Maxwell`s Equations 1.The concept of displacement current was a
... forth while the circuit is perpendicular to a uniform B-field, the system will be an example of a Ans:B A) AC motor B) AC generator C) DC motor D) DC generator 3. If the North pole of a bar magnet is moved down toward a wire loop on the floor, the current induced in the wire will flow Ans:B A) clock ...
... forth while the circuit is perpendicular to a uniform B-field, the system will be an example of a Ans:B A) AC motor B) AC generator C) DC motor D) DC generator 3. If the North pole of a bar magnet is moved down toward a wire loop on the floor, the current induced in the wire will flow Ans:B A) clock ...
Physics 142 Syllabus
... This is the second of a two semester sequence in introductory physics, covering electrostatics, magnetostatics, the electromagnetic wave equation, light, and optics, with calculus. Its intended targets are math/science majors other than physics or mathematics (who are better advised to take Physics ...
... This is the second of a two semester sequence in introductory physics, covering electrostatics, magnetostatics, the electromagnetic wave equation, light, and optics, with calculus. Its intended targets are math/science majors other than physics or mathematics (who are better advised to take Physics ...
Lecture_7_Magnets and Magnetism print
... Magnetic Theories Electron theory of magnetism • Electrons spin as they orbit (similar to earth) • Spin produces magnetic field • Magnetic direction depends on direction of rotation • Non-magnets → equal number of electrons spinning in opposite direction • Magnets → more spin one way than other ...
... Magnetic Theories Electron theory of magnetism • Electrons spin as they orbit (similar to earth) • Spin produces magnetic field • Magnetic direction depends on direction of rotation • Non-magnets → equal number of electrons spinning in opposite direction • Magnets → more spin one way than other ...
On Faraday`s Lines of Force
... 2b. Michael Faraday 1791 - 1867 •1821 First proposes ideas of “Lines of Force” • Example: iron filings over a magnetic show field lines ...
... 2b. Michael Faraday 1791 - 1867 •1821 First proposes ideas of “Lines of Force” • Example: iron filings over a magnetic show field lines ...
Concept Questions
... d) An electron moving perpendicular to a constant electric field. e) An electron moving perpendicular to a constant magnetic field. 27) Draw force diagrams and fields for a) A hydrogen ion in the TRIUMF cyclotron when between the dees. b) An ion passing through a mass spectrometer c) An electron and ...
... d) An electron moving perpendicular to a constant electric field. e) An electron moving perpendicular to a constant magnetic field. 27) Draw force diagrams and fields for a) A hydrogen ion in the TRIUMF cyclotron when between the dees. b) An ion passing through a mass spectrometer c) An electron and ...
Magnetic Fields - Rice University
... of wire on the right carries a current I in a uniform magnetic field. • No magnetic force acts on sides 1 & 3 – The wires are parallel to the field and L x B = ...
... of wire on the right carries a current I in a uniform magnetic field. • No magnetic force acts on sides 1 & 3 – The wires are parallel to the field and L x B = ...
EC6403
... Fundamental relations for Electrostatic and Magnetostatic fields, Faraday‟s law for Electromagnetic induction, Transformers, Motional Electromotive forces, Differential form of Maxwell‟s equations, Integral form of Maxwell‟s equations, Potential functions, Electromagnetic boundary conditions, Wave e ...
... Fundamental relations for Electrostatic and Magnetostatic fields, Faraday‟s law for Electromagnetic induction, Transformers, Motional Electromotive forces, Differential form of Maxwell‟s equations, Integral form of Maxwell‟s equations, Potential functions, Electromagnetic boundary conditions, Wave e ...
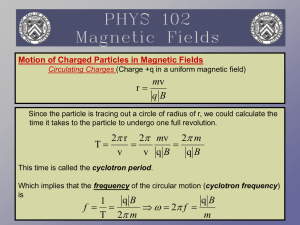
The Movement of Charged Particles in a Magnetic Field
... Some solar wind particles, however, do escape the earth’s magnetosphere and contribute to the Van Allen radiation belts. When these particles do enter the magnetic field, they go through three motions: • Spiral- the particle takes a spiraling motion around a magnetic field line. • Bounce- the parti ...
... Some solar wind particles, however, do escape the earth’s magnetosphere and contribute to the Van Allen radiation belts. When these particles do enter the magnetic field, they go through three motions: • Spiral- the particle takes a spiraling motion around a magnetic field line. • Bounce- the parti ...
Lecture 1: Introduction to Electromagnetism
... • How an electric field is produced by charges (Lectures 2-5) • How a magnetic field is produced by currents (Lectures 7-9) • How these fields are modified in materials (Lectures 6, 11) • Electromagnetic forces and their applications (Lecture 10) • How a changing magnetic field produces an electric ...
... • How an electric field is produced by charges (Lectures 2-5) • How a magnetic field is produced by currents (Lectures 7-9) • How these fields are modified in materials (Lectures 6, 11) • Electromagnetic forces and their applications (Lecture 10) • How a changing magnetic field produces an electric ...