Solar System in Your Pocket
... night sky? Both are covered with highly reflective clouds, and although it is much smaller, Venus is also much, much closer. ...
... night sky? Both are covered with highly reflective clouds, and although it is much smaller, Venus is also much, much closer. ...
L 29 Electricity and Magnetism [6] Laws of Magnetism The electric
... • the EM wave propagates because the electric field recreates the magnetic field and the magnetic field recreates the electric field • an oscillating voltage applied to the antenna makes the charges in the antenna vibrate up and down sending out a synchronized pattern of electric and magnetic fields ...
... • the EM wave propagates because the electric field recreates the magnetic field and the magnetic field recreates the electric field • an oscillating voltage applied to the antenna makes the charges in the antenna vibrate up and down sending out a synchronized pattern of electric and magnetic fields ...
Magnetism
... • The magnetosphere (fields created by this giant magnet) stretch between 200 km and 5000 km beyond Earth’s surface. ...
... • The magnetosphere (fields created by this giant magnet) stretch between 200 km and 5000 km beyond Earth’s surface. ...
Chapter 11
... 1. Three possible methods by which energy can be transferred from the center of the Sun outward: (a) Conduction: The transfer of energy in a solid by collisions between atoms and/or molecules. This is not a significant factor in transporting energy within the Sun. (b) Convection: the transfer of ene ...
... 1. Three possible methods by which energy can be transferred from the center of the Sun outward: (a) Conduction: The transfer of energy in a solid by collisions between atoms and/or molecules. This is not a significant factor in transporting energy within the Sun. (b) Convection: the transfer of ene ...
Warm Up #7 What are two ways that magnets interact with each
... ▪ Magnetic material – any material that a magnet attracts (iron, aluminum, nickel) ...
... ▪ Magnetic material – any material that a magnet attracts (iron, aluminum, nickel) ...
generalsciencenotes - Geoscience Research Institute
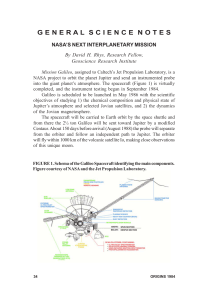
... resolution 20 to 300 times better than that of the cameras on Voyager. a near-infrared mapping spectrometer which will also measure heat from Io’s volcanoes. an ultraviolet spectrometer to study the composition and structure of the atmospheres and the cloud of charged atoms injected into the magneto ...
... resolution 20 to 300 times better than that of the cameras on Voyager. a near-infrared mapping spectrometer which will also measure heat from Io’s volcanoes. an ultraviolet spectrometer to study the composition and structure of the atmospheres and the cloud of charged atoms injected into the magneto ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... The force (F) is equal to the charge (q) times the speed of the particle (v) times the magnitude of the field (B), or F = q*v x B, where the direction of F is at right angles to both v and B as a result of the cross product. This defines the magnetic field's strength and direction at any point. ...
... The force (F) is equal to the charge (q) times the speed of the particle (v) times the magnitude of the field (B), or F = q*v x B, where the direction of F is at right angles to both v and B as a result of the cross product. This defines the magnetic field's strength and direction at any point. ...
chapter24b
... magnetic storms on the sun can hurl gigantic clouds of plasma into space. If they happen to come our way, they can cause problems like surges in power grids and breakdown of satellite communication. http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4541101546/ ...
... magnetic storms on the sun can hurl gigantic clouds of plasma into space. If they happen to come our way, they can cause problems like surges in power grids and breakdown of satellite communication. http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4541101546/ ...
Unit 07 Magnetic Fields
... except for one major difference: there are no such things as magnetic monopoles. Magnetic “charge,” like electric charge, comes in two possible flavors – instead of positive and negative we call them “north” and “south.” However, unlike electric charges, magnetic charges never appear by themselves – ...
... except for one major difference: there are no such things as magnetic monopoles. Magnetic “charge,” like electric charge, comes in two possible flavors – instead of positive and negative we call them “north” and “south.” However, unlike electric charges, magnetic charges never appear by themselves – ...
Magnetism
... An electric current flowing through a wire gives rise to a magnetic field whose direction depends upon the direction of the current. Coiling a conductor around a piece of soft iron will produce a powerful magnet. This is temporary and is only magnetic as long as current passes through the wire The s ...
... An electric current flowing through a wire gives rise to a magnetic field whose direction depends upon the direction of the current. Coiling a conductor around a piece of soft iron will produce a powerful magnet. This is temporary and is only magnetic as long as current passes through the wire The s ...
Geomagnetic storm

A geomagnetic storm is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase in electric current in the magnetosphere and ionosphere.During the main phase of a geomagnetic storm, electric current in the magnetosphere creates a magnetic force that pushes out the boundary between the magnetosphere and the solar wind. The disturbance in the interplanetary medium that drives the storm may be due to a solar coronal mass ejection (CME) or a high speed stream (co-rotating interaction region or CIR) of the solar wind originating from a region of weak magnetic field on the Sun’s surface. The frequency of geomagnetic storms increases and decreases with the sunspot cycle. CME driven storms are more common during the maximum of the solar cycle, while CIR driven storms are more common during the minimum of the solar cycle.Several space weather phenomena tend to be associated with or are caused by a geomagnetic storm. These include: solar energetic Particle (SEP) events, geomagnetically induced currents (GIC), ionospheric disturbances that cause radio and radar scintillation, disruption of navigation by magnetic compass and auroral displays at much lower latitudes than normal. In 1989, a geomagnetic storm energized ground induced currents that disrupted electric power distribution throughout most of the province of Quebec and caused aurorae as far south as Texas.

![L 29 Electricity and Magnetism [6] Laws of Magnetism The electric](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015457348_1-45ec1c6d8804a0bbd57ecd8a52999a34-300x300.png)