magnetic energy acumulation in the coronal current sheet
... energy 1032 - 1033 erg, which corresponds to the explosion of a million of hydrogen bombs, is released above AR. The existence of such gigantic explosions has remained long time outside the focus of attention of researchers because the power of Sun radiation (~1033 erg/s) at the solar flare increase ...
... energy 1032 - 1033 erg, which corresponds to the explosion of a million of hydrogen bombs, is released above AR. The existence of such gigantic explosions has remained long time outside the focus of attention of researchers because the power of Sun radiation (~1033 erg/s) at the solar flare increase ...
Lecture #13 – magnetic reversals
... When a hot magma cools from >1000°C to form a solid rocks, tiny magnetic minerals -iron oxides -- in the rock line up like little bar magnets along the direction of the earth’s magnetic field and preserve information about the orientation of the magnetic field lines and strength of the field at the ...
... When a hot magma cools from >1000°C to form a solid rocks, tiny magnetic minerals -iron oxides -- in the rock line up like little bar magnets along the direction of the earth’s magnetic field and preserve information about the orientation of the magnetic field lines and strength of the field at the ...
Lecture Note - Department of Electronic and Telecommunication
... • Sun's surface will be much cooler, about 2600 K than now and its luminosity much higher—up to 2700 times current solar luminosity • Sun will have a strong stellar wind which will carry away around 33% of its mass • As the Sun expands, it will most likely swallow the planets Mercury and Venus. Eart ...
... • Sun's surface will be much cooler, about 2600 K than now and its luminosity much higher—up to 2700 times current solar luminosity • Sun will have a strong stellar wind which will carry away around 33% of its mass • As the Sun expands, it will most likely swallow the planets Mercury and Venus. Eart ...
Grades 3-4 Lessons - Starry Night Education
... Lesson One: The Solar System Question 1: The Earth and Moon Can you describe the motion of the Earth and the Moon? Possible Answer: The Earth is rotating on its axis. The Moon goes (or orbits) around the Earth. ...
... Lesson One: The Solar System Question 1: The Earth and Moon Can you describe the motion of the Earth and the Moon? Possible Answer: The Earth is rotating on its axis. The Moon goes (or orbits) around the Earth. ...
Earths-Magnetic-Field
... Do you like to read science fiction? Science fiction writers are really creative. For example, an author might write about a time in the distant past when compasses pointed south instead of north. Actually, this idea isn’t fiction—it’s a fact! Earth’s magnetic poles have switched places repeatedly o ...
... Do you like to read science fiction? Science fiction writers are really creative. For example, an author might write about a time in the distant past when compasses pointed south instead of north. Actually, this idea isn’t fiction—it’s a fact! Earth’s magnetic poles have switched places repeatedly o ...
Neptune - ClassZone
... Uranus is usually one smooth color, but light and dark areas often appear on Neptune. Clouds of methane ice crystals can form high enough in the atmosphere of Neptune to look white. Storm systems can appear in darker shades of blue than the rest of the planet. One storm, seen during the flyby of the ...
... Uranus is usually one smooth color, but light and dark areas often appear on Neptune. Clouds of methane ice crystals can form high enough in the atmosphere of Neptune to look white. Storm systems can appear in darker shades of blue than the rest of the planet. One storm, seen during the flyby of the ...
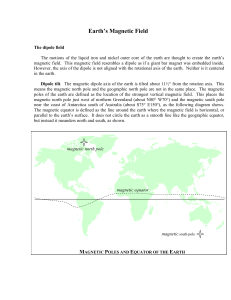
Chapter 1 Earth`s Magnetic Field
... Dipole offset. The magnetic dipole of the earth is not centered on the earth’s core, but instead is offset by about 700 kilometers towards the direction of southeastern Asia. This creates two features in the magnetic field at the earth’s surface. The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA). The point on the e ...
... Dipole offset. The magnetic dipole of the earth is not centered on the earth’s core, but instead is offset by about 700 kilometers towards the direction of southeastern Asia. This creates two features in the magnetic field at the earth’s surface. The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA). The point on the e ...
Magnetic Fields
... It is important to note that magnetic fields are force fields and therefore we need to represent the lines as arrows. In fact we define the direction of a magnetic field as the direction a compass would point in that field. In a permanent magnet these lines go from north to south. ...
... It is important to note that magnetic fields are force fields and therefore we need to represent the lines as arrows. In fact we define the direction of a magnetic field as the direction a compass would point in that field. In a permanent magnet these lines go from north to south. ...
F = BIL (f=force, b=magnetic field, i=current, l
... -Armature- is the power producing part of a motor -Domain- is a region in which the magnetic field of atoms are grouped together and aligned -Electric Motor- converts electrical energy into mechanical energy -Electromagnet- is a type of magnet whose magnetic field is produced by an electric current ...
... -Armature- is the power producing part of a motor -Domain- is a region in which the magnetic field of atoms are grouped together and aligned -Electric Motor- converts electrical energy into mechanical energy -Electromagnet- is a type of magnet whose magnetic field is produced by an electric current ...
