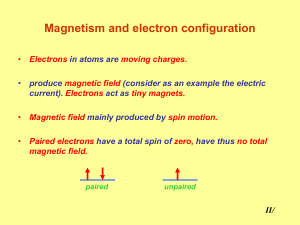
Magnetism
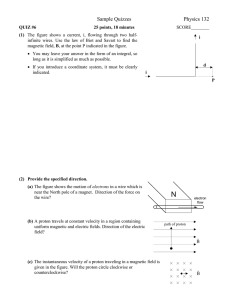
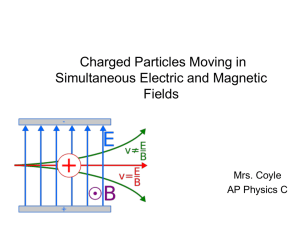
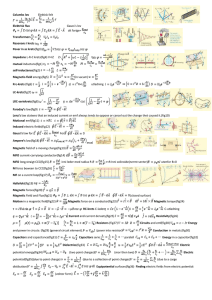
... Motion of a Charged Particle in a Magnetic Field If a charged particle is moving perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field, its path will be a circle. ...
... Motion of a Charged Particle in a Magnetic Field If a charged particle is moving perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field, its path will be a circle. ...
Chapter27_11
... – Magnetic fields & magnets (initial ideas) – Magnetic field and currents (initial ideas) – Force on a current in a B-field – Force on a charge in a B-field – Torque on a current loop in a B-field – The Hall Effect ...
... – Magnetic fields & magnets (initial ideas) – Magnetic field and currents (initial ideas) – Force on a current in a B-field – Force on a charge in a B-field – Torque on a current loop in a B-field – The Hall Effect ...
Week 8 Homework 1 Serway 20.1 Physics 1B
... field changed, this would cause a change in flux which would induce an emf in the bracelet. If the bracelet was a continuous band, this would create a large current, causing the bracelet to heat up. If the bracelet had a gap, the high voltage difference across the gap could cause charge carriers to ...
... field changed, this would cause a change in flux which would induce an emf in the bracelet. If the bracelet was a continuous band, this would create a large current, causing the bracelet to heat up. If the bracelet had a gap, the high voltage difference across the gap could cause charge carriers to ...
Earth`s Magnetic Field
... The Origin of Earth’s Magnetic Field The Spinning of the metallic Inner Core and convection currents in the metallic Outer Core creates a magnetic field around the Earth The magnetic poles are close to but not exactly the same as the geographic poles of Earth The Strength of the field is directly r ...
... The Origin of Earth’s Magnetic Field The Spinning of the metallic Inner Core and convection currents in the metallic Outer Core creates a magnetic field around the Earth The magnetic poles are close to but not exactly the same as the geographic poles of Earth The Strength of the field is directly r ...
Magnetic Storm Video Questions
... 8. What written record has provided scientists with valuable information regarding the magnetic field of the planet Earth? ...
... 8. What written record has provided scientists with valuable information regarding the magnetic field of the planet Earth? ...
Columbs lov Elektrisk flux Transformers Resonans i krets
... LC-krets(fig(7) LRC-seriekrets(fig8) Faraday’s law(fig9) Lenz’s law statwes that an induced current or emf always tends to oppose or cancel out the change thet caused it.(fig10) Motional emf(fig11) Induced electric fields(fig12) Gauss’s law for ...
... LC-krets(fig(7) LRC-seriekrets(fig8) Faraday’s law(fig9) Lenz’s law statwes that an induced current or emf always tends to oppose or cancel out the change thet caused it.(fig10) Motional emf(fig11) Induced electric fields(fig12) Gauss’s law for ...
Magnetometer

Magnetometers are measurement instruments used for two general purposes: to measure the magnetization of a magnetic material like a ferromagnet, or to measure the strength and, in some cases, the direction of the magnetic field at a point in space.The first magnetometer was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall Effect which is still widely used.Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field and in geophysical surveys to detect magnetic anomalies of various types. They are also used militarily to detect submarines. Consequently, some countries, such as the USA, Canada and Australia classify the more sensitive magnetometers as military technology, and control their distribution.Magnetometers can be used as metal detectors: they can detect only magnetic (ferrous) metals, but can detect such metals at a much larger depth than conventional metal detectors; they are capable of detecting large objects, such as cars, at tens of metres, while a metal detector's range is rarely more than 2 metres.In recent years magnetometers have been miniaturized to the extent that they can be incorporated in integrated circuits at very low cost and are finding increasing use as compasses in consumer devices such as mobile phones and tablet computers.