Atomic Theory
... John Dalton (1803) – Compiled past research to develop the first useful atomic theory ...
... John Dalton (1803) – Compiled past research to develop the first useful atomic theory ...
9.3 Atoms and Elements notes
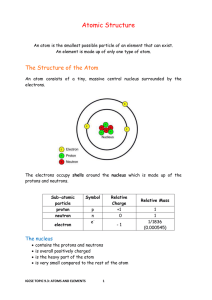
... number of electrons in an atom = number of protons Electrons are arranged in energy levels (also known as shells) around the nucleus. The lowest energy levels are always filled first. These are closer to the nucleus and hold the least numbers of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 el ...
... number of electrons in an atom = number of protons Electrons are arranged in energy levels (also known as shells) around the nucleus. The lowest energy levels are always filled first. These are closer to the nucleus and hold the least numbers of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 el ...
Any substance that cannot be decomposed into
... oxygen, 16. Precise atomic weights of elements as found in nature vary slightly from these figures. Carbon's atomic weight, for example, is 12.01115 because small amounts of carbon-13 and carbon14 (which are isotopes with additional neutrons) are present in addition to carbon-12. Atomic weights can ...
... oxygen, 16. Precise atomic weights of elements as found in nature vary slightly from these figures. Carbon's atomic weight, for example, is 12.01115 because small amounts of carbon-13 and carbon14 (which are isotopes with additional neutrons) are present in addition to carbon-12. Atomic weights can ...
Atomic Mass- composed mostly of protons and neutrons in the
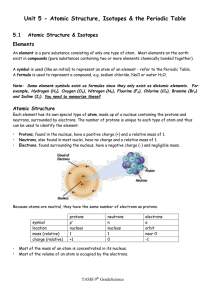
... Isotopes – An isotope is an alternative form of an element. Each isotope of an element has the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons. The isotope is represented by the atomic symbol and mass number, such as He-4. Some isotopes are stable, while others are radioactive, which mean ...
... Isotopes – An isotope is an alternative form of an element. Each isotope of an element has the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons. The isotope is represented by the atomic symbol and mass number, such as He-4. Some isotopes are stable, while others are radioactive, which mean ...
ISOSTOPE NOTES - Mr. Collier`s 9th Grade Physical Science
... • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses because they have different numbers of neutrons. –Subatomic particles are so small that we don’t use grams, we use AMU (atomic mass units) –Protons and Neutrons have about the same mass: 1AMU. –Electrons have so little mass they do ...
... • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses because they have different numbers of neutrons. –Subatomic particles are so small that we don’t use grams, we use AMU (atomic mass units) –Protons and Neutrons have about the same mass: 1AMU. –Electrons have so little mass they do ...
chapter 4: chemical foundations
... atom: smallest identifiable unit of an element – All matter is made up of atoms. → The properties of specific atoms determine the properties of matter with those atoms. Greek philosophers were the first to propose explanations for what was observed in nature. – Surprisingly, some of these Greek idea ...
... atom: smallest identifiable unit of an element – All matter is made up of atoms. → The properties of specific atoms determine the properties of matter with those atoms. Greek philosophers were the first to propose explanations for what was observed in nature. – Surprisingly, some of these Greek idea ...
Atoms, Ions and Molecules
... The number of neutrons does not change which element an atom belongs to. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are known as isotopes. Isotopes have idenBcal chemical properBes ...
... The number of neutrons does not change which element an atom belongs to. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are known as isotopes. Isotopes have idenBcal chemical properBes ...
Chapter 1
... C. Building Bigger Atoms D. Protons and Atomic Number *Notes-The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom give the element its _______atomic number______________. (also the number of electrons) ...
... C. Building Bigger Atoms D. Protons and Atomic Number *Notes-The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom give the element its _______atomic number______________. (also the number of electrons) ...
Chapter 3 - WordPress.com
... particles at a very thin sheet of gold foil. • Based on Thomson’s model of the atom he expected the alpha particles to pass through the foil but not all did! ...
... particles at a very thin sheet of gold foil. • Based on Thomson’s model of the atom he expected the alpha particles to pass through the foil but not all did! ...
Atoms and Atomic Theory
... a. Dalton (England, 1800’s) atoms. 1. All elements are composed of atoms and they are indestructible-like a solid sphere. They cannot be created or destroyed-LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MATTER 2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike. 3. Atoms of different elements are different. 4. Compounds are f ...
... a. Dalton (England, 1800’s) atoms. 1. All elements are composed of atoms and they are indestructible-like a solid sphere. They cannot be created or destroyed-LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MATTER 2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike. 3. Atoms of different elements are different. 4. Compounds are f ...
Atomic Structure of hydrogen
... Some isotopes have a nucleus that is unstable. The balance between the numbers of protons and neutrons is not stable. These atoms spontaneously throw particles out of their nucleus in order to become more stable, in a process is known as decay. Unstable isotopes are said to be radioactive and their ...