The Sun Times
... streams of protons and electrons outward into space. Solar flares can interrupt the communications network here on Earth. Solar winds are the result of gas expansion in the corona. This expansion leads to streams of gas particles that flow out from the sun’s surface. Solar prominences are storms of ...
... streams of protons and electrons outward into space. Solar flares can interrupt the communications network here on Earth. Solar winds are the result of gas expansion in the corona. This expansion leads to streams of gas particles that flow out from the sun’s surface. Solar prominences are storms of ...
Magnetism I. Magnetic Forces Magnetism and electrostatic attraction
... Magnetism and electrostatic attraction are not the same, but they are related. Magnetism is caused by the movement of electrons. In all atoms, electrons are moving around the nucleus in areas of probability called orbitals. Electrons are also “spinning.” In most atoms electrons spinning in one direc ...
... Magnetism and electrostatic attraction are not the same, but they are related. Magnetism is caused by the movement of electrons. In all atoms, electrons are moving around the nucleus in areas of probability called orbitals. Electrons are also “spinning.” In most atoms electrons spinning in one direc ...
615-0185 (20-010) Instructions for Dip Needle
... a very useful tool in iron prospecting. Today this method is not as accurate as computer modeling and high tech scanners, but in early years it was indispensable. Your dip needle is equipped with banana jacks on the gimbal. If you connect a low voltage source to these, the gimbal will become electri ...
... a very useful tool in iron prospecting. Today this method is not as accurate as computer modeling and high tech scanners, but in early years it was indispensable. Your dip needle is equipped with banana jacks on the gimbal. If you connect a low voltage source to these, the gimbal will become electri ...
THE EARTH`S REVERSIBLE MAGNETIC FIELD. By William Reville
... the global magnetic field that prevailed when the rocks cooled and hardened. Rocks from widely scattered parts of the world, but of about the same age, display reverse polarity. The earth's poles have flipped over up to 25 times during the past five million years - on average, once every 200,000 yea ...
... the global magnetic field that prevailed when the rocks cooled and hardened. Rocks from widely scattered parts of the world, but of about the same age, display reverse polarity. The earth's poles have flipped over up to 25 times during the past five million years - on average, once every 200,000 yea ...
Page 1
... a) Sketch the entire magnetosphere, both the dayside and the nightside. Label all regions and boundaries of interest! (6 points) a. 1 pt for correct drawing, bow shock, magnetosheath, magnetopause, lobes, plasma sheet b) Describe the frozen-in concept! What is magnetic reconnection and why does the ...
... a) Sketch the entire magnetosphere, both the dayside and the nightside. Label all regions and boundaries of interest! (6 points) a. 1 pt for correct drawing, bow shock, magnetosheath, magnetopause, lobes, plasma sheet b) Describe the frozen-in concept! What is magnetic reconnection and why does the ...
Magnetic field lines and flux
... has never been observed (and that is why physicists keep looking for it -> “I want my Nobel prize” ) ...
... has never been observed (and that is why physicists keep looking for it -> “I want my Nobel prize” ) ...
01-01BasicMagnetism
... •How magnets pick things up •Wires with current •Whiteboard – direction of B field around wire •Loops •Whiteboard – direction of North pole ...
... •How magnets pick things up •Wires with current •Whiteboard – direction of B field around wire •Loops •Whiteboard – direction of North pole ...
Preparation PHYS2425 Magnetism lab. Charges cause
... A magnetic field will not only exert a force on a current carrying wire, but also on a small permanent magnet. You saw in class the effect a magnetic field has on a compass needle. Also you might have seen demonstrations of iron filings used to show the magnetic field line pattern. The small magnet ...
... A magnetic field will not only exert a force on a current carrying wire, but also on a small permanent magnet. You saw in class the effect a magnetic field has on a compass needle. Also you might have seen demonstrations of iron filings used to show the magnetic field line pattern. The small magnet ...
Geomagnetic storm

A geomagnetic storm is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase in electric current in the magnetosphere and ionosphere.During the main phase of a geomagnetic storm, electric current in the magnetosphere creates a magnetic force that pushes out the boundary between the magnetosphere and the solar wind. The disturbance in the interplanetary medium that drives the storm may be due to a solar coronal mass ejection (CME) or a high speed stream (co-rotating interaction region or CIR) of the solar wind originating from a region of weak magnetic field on the Sun’s surface. The frequency of geomagnetic storms increases and decreases with the sunspot cycle. CME driven storms are more common during the maximum of the solar cycle, while CIR driven storms are more common during the minimum of the solar cycle.Several space weather phenomena tend to be associated with or are caused by a geomagnetic storm. These include: solar energetic Particle (SEP) events, geomagnetically induced currents (GIC), ionospheric disturbances that cause radio and radar scintillation, disruption of navigation by magnetic compass and auroral displays at much lower latitudes than normal. In 1989, a geomagnetic storm energized ground induced currents that disrupted electric power distribution throughout most of the province of Quebec and caused aurorae as far south as Texas.