What is a magnet? - Northern Highlands
... The interaction between two magnets really occurs in two steps. First, a magnet creates a magnetic field. Then the magnetic field creates forces on other magnets. In the drawing the field is represented by the arrows. ...
... The interaction between two magnets really occurs in two steps. First, a magnet creates a magnetic field. Then the magnetic field creates forces on other magnets. In the drawing the field is represented by the arrows. ...
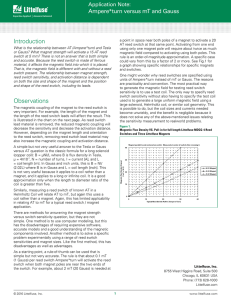
Ampere*turn versus mT and Gauss
... using only one magnet pole will require about twice as much magnetic field compared to activating using both poles. This rule is an order-of-magnitude approximation. A specific case could vary from this by a factor of 2 or more. See Fig.1 for a graph showing specific relationships for specific magne ...
... using only one magnet pole will require about twice as much magnetic field compared to activating using both poles. This rule is an order-of-magnitude approximation. A specific case could vary from this by a factor of 2 or more. See Fig.1 for a graph showing specific relationships for specific magne ...
Magnetic Particle Testing
... According to their interaction with a magnetic field, materials can be classified as: Diamagnetic materials which have a weak, negative susceptibility to magnetic fields. Diamagnetic materials are slightly repelled by a magnetic field and the material does not retain the magnetic properties when the ...
... According to their interaction with a magnetic field, materials can be classified as: Diamagnetic materials which have a weak, negative susceptibility to magnetic fields. Diamagnetic materials are slightly repelled by a magnetic field and the material does not retain the magnetic properties when the ...
Magnetism K-3 Teacher Guide
... more like a magicwhen show out of sight of landmarks there were no stars or sun Europe by covering your cardboard with a piece of cloth. Dena found Remember, part of the show is talking to your or moon to use for navigation. Eventually the compass audience so they forget about the hand under the out ...
... more like a magicwhen show out of sight of landmarks there were no stars or sun Europe by covering your cardboard with a piece of cloth. Dena found Remember, part of the show is talking to your or moon to use for navigation. Eventually the compass audience so they forget about the hand under the out ...
Chapter 33. The Magnetic Field
... The Source of the Magnetic Field: Moving Charges The magnetic field of a charged particle q moving with velocity v is given by the Biot-Savart law: ...
... The Source of the Magnetic Field: Moving Charges The magnetic field of a charged particle q moving with velocity v is given by the Biot-Savart law: ...
Floating Garden of Magnets
... protons and neutrons. Two or more atoms can combine to form molecules - the smallest pieces of more complex types of matter. Electrons and protons have an electrical property called charge. Charges can be positive (+) or negative (-). When a charged particle moves, a magnetic field is created around ...
... protons and neutrons. Two or more atoms can combine to form molecules - the smallest pieces of more complex types of matter. Electrons and protons have an electrical property called charge. Charges can be positive (+) or negative (-). When a charged particle moves, a magnetic field is created around ...
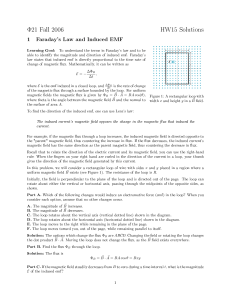
Physics 121 Fall 2002
... Currents produce magnetic fields (Ampere) & deflect a compass needle (Oersted 1820) Generator principle (Induction): changing magnetic fields produce electric fields (Faraday) Action at a distance “fields” applied to E&M. Maxwell’s Equations unify Electricity & Magnetism (James Clerk Maxwell, ~ 1865 ...
... Currents produce magnetic fields (Ampere) & deflect a compass needle (Oersted 1820) Generator principle (Induction): changing magnetic fields produce electric fields (Faraday) Action at a distance “fields” applied to E&M. Maxwell’s Equations unify Electricity & Magnetism (James Clerk Maxwell, ~ 1865 ...
All about Magnets
... (1) Like (Same) Poles repel, eg. A north and a north poles (2) Opposite Poles attract, eg. A north and a south pole 9. A compass consists of a needle which is actually a magnet. 10. The Earth also acts like a giant magnet consisting of a North and a South Poles. It consists mainly iron and nickel. 1 ...
... (1) Like (Same) Poles repel, eg. A north and a north poles (2) Opposite Poles attract, eg. A north and a south pole 9. A compass consists of a needle which is actually a magnet. 10. The Earth also acts like a giant magnet consisting of a North and a South Poles. It consists mainly iron and nickel. 1 ...