Unpacking Outcomes - NESD Curriculum Corner
... Recognize that electric fields act on point charges similar to the ways that gravitational fields act on point masses, including action at a distance and following the inverse-square law to determine strength of field. Draw and describe electric field lines for like and unlike point charges and plat ...
... Recognize that electric fields act on point charges similar to the ways that gravitational fields act on point masses, including action at a distance and following the inverse-square law to determine strength of field. Draw and describe electric field lines for like and unlike point charges and plat ...
Chapter 32 Maxwell`s Equations
... *Write each of Maxwell’s Equations in your own words, without using any mathematical symbols. ...
... *Write each of Maxwell’s Equations in your own words, without using any mathematical symbols. ...
t=0
... Find the torque about the left hand segment on the loop as a function of θ, the angle the plane makes with the horizontal plane. ...
... Find the torque about the left hand segment on the loop as a function of θ, the angle the plane makes with the horizontal plane. ...
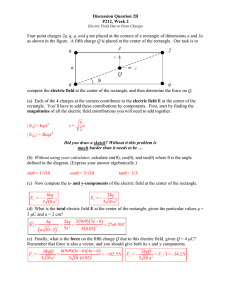
q q q 2 x y Q 3 a ϑ
... compute the electric field at the center of the rectangle, and then determine the force on Q. (a) Each of the 4 charges at the corners contributes to the electric field E at the center of the rectangle. You’ll have to add these contributions by components. First, start by finding the magnitudes of a ...
... compute the electric field at the center of the rectangle, and then determine the force on Q. (a) Each of the 4 charges at the corners contributes to the electric field E at the center of the rectangle. You’ll have to add these contributions by components. First, start by finding the magnitudes of a ...
EM Guided Notes KEY
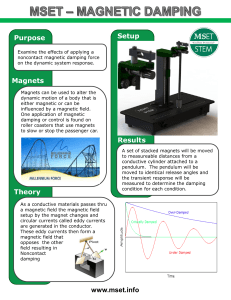
... Another common tool that uses this concept is a credit card. The card has a magnetic strip incorporated in it. If the strip is not moving, there is no current. But when the strip moves through a reader, a particular current is formed which carries information about the cardholder. That is how the st ...
... Another common tool that uses this concept is a credit card. The card has a magnetic strip incorporated in it. If the strip is not moving, there is no current. But when the strip moves through a reader, a particular current is formed which carries information about the cardholder. That is how the st ...
Equation sheet #1
... September 29, 2004 12:10 to 1:10 pm Constants and equations for exam 1. You may detach this page if you wish. ________________________________________________________________________________ Coulumb’s Law constant k=8.99 x109 N m2/C2 Permittivity of free space 0=8.85 x10-12 C2/N m2 Charge of one el ...
... September 29, 2004 12:10 to 1:10 pm Constants and equations for exam 1. You may detach this page if you wish. ________________________________________________________________________________ Coulumb’s Law constant k=8.99 x109 N m2/C2 Permittivity of free space 0=8.85 x10-12 C2/N m2 Charge of one el ...



![Physics 431: Electricity and Magnetism [.pdf] (Dr. Tom Callcott)](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008774277_1-66222afe36519fd20b954143a2878995-300x300.png)