atomic numbers
... over time to become more stable. ► Half-Life: the amount of time that it takes half of a radioisotope sample to decay. ...
... over time to become more stable. ► Half-Life: the amount of time that it takes half of a radioisotope sample to decay. ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... Later on, the discovery of protons and neutrons were discovered in the nucleus. And it was later concluded that all atoms are neutral in charge. The number of protons and electrons in any atom are always equal. ...
... Later on, the discovery of protons and neutrons were discovered in the nucleus. And it was later concluded that all atoms are neutral in charge. The number of protons and electrons in any atom are always equal. ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... The Modern Atomic Theory Modern Atomic theory has four assumptions: 1. Atoms make up all matter. 2. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of another element. 3. Atoms combine in definite ratios to make compounds. 4 Combinations of atoms in compounds can change ...
... The Modern Atomic Theory Modern Atomic theory has four assumptions: 1. Atoms make up all matter. 2. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of another element. 3. Atoms combine in definite ratios to make compounds. 4 Combinations of atoms in compounds can change ...
3. atomic structure
... nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found (probability of location) The exact path of an electron in this area is not known ...
... nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found (probability of location) The exact path of an electron in this area is not known ...
Introduction to Atoms
... the disks became charged and glowing beam appeared in the tube. – The beam bent toward a positively charged plate placed outside the tube. • He concluded that the particles in the beam had a negative charge because they were attracted to the positive plate. ...
... the disks became charged and glowing beam appeared in the tube. – The beam bent toward a positively charged plate placed outside the tube. • He concluded that the particles in the beam had a negative charge because they were attracted to the positive plate. ...
Matter and Chemical Change PPT
... electron. This electron is found in the first orbital and has room to gain 1 more electron if it comes in contact with another atom. This would then completely fill the first orbital. Nitrogen’s atom has the atomic number of 7 and thus contains 7 electrons. Two of the seven electrons fill the first ...
... electron. This electron is found in the first orbital and has room to gain 1 more electron if it comes in contact with another atom. This would then completely fill the first orbital. Nitrogen’s atom has the atomic number of 7 and thus contains 7 electrons. Two of the seven electrons fill the first ...
Chemistrypart107
... the nucleus in shells or energy levels. 2. As an element looses an electron it looses energy and as an element gains electrons it gains energy. 3. Each circle or shell is limited to how many electrons it can hold. ...
... the nucleus in shells or energy levels. 2. As an element looses an electron it looses energy and as an element gains electrons it gains energy. 3. Each circle or shell is limited to how many electrons it can hold. ...
atomic number - geraldinescience
... Valence Electrons and Periodic Properties, continued • When an atom has 8 valence electrons, it is considered stable, or chemically unreactive. Unreactive atoms do not easily lose or gain electrons. • Elements whose atoms have only one, two, or three valence electrons tend to lose electrons easily. ...
... Valence Electrons and Periodic Properties, continued • When an atom has 8 valence electrons, it is considered stable, or chemically unreactive. Unreactive atoms do not easily lose or gain electrons. • Elements whose atoms have only one, two, or three valence electrons tend to lose electrons easily. ...
Atomic Model Power Point
... retains its identity in a chemical reaction. Democritus believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. Dalton’s atomic theory states that ...
... retains its identity in a chemical reaction. Democritus believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. Dalton’s atomic theory states that ...
John Dalton is known as the father of modern atomic theory because
... ‘make’ gold from less valuable metals. Dalton’s theory suggested that every single atom of an element such as oxygen is identical to every other oxygen atom; furthermore, atoms of different elements, such as oxygen and mercury, are different from each other. Dalton was the first to describe elements ...
... ‘make’ gold from less valuable metals. Dalton’s theory suggested that every single atom of an element such as oxygen is identical to every other oxygen atom; furthermore, atoms of different elements, such as oxygen and mercury, are different from each other. Dalton was the first to describe elements ...
Ch 4 and Ch 5 Study Guide (ICP) Multiple Choice Identify the choice
... 53. When an atom gains or loses energy, _______________________ jump between energy levels. 54. An electron that gains energy enters an excited state and absorbs a particle of light called a(n) ______________________. 55. The chemical properties of an atom are determined by _______________________, ...
... 53. When an atom gains or loses energy, _______________________ jump between energy levels. 54. An electron that gains energy enters an excited state and absorbs a particle of light called a(n) ______________________. 55. The chemical properties of an atom are determined by _______________________, ...
