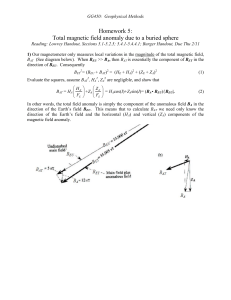
Presentation 1
... A pan on the stove being heated. Temperature at different points of the pan is a scalar field Vector Field example: Water flowing through a canal. Velocity highest at middle, zero at the ...
... A pan on the stove being heated. Temperature at different points of the pan is a scalar field Vector Field example: Water flowing through a canal. Velocity highest at middle, zero at the ...
Ch 28 Magnetic Fields
... The magnetic force on a charged particle, FB, is found to be: (Only the magnitude, therefore the unit, is defined.) Here q is the charge of the particle, v is its velocity, and B the magnetic field in the region. The magnitude of this force is then: Here f is the angle between vectors v and B. # Th ...
... The magnetic force on a charged particle, FB, is found to be: (Only the magnitude, therefore the unit, is defined.) Here q is the charge of the particle, v is its velocity, and B the magnetic field in the region. The magnitude of this force is then: Here f is the angle between vectors v and B. # Th ...
Chapter 29A Worksheet - Rose
... able to slide with negligible friction on the conductor. The apparatus is in a uniform magnetic field of 0.800 T, perpendicular to the plane of the figure. (A) Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the rod when it is moving toward the right with a speed of 7.50 m/s. (B) In what direction does the ...
... able to slide with negligible friction on the conductor. The apparatus is in a uniform magnetic field of 0.800 T, perpendicular to the plane of the figure. (A) Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the rod when it is moving toward the right with a speed of 7.50 m/s. (B) In what direction does the ...
File
... __d__ 2. Which of the following actions will decrease the strength of the magnetic field of an electromagnet? a. using fewer loops of wire per meter in the coil b. decreasing the current in the wire c. removing the iron core d. All of the above 3. Describe what happens when you hold a compass close ...
... __d__ 2. Which of the following actions will decrease the strength of the magnetic field of an electromagnet? a. using fewer loops of wire per meter in the coil b. decreasing the current in the wire c. removing the iron core d. All of the above 3. Describe what happens when you hold a compass close ...
Lecture
... • Charge outside not included • Exact location of charges inside doesn’t matter, only magnitude and sign • But, E is the resultant of all charges, both inside and outside ...
... • Charge outside not included • Exact location of charges inside doesn’t matter, only magnitude and sign • But, E is the resultant of all charges, both inside and outside ...
Lecture
... • Charge outside not included • Exact location of charges inside doesn’t matter, only magnitude and sign • But, E is the resultant of all charges, both inside and outside ...
... • Charge outside not included • Exact location of charges inside doesn’t matter, only magnitude and sign • But, E is the resultant of all charges, both inside and outside ...
Chapter 33. The Magnetic Field
... Current counterclockwise, north pole on bottom Current clockwise; north pole on bottom Current counterclockwise, north pole on top Current clockwise; north pole on top ...
... Current counterclockwise, north pole on bottom Current clockwise; north pole on bottom Current counterclockwise, north pole on top Current clockwise; north pole on top ...
Technical Description of an MIR Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI
... MRI scanners vary in size and shape, and some newer models have a greater degree of openness around the sides. Still, the basic design is the same, and the patient is pushed into a tube that's only about 24 inches in diameter The biggest and most important component of an MRI system is the magnet. T ...
... MRI scanners vary in size and shape, and some newer models have a greater degree of openness around the sides. Still, the basic design is the same, and the patient is pushed into a tube that's only about 24 inches in diameter The biggest and most important component of an MRI system is the magnet. T ...
Magnetic stripes on the ocean floor: a lab simulation
... the Earth’s magnetic field has ‘flipped’ (the N pole becoming the S pole, and vice versa) many times over geological time ...
... the Earth’s magnetic field has ‘flipped’ (the N pole becoming the S pole, and vice versa) many times over geological time ...
Magnetism - BAschools.org
... energy to electrical energy these work by changing the direction of the electric current ...
... energy to electrical energy these work by changing the direction of the electric current ...
Magnetic Fields - Grade 11 Physics
... Green: At lower altitudes the more frequent collisions suppress this mode and the 557.7 nm emission (green) dominates; fairly high concentration of atomic oxygen and higher eye sensitivity in green make green auroras the most common. The excited molecular nitrogen (atomic nitrogen being rare due to ...
... Green: At lower altitudes the more frequent collisions suppress this mode and the 557.7 nm emission (green) dominates; fairly high concentration of atomic oxygen and higher eye sensitivity in green make green auroras the most common. The excited molecular nitrogen (atomic nitrogen being rare due to ...
Magnetism (Part 1)
... South If a compass is held on the east end of the wire, in what direction is the needle deflected (assuming it can point any direction it wants to)? 8. Is it possible to orient a current-carrying loop of wire in a uniform magnetic field so that the loop of wire doesn’t rotate? Explain. 9. If a solen ...
... South If a compass is held on the east end of the wire, in what direction is the needle deflected (assuming it can point any direction it wants to)? 8. Is it possible to orient a current-carrying loop of wire in a uniform magnetic field so that the loop of wire doesn’t rotate? Explain. 9. If a solen ...