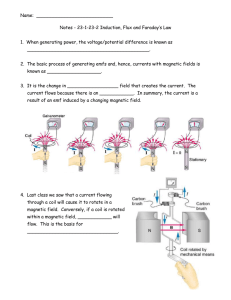
Name: Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday`s Law 1. When
... Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday’s Law 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the chan ...
... Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday’s Law 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the chan ...
VOICE OVER FOR TLM for Project 5 - Class CBSE
... The particles, whose magnitude of velocity is equal to the ratio of E to B, pass through the combination of electric field and magnetic field without deviation and the remaining particles whose velocity is not equal to the ratio of E to B, deviate on either side of the electric field. This principle ...
... The particles, whose magnitude of velocity is equal to the ratio of E to B, pass through the combination of electric field and magnetic field without deviation and the remaining particles whose velocity is not equal to the ratio of E to B, deviate on either side of the electric field. This principle ...
EE 333 Electricity and Magnetism
... 4. Ability to use differential vector mathematics to solve electromagnetic problems. 5. Knowledge of analytical and numerical techniques for solving static and time-dependent problems in vacuum and in materials. Prerequisites: MATH 332 (Vector Analysis). Physics 122 or 132 (General physics II). Topi ...
... 4. Ability to use differential vector mathematics to solve electromagnetic problems. 5. Knowledge of analytical and numerical techniques for solving static and time-dependent problems in vacuum and in materials. Prerequisites: MATH 332 (Vector Analysis). Physics 122 or 132 (General physics II). Topi ...
magnetic fields - King`s Senior Science
... points from “North” to “South” poles opposite poles attract like poles repel ...
... points from “North” to “South” poles opposite poles attract like poles repel ...
Electric Field – Notes and Examples
... Electric Field – Notes and Examples An electric field is an area of influence around a charged object It is given as the amount of electrical force exerted on a positive test charge placed at a given point in the field ...
... Electric Field – Notes and Examples An electric field is an area of influence around a charged object It is given as the amount of electrical force exerted on a positive test charge placed at a given point in the field ...
TAP410-0: Preparation for electromagnetic topic
... have to be measured both for permanent magnets and with simple geometries of wires and coils. A Hall probe, especially one that is calibrated, is helpful but search coils can also be used; the latter will need a mains supply that can produce a current of a few amperes and/or a signal generator. Some ...
... have to be measured both for permanent magnets and with simple geometries of wires and coils. A Hall probe, especially one that is calibrated, is helpful but search coils can also be used; the latter will need a mains supply that can produce a current of a few amperes and/or a signal generator. Some ...
Brief History of electromagnetism Contents
... 1860. James Clerk Maxwell, a Scottish physicist and mathematician, puts the theory of electromagnetism on mathematical basis. 1873.Maxwell publishes "Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism" in which he summarizes and synthesizes the discoveries of Coloumb, Oersted, Ampere, Faraday, et. al. in four ma ...
... 1860. James Clerk Maxwell, a Scottish physicist and mathematician, puts the theory of electromagnetism on mathematical basis. 1873.Maxwell publishes "Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism" in which he summarizes and synthesizes the discoveries of Coloumb, Oersted, Ampere, Faraday, et. al. in four ma ...
Magnetism 4 Electromagnets
... Discovered that an electric current causes a magnetic field How? Connected a series circuit and turned on the power. A nearby compass moved! ...
... Discovered that an electric current causes a magnetic field How? Connected a series circuit and turned on the power. A nearby compass moved! ...