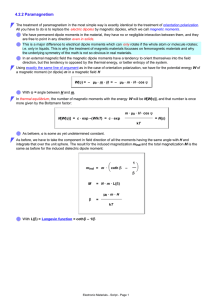
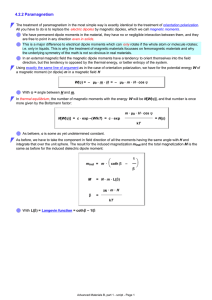
presentation source
... • Used to change voltage of alternating currents • The same amount of electric power can be delivered through wires at low voltage and high current as at high voltage and low current • Using low electrical current for electric energy transportation is more efficient: loss of electric energy in the w ...
... • Used to change voltage of alternating currents • The same amount of electric power can be delivered through wires at low voltage and high current as at high voltage and low current • Using low electrical current for electric energy transportation is more efficient: loss of electric energy in the w ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetism
... magnet where the magnet can make things move. Charged particles have an electric field. In the picture to the right, the magnet made the iron shavings move ...
... magnet where the magnet can make things move. Charged particles have an electric field. In the picture to the right, the magnet made the iron shavings move ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... If the north pole of a bar magnet is pointing to the north on Earth, what pole of the Earth is the bar magnet pointing to? A bar magnet’s north pole is attracted to the Earth’s south pole. ...
... If the north pole of a bar magnet is pointing to the north on Earth, what pole of the Earth is the bar magnet pointing to? A bar magnet’s north pole is attracted to the Earth’s south pole. ...
EECS 215: Introduction to Circuits
... Because a circular loop exhibits a magnetic field pattern similar to the electric field of an electric dipole, it is called a magnetic dipole ...
... Because a circular loop exhibits a magnetic field pattern similar to the electric field of an electric dipole, it is called a magnetic dipole ...
VOICE OVER FOR TLM for Project 5 - Class CBSE
... kinetic energy of the charged particle and the magnitude of the velocity of the charged particle remains constant. As the magnetic force acting on the charged particle is perpendicular to both the direction of its velocity and magnetic field, the charged particle moves in a circular path and the mag ...
... kinetic energy of the charged particle and the magnitude of the velocity of the charged particle remains constant. As the magnetic force acting on the charged particle is perpendicular to both the direction of its velocity and magnetic field, the charged particle moves in a circular path and the mag ...