... ________ 16. Beta radiation is emitted when a radioisotope decays. ________ 17. Gamma radiation has a negative charge ________ 18. Gamma radiation is high-energy electromagnetic radiation. ________ 19. ...
... ________ 16. Beta radiation is emitted when a radioisotope decays. ________ 17. Gamma radiation has a negative charge ________ 18. Gamma radiation is high-energy electromagnetic radiation. ________ 19. ...
Periodicity - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... THE ORIGINS OF NATURALLY OCCURING ELEMENTS Natural and synthetic elements are created in different ways ...
... THE ORIGINS OF NATURALLY OCCURING ELEMENTS Natural and synthetic elements are created in different ways ...
Subatomic Particles
... For example, hydrogen has the atomic number 1; all hydrogen atoms have 1 proton in their nuclei. Helium has the atomic number 2; all helium atoms have 2 protons in their nuclei. There is no such thing as a hydrogen atom with 2 protons in its nucleus; a nucleus with 2 protons would be a helium atom. ...
... For example, hydrogen has the atomic number 1; all hydrogen atoms have 1 proton in their nuclei. Helium has the atomic number 2; all helium atoms have 2 protons in their nuclei. There is no such thing as a hydrogen atom with 2 protons in its nucleus; a nucleus with 2 protons would be a helium atom. ...
Chemistry Readings
... the nucleus). The shells are also called energy levels or orbitals. We will use the term shell. Chemists use letters to name the shells around a nucleus. They use the letters "k, l, m, n, o, p, and q". The "k" shell is the one closest to the nucleus and "q" is the farthest away. Not all shells hold ...
... the nucleus). The shells are also called energy levels or orbitals. We will use the term shell. Chemists use letters to name the shells around a nucleus. They use the letters "k, l, m, n, o, p, and q". The "k" shell is the one closest to the nucleus and "q" is the farthest away. Not all shells hold ...
Elements, Atoms, Ions PPT
... Nonmetals tend to gain one or more electrons to form negative ions called anions. ...
... Nonmetals tend to gain one or more electrons to form negative ions called anions. ...
chapter 3 pp - Bridgewater
... Nonmetals tend to gain one or more electrons to form negative ions called anions. ...
... Nonmetals tend to gain one or more electrons to form negative ions called anions. ...
Chapter 3-3—Parts of the Atom - Phoenix Union High School District
... chemical symbol, atomic mass and atomic number: ...
... chemical symbol, atomic mass and atomic number: ...
MID-COURSE REVISION QUESTIONS The following questions are
... (c) Cations and anions differ from each other in the sign of the electrical charge which they bear. Cations are species which bear an overall positive electrical charge. Atoms can be converted to cations by the loss of one or more electrons, leaving an overall excess of protons and hence positive ch ...
... (c) Cations and anions differ from each other in the sign of the electrical charge which they bear. Cations are species which bear an overall positive electrical charge. Atoms can be converted to cations by the loss of one or more electrons, leaving an overall excess of protons and hence positive ch ...
MID-COURSE REVISION QUESTIONS The following questions are
... overall symmetry of the charge is not achieved, the molecule will have an overall molecular dipole and it is said to be a polar molecule. Water is an angular molecule and is an example of a polar molecule while carbon dioxide, due to its linear shape, is a non-polar molecule. Question 2 Water is a h ...
... overall symmetry of the charge is not achieved, the molecule will have an overall molecular dipole and it is said to be a polar molecule. Water is an angular molecule and is an example of a polar molecule while carbon dioxide, due to its linear shape, is a non-polar molecule. Question 2 Water is a h ...
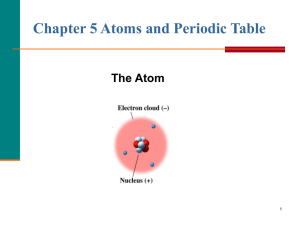
Atoms - Discover Earth Science
... electrons So electrons. So, it has either more positive protons (+ charged) or more negative electrons (( charged) Ex – all Na atoms have 11 protons, but say an atom has only 10 electrons electrons, it has an extra positive charge (proton), so it’s a “+1 ion”. ...
... electrons So electrons. So, it has either more positive protons (+ charged) or more negative electrons (( charged) Ex – all Na atoms have 11 protons, but say an atom has only 10 electrons electrons, it has an extra positive charge (proton), so it’s a “+1 ion”. ...
electrons - Science Department
... A similar number did not pass through the foil at all, but bounced back in the direction from which they had come. ...
... A similar number did not pass through the foil at all, but bounced back in the direction from which they had come. ...
Name: Period:______ Table Number:______
... 86. The names of the different energy levels, shells or orbitals of electrons which compose the electron cloud of an atom, starting with the shell of electrons which is closest to the nucleus are the ___________ shell, ___________ shell, __________ shell, and __________ shell. 87. The maximum number ...
... 86. The names of the different energy levels, shells or orbitals of electrons which compose the electron cloud of an atom, starting with the shell of electrons which is closest to the nucleus are the ___________ shell, ___________ shell, __________ shell, and __________ shell. 87. The maximum number ...
isotopes
... one more proton than electron. One more proton means one more positive charge. This makes the total charge of the atom POSITIVE. This atom has gained an electron. Now it has one less proton than electron. One less proton means one less positive charge. This makes the total charge of the atom NEGATIV ...
... one more proton than electron. One more proton means one more positive charge. This makes the total charge of the atom POSITIVE. This atom has gained an electron. Now it has one less proton than electron. One less proton means one less positive charge. This makes the total charge of the atom NEGATIV ...
In actual laboratories, isotopes in a sample can be
... For example, atoms with 17 protons are chlorine atoms. However, not all chlorine atoms have the same number of neutrons. Atoms of the same element (i.e., with same number of protons) that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. One isotope of chlorine has 18 neutrons and a different ...
... For example, atoms with 17 protons are chlorine atoms. However, not all chlorine atoms have the same number of neutrons. Atoms of the same element (i.e., with same number of protons) that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. One isotope of chlorine has 18 neutrons and a different ...
Protons are the identity of an atom!
... protons. The number of protons is called the element’s atomic number. Atoms that are electrically neutral will have the same number of protons and electrons. If an atom has an electrical charge, it is because it has more or less electrons than its’ number of protons. In this case, the atom is called ...
... protons. The number of protons is called the element’s atomic number. Atoms that are electrically neutral will have the same number of protons and electrons. If an atom has an electrical charge, it is because it has more or less electrons than its’ number of protons. In this case, the atom is called ...
Grade 11 Unit 4 - Amazon Web Services
... This section is designed to help you get a better idea and appreciation for eight scientists who made great contributions to the development of our present-day atomic theory. Information on each scientist is taken from the “Atomic Pioneer Series.” United States Energy Research and Development Admini ...
... This section is designed to help you get a better idea and appreciation for eight scientists who made great contributions to the development of our present-day atomic theory. Information on each scientist is taken from the “Atomic Pioneer Series.” United States Energy Research and Development Admini ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure Notes
... When an atom has the same number of protons as electrons. (+) = (-) if the atom is neutral then it has not lost or gained electrons. Atomic charge- an atom will have a charge when the protons and the electrons are not equal in number. Atoms will lose or gain electrons to become charged. Atoms that ...
... When an atom has the same number of protons as electrons. (+) = (-) if the atom is neutral then it has not lost or gained electrons. Atomic charge- an atom will have a charge when the protons and the electrons are not equal in number. Atoms will lose or gain electrons to become charged. Atoms that ...