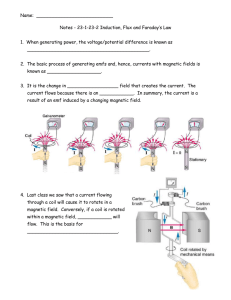
Name: Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday`s Law 1. When
... Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday’s Law 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the chan ...
... Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday’s Law 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the chan ...
Magnetic Island Dynamics under External Magnetic Perturbation in
... magnetic surface in the direction of the mode phase velocity is measured with the heavy ion beam diagnostic ...
... magnetic surface in the direction of the mode phase velocity is measured with the heavy ion beam diagnostic ...
Physical Science Chapter 15 Exam
... c. Domainosphere d. Exosphere 11. The continuous stream of high speed particles emanating from the sun is called the ____. a. Solar jet stream b. Solar wind c. Van Allen Belt d. Aurora Matching: Match the description to the correct term. 12. unlike poles attract, like poles repel 13. Device for prot ...
... c. Domainosphere d. Exosphere 11. The continuous stream of high speed particles emanating from the sun is called the ____. a. Solar jet stream b. Solar wind c. Van Allen Belt d. Aurora Matching: Match the description to the correct term. 12. unlike poles attract, like poles repel 13. Device for prot ...
numerical code balmer-szdyn for spectroscopy of hydrogen isotopes
... fluctuating frequency), which gives a universal description of the spectral line shapes in the general case of dynamical plasma electric microfield in terms of the static line shapes, in the presence of a strong magnetic field. The spectral distribution of the Stark components of the static Balmer l ...
... fluctuating frequency), which gives a universal description of the spectral line shapes in the general case of dynamical plasma electric microfield in terms of the static line shapes, in the presence of a strong magnetic field. The spectral distribution of the Stark components of the static Balmer l ...
Magnetic Reconnection
... the ionospheric foot, momentum is transferred from the solar wind plasma to the ionospheric plasma, both to move the foot, and to move surrounding ionospheric plasma out of the way. As the kink at the magnetopause straightens out, the open magnetospheric field line moves through the cusp region and ...
... the ionospheric foot, momentum is transferred from the solar wind plasma to the ionospheric plasma, both to move the foot, and to move surrounding ionospheric plasma out of the way. As the kink at the magnetopause straightens out, the open magnetospheric field line moves through the cusp region and ...
Magnetism and Induction Review
... Magnetism and Induction Review 1. How will a magnet that is free to rotate, like a compass, align itself with earth’s magnetic field? 2. How do opposite poles affect each other? What about like poles? 3. What do you get when you break a magnet in half? 4. Can you ever make it small enough to get jus ...
... Magnetism and Induction Review 1. How will a magnet that is free to rotate, like a compass, align itself with earth’s magnetic field? 2. How do opposite poles affect each other? What about like poles? 3. What do you get when you break a magnet in half? 4. Can you ever make it small enough to get jus ...
Fun Facts about Earth`s Magnetism caused by the Dynamo Effect
... Heat and the Earth’s spin or rotation keep the outer core moving. The Earth’s rotation and the spinning of the outer core is not at the same speed. This movement causes electrical currents in the core, which is mostly made up of iron. The electrical currents create a magnetic field that extends into ...
... Heat and the Earth’s spin or rotation keep the outer core moving. The Earth’s rotation and the spinning of the outer core is not at the same speed. This movement causes electrical currents in the core, which is mostly made up of iron. The electrical currents create a magnetic field that extends into ...
Universe 8e Lecture Chapter 12 Jupiter and Saturn
... best explains the source of heat? A. As a satellite rotates on its axis, it “flexes” due to the nearby tidal forces of Jupiter. The friction that accompanies the flexing creates heat. B. As the satellite changes its distance from Jupiter in its elliptical orbit, it “flexes” due to the tidal forces o ...
... best explains the source of heat? A. As a satellite rotates on its axis, it “flexes” due to the nearby tidal forces of Jupiter. The friction that accompanies the flexing creates heat. B. As the satellite changes its distance from Jupiter in its elliptical orbit, it “flexes” due to the tidal forces o ...
Magnetosphere of Saturn

The magnetosphere of Saturn is the cavity created in the flow of the solar wind by the planet's internally generated magnetic field. Discovered in 1979 by the Pioneer 11 spacecraft, Saturn's magnetosphere is the second largest of any planet in the Solar System after Jupiter. The magnetopause, the boundary between Saturn's magnetosphere and the solar wind, is located at a distance of about 20 Saturn radii from the planet's center, while its magnetotail stretches hundreds of radii behind it.Saturn's magnetosphere is filled with plasmas originating from both the planet and its moons. The main source is the small moon Enceladus, which ejects as much as 1,000 kg/s of water vapor from the geysers on its south pole, a portion of which is ionized and forced to co-rotate with the Saturn’s magnetic field. This loads the field with as much as 100 kg of water group ions per second. This plasma gradually moves out from the inner magnetosphere via the interchange instability mechanism and then escapes through the magnetotail.The interaction between Saturn's magnetosphere and the solar wind generates bright oval aurorae around the planet's poles observed in visible, infrared and ultraviolet light. The aurorae are related to the powerful saturnian kilometric radiation (SKR), which spans the frequency interval between 100 kHz to 1300 kHz and was once thought to modulate with a period equal to the planet's rotation. However, later measurements showed that the periodicity of the SKR's modulation varies by as much as 1%, and so probably does not exactly coincide with Saturn’s true rotational period, which as of 2010 remains unknown. Inside the magnetosphere there are radiation belts, which house particles with energy as high as tens of megaelectronvolts. The energetic particles have significant influence on the surfaces of inner icy moons of Saturn.In 1980–1981 the magnetosphere of Saturn was studied by the Voyager spacecraft. As of 2010 it is a subject of the ongoing investigation by Cassini mission, which arrived in 2004.