... Some isotopes have a nucleus that is unstable. The balance between the numbers of protons and neutrons is not stable. These atoms spontaneously throw particles out of their nucleus in order to become more stable, in a process is known as decay. Unstable isotopes are said to be radioactive and their ...
chapter 19 - Celina City Schools
... A) Quarks - particles of matter that makeup protons and neutrons 1) Six (6) different types of quarks a) Three (3) makeup the ____________ and three (3) makeup the ____________. 2) Finding quarks… a) ____________ - a machine designed to generate enough energy to study quarks Located in Batavia, IL ...
... A) Quarks - particles of matter that makeup protons and neutrons 1) Six (6) different types of quarks a) Three (3) makeup the ____________ and three (3) makeup the ____________. 2) Finding quarks… a) ____________ - a machine designed to generate enough energy to study quarks Located in Batavia, IL ...
Atomic Structure
... Decay (p. 841) According to the band of stability graph (Figure 18.1) this nuclide is neutron-poor, so it must do something to decrease the number of protons or increase the number of neutrons. ...
... Decay (p. 841) According to the band of stability graph (Figure 18.1) this nuclide is neutron-poor, so it must do something to decrease the number of protons or increase the number of neutrons. ...
Atomic Information
... • If electrons are added to the atom, then there are more negative charges than positive charges. The atom becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. • If electrons are removed from the atom, then there are less negative charges than positive charges. The atom becomes positively charged and ...
... • If electrons are added to the atom, then there are more negative charges than positive charges. The atom becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. • If electrons are removed from the atom, then there are less negative charges than positive charges. The atom becomes positively charged and ...
Atomic Structure - Mr. Cervantes Science Classes
... reasonable to think that the mass of an atom should be expressed as a whole number B. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of all the isotopes of that element 1. When calculating the average atomic mass you must take into account the relative abundance of each isotope ...
... reasonable to think that the mass of an atom should be expressed as a whole number B. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of all the isotopes of that element 1. When calculating the average atomic mass you must take into account the relative abundance of each isotope ...
Inside an Atom - Mrs. Ericka Williams
... They are identified by the number or protons because this number never changes without changing the identity of the element Are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons; for example, the three isotopes of carbon differ in the number of neutrons in each nucleus such as Carbon ...
... They are identified by the number or protons because this number never changes without changing the identity of the element Are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons; for example, the three isotopes of carbon differ in the number of neutrons in each nucleus such as Carbon ...
Atomic terms Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every
... Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. - MASS NUMBER: The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus, Atoms of the same element may have DIFFERENT mass numbers. - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mas ...
... Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. - MASS NUMBER: The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus, Atoms of the same element may have DIFFERENT mass numbers. - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mas ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... Atoms have very small masses - the heaviest known atom is about 4 x 10−22 g Therefore, atomic mass unit (amu) is used to describe the mass of an individual atom The proton and neutron have nearly identical mass, and are much heavier than the electron (1 proton has same mass as 1836 electrons) ...
... Atoms have very small masses - the heaviest known atom is about 4 x 10−22 g Therefore, atomic mass unit (amu) is used to describe the mass of an individual atom The proton and neutron have nearly identical mass, and are much heavier than the electron (1 proton has same mass as 1836 electrons) ...
Isotopes Article
... We all know what an atom is by now and we are aware that all matter is made up of them. Atoms themselves are made up of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each of those has different charges. The protons (positive) and neutrons (no charge) are found in the densest area of t ...
... We all know what an atom is by now and we are aware that all matter is made up of them. Atoms themselves are made up of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each of those has different charges. The protons (positive) and neutrons (no charge) are found in the densest area of t ...
CHEM 1305 - HCC Learning Web
... 22a. Predict the missing value (?) for each property listed below. The atomic radius, density, and boiling point are given for elements in group VIIA/17 Element Cl Br I ...
... 22a. Predict the missing value (?) for each property listed below. The atomic radius, density, and boiling point are given for elements in group VIIA/17 Element Cl Br I ...
Chocolate Challenge - Waterford Public Schools
... Protons determine element’s identity # of protons is unique for each element Electrons determine element’s chemical properties Neutrons act as a “glue” for the protons to minimize charge repulsions ...
... Protons determine element’s identity # of protons is unique for each element Electrons determine element’s chemical properties Neutrons act as a “glue” for the protons to minimize charge repulsions ...
Electrons and the Atom PPT
... a shell contains the maximum number of electrons, it is said to be filled. Electrons in the outer shell of an atom are known as valence electrons and the shell is the valence shell. The valence electrons are the only electrons involved in forming chemical bonds ...
... a shell contains the maximum number of electrons, it is said to be filled. Electrons in the outer shell of an atom are known as valence electrons and the shell is the valence shell. The valence electrons are the only electrons involved in forming chemical bonds ...