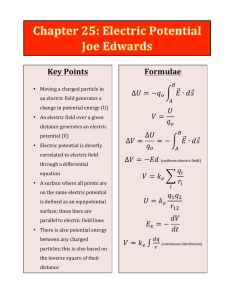
Key Points Formulae
... m, and the other is at x = -‐1.00 m. (a) Determine the electric potential on the y axis at y=0.500 m. (b) Calculate the change in electric potential energy of the system as a third charged ...
... m, and the other is at x = -‐1.00 m. (a) Determine the electric potential on the y axis at y=0.500 m. (b) Calculate the change in electric potential energy of the system as a third charged ...
zahn
... The primary focus of Prof. Zahn’s research group is the development of theory and applications that combine electromagnetism and other disciplines. Examples of the research include smart electric and magnetic liquids (electrohydrodynamics and ferrohydrodynamics respectively) for microfluidic, biomed ...
... The primary focus of Prof. Zahn’s research group is the development of theory and applications that combine electromagnetism and other disciplines. Examples of the research include smart electric and magnetic liquids (electrohydrodynamics and ferrohydrodynamics respectively) for microfluidic, biomed ...
Problem Set 02
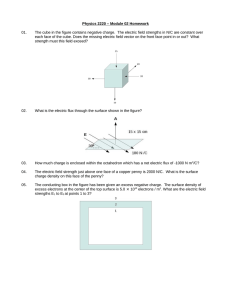
... The cube in the figure contains negative charge. The electric field strengths in N/C are constant over each face of the cube. Does the missing electric field vector on the front face point in or out? What strength must this field exceed? ...
... The cube in the figure contains negative charge. The electric field strengths in N/C are constant over each face of the cube. Does the missing electric field vector on the front face point in or out? What strength must this field exceed? ...
Physics with Mathematica Fall 2013 Exercise #4 17 Sep 2012
... Consider a straight line segment of uniformly distributed charge Q and length L, lying along the x-axis and centered on the origin. The line charge density is then simply λ = Q/L. Find the electrostatic potential along the z-axis, that is V (x) = V (0, 0, z). Express your result in the simplest form ...
... Consider a straight line segment of uniformly distributed charge Q and length L, lying along the x-axis and centered on the origin. The line charge density is then simply λ = Q/L. Find the electrostatic potential along the z-axis, that is V (x) = V (0, 0, z). Express your result in the simplest form ...
Questions:
... #1.) Which of the following statements are true? i. Electric field lines are always perpendicular to potential field equipotential lines. ii. The more closely spaced the equipotential lines are, the greater the potential. iii. The more closely spaced the electric field lines are, the stronger the el ...
... #1.) Which of the following statements are true? i. Electric field lines are always perpendicular to potential field equipotential lines. ii. The more closely spaced the equipotential lines are, the greater the potential. iii. The more closely spaced the electric field lines are, the stronger the el ...
EMT MODEL SET 2
... Part-A (Answer all the questions) 1. Give the applications of Divergence of a vector. 2. Give the effect of electromagnetic fields on human beings. 3. What is Dielectric Strength? 4. Plot the electric field and equipotential surfaces in a parallel plate capacitor. 5. What is magnetization? 6. What a ...
... Part-A (Answer all the questions) 1. Give the applications of Divergence of a vector. 2. Give the effect of electromagnetic fields on human beings. 3. What is Dielectric Strength? 4. Plot the electric field and equipotential surfaces in a parallel plate capacitor. 5. What is magnetization? 6. What a ...
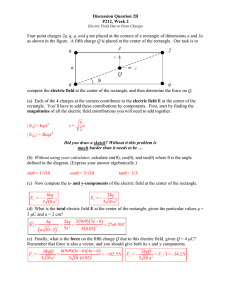
q q q 2 x y Q 3 a ϑ
... compute the electric field at the center of the rectangle, and then determine the force on Q. (a) Each of the 4 charges at the corners contributes to the electric field E at the center of the rectangle. You’ll have to add these contributions by components. First, start by finding the magnitudes of a ...
... compute the electric field at the center of the rectangle, and then determine the force on Q. (a) Each of the 4 charges at the corners contributes to the electric field E at the center of the rectangle. You’ll have to add these contributions by components. First, start by finding the magnitudes of a ...
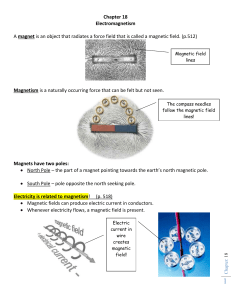
AO Electricity
... of negative charges in a material produces noticeable electric forces. Different kinds of materials respond differently to electric forces. In conducting materials such as metals, electric charges flow easily, whereas in insulating materials such as glass, they can move hardly at all. At very low ...
... of negative charges in a material produces noticeable electric forces. Different kinds of materials respond differently to electric forces. In conducting materials such as metals, electric charges flow easily, whereas in insulating materials such as glass, they can move hardly at all. At very low ...
Electric Field – Notes and Examples
... Electric Field – Notes and Examples An electric field is an area of influence around a charged object It is given as the amount of electrical force exerted on a positive test charge placed at a given point in the field ...
... Electric Field – Notes and Examples An electric field is an area of influence around a charged object It is given as the amount of electrical force exerted on a positive test charge placed at a given point in the field ...
Winter wk 3 – Thus.20.Jan.05
... • charges make scalar potential differences dV • E can be found from V • Electric forces move charges • Electric fields store energy (capacitance) ...
... • charges make scalar potential differences dV • E can be found from V • Electric forces move charges • Electric fields store energy (capacitance) ...
PHYS 222 Exam 1 Study Guide
... PHYS 222 Final Exam Study Guide Exam 1: - Superposition: Electric and potential fields do not interact with one another, they only interact with the particles. - Rules for drawing and interpreting electric field diagrams: Lines cannot intersect, correct directions of arrows, perpendicular to conduct ...
... PHYS 222 Final Exam Study Guide Exam 1: - Superposition: Electric and potential fields do not interact with one another, they only interact with the particles. - Rules for drawing and interpreting electric field diagrams: Lines cannot intersect, correct directions of arrows, perpendicular to conduct ...
Atomic View of Dielectrics -Electric Dipole in an Electric Field
... An external field can polarize the dielectric whether the molecules are polar or nonpolar ...
... An external field can polarize the dielectric whether the molecules are polar or nonpolar ...
Electroactive polymers

Electroactive polymers, or EAPs, are polymers that exhibit a change in size or shape when stimulated by an electric field. The most common applications of this type of material are in actuators and sensors. A typical characteristic property of an EAP is that they will undergo a large amount of deformation while sustaining large forces.The majority of historic actuators are made of ceramic piezoelectric materials. While these materials are able to withstand large forces, they commonly will only deform a fraction of a percent. In the late 1990s, it has been demonstrated that some EAPs can exhibit up to a 380% strain, which is much more than any ceramic actuator. One of the most common applications for EAPs is in the field of robotics in the development of artificial muscles; thus, an electroactive polymer is often referred to as an artificial muscle.