File
... Some metal atoms, depending on the nature of the chemical reaction, can form stable ions with more than one charge. For example copper atoms will lose either one or two electrons. ...
... Some metal atoms, depending on the nature of the chemical reaction, can form stable ions with more than one charge. For example copper atoms will lose either one or two electrons. ...
Lesson 3.1
... by grams and kilograms, so scientists use “atomic mass units” or “amu.” A proton OR a neutron is equal to one amu. Atomic Number – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number. Isotopes – All atoms of an element have the same number of protons, but sometimes the number of neu ...
... by grams and kilograms, so scientists use “atomic mass units” or “amu.” A proton OR a neutron is equal to one amu. Atomic Number – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number. Isotopes – All atoms of an element have the same number of protons, but sometimes the number of neu ...
electrons.
... through a gas caused the gas to give off particles that were too small to be atoms. These negative particles were eventually called “electrons.” ...
... through a gas caused the gas to give off particles that were too small to be atoms. These negative particles were eventually called “electrons.” ...
Isotopes and Shell Diagrams
... Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outer shell. ...
... Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outer shell. ...
Which has more atoms: a one gram sample of carbon
... Atoms of the same element may have different numbers of neutrons. Carbon may have 6, 7 or 8 neutrons. Hydrogen may have 0, 1 or 2 neutrons. These are called isotopes. Most elements have more than one isotope. Some isotopes are radioactive. Unstable, decay into other elements. Example: ...
... Atoms of the same element may have different numbers of neutrons. Carbon may have 6, 7 or 8 neutrons. Hydrogen may have 0, 1 or 2 neutrons. These are called isotopes. Most elements have more than one isotope. Some isotopes are radioactive. Unstable, decay into other elements. Example: ...
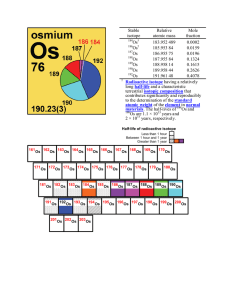
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... either positive or negative charge (an electron or positron). [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric charge and a rest mass of about 9.109 × 10–31 kg. element (chemical element) – a species of atoms; all atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus. ...
... either positive or negative charge (an electron or positron). [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric charge and a rest mass of about 9.109 × 10–31 kg. element (chemical element) – a species of atoms; all atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus. ...
Final Exam Class Review - Mrs. Kittrell`s Science Classes
... A beta particle is a fast moving electron which is emitted from the nucleus of an atom undergoing radioactive decay. ...
... A beta particle is a fast moving electron which is emitted from the nucleus of an atom undergoing radioactive decay. ...
Regents Chemistry
... Presently there are 110 different elements, of which 88 occur naturally (the rest have been made in laboratories) The elements vary tremendously in abundance For example, only 9 elements account for most of the compounds found in the Earth’s crust See pg. 87 tables 4.1 and 4.2 ...
... Presently there are 110 different elements, of which 88 occur naturally (the rest have been made in laboratories) The elements vary tremendously in abundance For example, only 9 elements account for most of the compounds found in the Earth’s crust See pg. 87 tables 4.1 and 4.2 ...
Early Atomic Theorists
... o Rays and particles emitted by radioactive materials are called radiation o Unstable nuclei decay until they form stable nonradioactive nuclei ...
... o Rays and particles emitted by radioactive materials are called radiation o Unstable nuclei decay until they form stable nonradioactive nuclei ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... ________________(16) and neutrons is the mass number. Atoms of the same element are identical in most respects, but they can differ in the number of ________________(17) in the nucleus. Atoms that have the same number of protons but different mass numbers are called ________________(18). The _______ ...
... ________________(16) and neutrons is the mass number. Atoms of the same element are identical in most respects, but they can differ in the number of ________________(17) in the nucleus. Atoms that have the same number of protons but different mass numbers are called ________________(18). The _______ ...
Periodic Table
... other elements. Besides that, a row goes from left to right, it’s is called a period. Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells. - Every element in the first column (group one) has one electron in its outer shell. Every element in the second column (group two) has two elect ...
... other elements. Besides that, a row goes from left to right, it’s is called a period. Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells. - Every element in the first column (group one) has one electron in its outer shell. Every element in the second column (group two) has two elect ...