Unit 13 Electromagnetic Fields
... P. 5G Investigate and describe the relationship between electric and magnetic fields in applications such as generators, motors and transformers See Instructional Focus Document (IFD) for TEK Specificity ...
... P. 5G Investigate and describe the relationship between electric and magnetic fields in applications such as generators, motors and transformers See Instructional Focus Document (IFD) for TEK Specificity ...
It must have domains (north and south poles) The
... Inside the Earth’s surface there is a huge amount of ferromagnetic liquids. These liquids are constantly in motion around a solid iron core and produce a massive magnetic field which can be felt anywhere around the ...
... Inside the Earth’s surface there is a huge amount of ferromagnetic liquids. These liquids are constantly in motion around a solid iron core and produce a massive magnetic field which can be felt anywhere around the ...
3-8 electricity1 - Worth County Schools
... Smaller, positively charged particles rise to the top of the cloud and larger, negatively charged particles gather at the bottom. When the buildup of charge is great enough, the oppositely charged particles attract and discharge their energy as a bolt of lightning. ...
... Smaller, positively charged particles rise to the top of the cloud and larger, negatively charged particles gather at the bottom. When the buildup of charge is great enough, the oppositely charged particles attract and discharge their energy as a bolt of lightning. ...
Magnetization Reversal of Synthetic Antiferromagnets Using
... non-magnetic spacer. Previous works devoted to the investigation of spin dynamics revealed collective acoustical and optical spin resonant modes in such systems. High-frequency investigations of the two coupled macrospins in SAF cell showed that system’s behavior is similar to Kapitsa pendulum. In-p ...
... non-magnetic spacer. Previous works devoted to the investigation of spin dynamics revealed collective acoustical and optical spin resonant modes in such systems. High-frequency investigations of the two coupled macrospins in SAF cell showed that system’s behavior is similar to Kapitsa pendulum. In-p ...
Magnetic field modelling Directional drilling Earth`s magnetic field
... Earth’s magnetic field can be mathematically ...
... Earth’s magnetic field can be mathematically ...
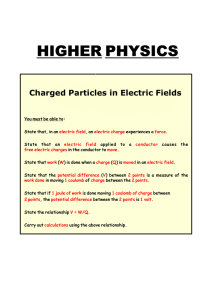
charged particles in electric fields
... charged particle (such as a proton) would accelerate if it was placed in the electric field. A negatively charged particle (such as an electron) would accelerate in the opposite direction to the arrow heads. ...
... charged particle (such as a proton) would accelerate if it was placed in the electric field. A negatively charged particle (such as an electron) would accelerate in the opposite direction to the arrow heads. ...
Magnetic Forces on a Current
... positive charge is in the direction of the electric field, and thus, the electric field line. The magnetic force is perpendicular to a moving charge so the field lines are not in the direction of the moving charge. 2. The electric field lines began on positive charges and ended on negative charges. ...
... positive charge is in the direction of the electric field, and thus, the electric field line. The magnetic force is perpendicular to a moving charge so the field lines are not in the direction of the moving charge. 2. The electric field lines began on positive charges and ended on negative charges. ...
For a long straight wire B = ( ìo I )/ ( 2 ð r) ìo = 4 ð x 10-7
... Recall that we first used Coulomb’s Law to calculate the electric force. Then we used F = qE and found the value of E by using Gauss’ Law. As we saw in the last chapter with F = qvB, if the magnetic field is known then we can easily calculate the magnetic force. Ampere’s Law helps us to find the mag ...
... Recall that we first used Coulomb’s Law to calculate the electric force. Then we used F = qE and found the value of E by using Gauss’ Law. As we saw in the last chapter with F = qvB, if the magnetic field is known then we can easily calculate the magnetic force. Ampere’s Law helps us to find the mag ...