Is petroleum exploration plausible in Nigerian inland basins? A case
... on a scale of 1:100,000 with a total 7,426,917 data points were used in this work. The whole data, which were procured from the Nigerian Geological Survey Agency (NGSA) and assembled into composite total magnetic field intensity (TMI) map (Fig. 2), range between 32487.96 and 33423.06 nT with an aver ...
... on a scale of 1:100,000 with a total 7,426,917 data points were used in this work. The whole data, which were procured from the Nigerian Geological Survey Agency (NGSA) and assembled into composite total magnetic field intensity (TMI) map (Fig. 2), range between 32487.96 and 33423.06 nT with an aver ...
Blizzard Bag 1 - Maplewood Career Center
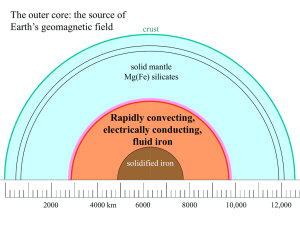
... various fields cancel one another because the electrons spin in opposite directions. IN materials such as iron, nickel, and cobalt, however, the fields do not cancel each other entirely. Each iron atom has four electrons whose spin magnetism is uncanceled. Each iron atom, then, is a tiny magnet. The ...
... various fields cancel one another because the electrons spin in opposite directions. IN materials such as iron, nickel, and cobalt, however, the fields do not cancel each other entirely. Each iron atom has four electrons whose spin magnetism is uncanceled. Each iron atom, then, is a tiny magnet. The ...
Section 15: Magnetic properties of materials
... more or less exactly for sufficiently high T. Here C and TC are positive constants independent of temperature and different for each material. It was found that in some materials TC=0 and this equation is obeyed down to the lowest temperatures at which measurements have been made. This class of mate ...
... more or less exactly for sufficiently high T. Here C and TC are positive constants independent of temperature and different for each material. It was found that in some materials TC=0 and this equation is obeyed down to the lowest temperatures at which measurements have been made. This class of mate ...
Chapter 19
... If a permanent magnetic is cut in half repeatedly, you will still have a north and a south pole This differs from electric charges There is some theoretical basis for monopoles, but none have been detected ...
... If a permanent magnetic is cut in half repeatedly, you will still have a north and a south pole This differs from electric charges There is some theoretical basis for monopoles, but none have been detected ...
Chapter 19
... If a permanent magnetic is cut in half repeatedly, you will still have a north and a south pole This differs from electric charges There is some theoretical basis for monopoles, but none have been detected ...
... If a permanent magnetic is cut in half repeatedly, you will still have a north and a south pole This differs from electric charges There is some theoretical basis for monopoles, but none have been detected ...
chapter19_PC
... If a permanent magnetic is cut in half repeatedly, you will still have a north and a south pole This differs from electric charges There is some theoretical basis for monopoles, but none have been detected ...
... If a permanent magnetic is cut in half repeatedly, you will still have a north and a south pole This differs from electric charges There is some theoretical basis for monopoles, but none have been detected ...
Microsoft Word Format - University of Toronto Physics
... As was first suggested by Goudsmit and Uhlenbeck, all electrons have an intrinsic angular momentum which may be attributed to a spin about an internal axis. Associated with this spin is a magnetic dipole moment. In most substances, the orbital angular momenta and the spin angular momenta of the elec ...
... As was first suggested by Goudsmit and Uhlenbeck, all electrons have an intrinsic angular momentum which may be attributed to a spin about an internal axis. Associated with this spin is a magnetic dipole moment. In most substances, the orbital angular momenta and the spin angular momenta of the elec ...
Computing the gravitational and magnetic anomalies - U
... and the geomagnetic azimuth (strike) of the polygon. This last quantity (0) should be determined with some care. It is the angle from magnetic north to the negative y-axis measured in the horizontal plane (Figure 3). The angle is positive when measured counterclockwise (looking down) from magnetic n ...
... and the geomagnetic azimuth (strike) of the polygon. This last quantity (0) should be determined with some care. It is the angle from magnetic north to the negative y-axis measured in the horizontal plane (Figure 3). The angle is positive when measured counterclockwise (looking down) from magnetic n ...
electromagnets arrangement for electromagnetic
... keep the windscreen clear during rainy weather. In general, the wipers move back and forth across the windshield in an oscillatory motion. The windshield wipers not only can be found on car windshields but also on some car headlights, airplanes and even on the space shuttle. The first windshield wip ...
... keep the windscreen clear during rainy weather. In general, the wipers move back and forth across the windshield in an oscillatory motion. The windshield wipers not only can be found on car windshields but also on some car headlights, airplanes and even on the space shuttle. The first windshield wip ...
Lab 7: Electric Guitar and Faraday`s Law
... calculate the volume of the string subjected to the magnetic field (the width of the magnet), and determine the number of atoms affected by the outside magnetic field. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic dipole moment that was induced on the string by the magnet. Did it reach saturation? What pe ...
... calculate the volume of the string subjected to the magnetic field (the width of the magnet), and determine the number of atoms affected by the outside magnetic field. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic dipole moment that was induced on the string by the magnet. Did it reach saturation? What pe ...
Magnetometer

Magnetometers are measurement instruments used for two general purposes: to measure the magnetization of a magnetic material like a ferromagnet, or to measure the strength and, in some cases, the direction of the magnetic field at a point in space.The first magnetometer was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall Effect which is still widely used.Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field and in geophysical surveys to detect magnetic anomalies of various types. They are also used militarily to detect submarines. Consequently, some countries, such as the USA, Canada and Australia classify the more sensitive magnetometers as military technology, and control their distribution.Magnetometers can be used as metal detectors: they can detect only magnetic (ferrous) metals, but can detect such metals at a much larger depth than conventional metal detectors; they are capable of detecting large objects, such as cars, at tens of metres, while a metal detector's range is rarely more than 2 metres.In recent years magnetometers have been miniaturized to the extent that they can be incorporated in integrated circuits at very low cost and are finding increasing use as compasses in consumer devices such as mobile phones and tablet computers.