Virology
... Viral zoonosis from animal to human, Orf Horizontal Skin route warts Oral route entrovirus Respiratory route rhinovirus Urogenital route (sexually transmitted) CMV ...
... Viral zoonosis from animal to human, Orf Horizontal Skin route warts Oral route entrovirus Respiratory route rhinovirus Urogenital route (sexually transmitted) CMV ...
Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus
... hamsters and mice infected prior to weaning. Among enzootically infected populations of mice, the most common route of transmission is in utero. ...
... hamsters and mice infected prior to weaning. Among enzootically infected populations of mice, the most common route of transmission is in utero. ...
Microorganisms
... that can be pathogenic Cause diseases – Ex. Ring worm, athlete’s foot, thrush, histopasmosis, and yeast vaginitis ...
... that can be pathogenic Cause diseases – Ex. Ring worm, athlete’s foot, thrush, histopasmosis, and yeast vaginitis ...
infection-control-policy
... Consideration shall be given to provision of a safe and healthy environment for all consumers and staff and specific procedures shall be applied for the prevention of communicable disease transmission. _____________ has the right to deny placement or employment based on such medical information. Sta ...
... Consideration shall be given to provision of a safe and healthy environment for all consumers and staff and specific procedures shall be applied for the prevention of communicable disease transmission. _____________ has the right to deny placement or employment based on such medical information. Sta ...
Chapter 18: Viruses and Prokaryotes
... Pathogen: any living organism or particle that can cause an infectious disease Living Virus An infectious particle made only of a strand of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat Non living Cannot be targeted by antibiotics Cannot reproduce by themselves Rely on living cells to repr ...
... Pathogen: any living organism or particle that can cause an infectious disease Living Virus An infectious particle made only of a strand of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat Non living Cannot be targeted by antibiotics Cannot reproduce by themselves Rely on living cells to repr ...
Foundations in Microbiology
... disseminated CMV, retinitis • Transplant patients - pneumonitis, hepatitis, myocarditis, meningoencephalitis • Treatment: ganciclovir, valvcyclovir, foscarnet ...
... disseminated CMV, retinitis • Transplant patients - pneumonitis, hepatitis, myocarditis, meningoencephalitis • Treatment: ganciclovir, valvcyclovir, foscarnet ...
HepatitisB
... mild fever, and dark urine The illness lasts for a few weeks then gradually improves In some cases, it can cause to liver failure which can lead to death Liver cancer ...
... mild fever, and dark urine The illness lasts for a few weeks then gradually improves In some cases, it can cause to liver failure which can lead to death Liver cancer ...
The Chain of Infection
... e.g., Lyme disease) • Viruses - smallest microbes (HIV, Hepatitis B and C) • Helmiths - parasitic worms ...
... e.g., Lyme disease) • Viruses - smallest microbes (HIV, Hepatitis B and C) • Helmiths - parasitic worms ...
Disease Fact Sheet Cytomegalovirus (CMV) What is CMV? CMV, or
... A blood test can tell a person if they have CMV, but this test is not commonly performed. Laboratory tests can detect the virus in a person’s body fluids (blood or urine) or by a tissue biopsy (a small piece of the body’s tissue). CMV can also be detected in the body by measuring the antibodies (imm ...
... A blood test can tell a person if they have CMV, but this test is not commonly performed. Laboratory tests can detect the virus in a person’s body fluids (blood or urine) or by a tissue biopsy (a small piece of the body’s tissue). CMV can also be detected in the body by measuring the antibodies (imm ...
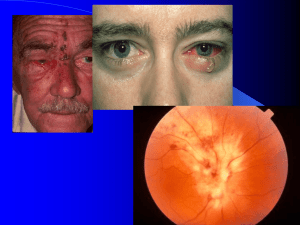
viral eye infections and treatment
... _Many PHN treatments don’t work -PHN is multifactorial syndrome ...
... _Many PHN treatments don’t work -PHN is multifactorial syndrome ...
West Nile Virus Quiz #1
... 1. Mosquitoes that become infected with the West Nile Virus can transmit the virus to another bird, person, or other animal after __________________ days. a. b. c. d. ...
... 1. Mosquitoes that become infected with the West Nile Virus can transmit the virus to another bird, person, or other animal after __________________ days. a. b. c. d. ...
HIV-Related Conditions and Opportunistic Infections
... • Infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis; pulmonary type is caused by acute or chronic bacterial infection that affects lungs, but it may also affect bones, brain, kidneys, and lymph nodes. • Disseminated type spreads from lungs to other body organs via circulatory or lymphatic ...
... • Infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis; pulmonary type is caused by acute or chronic bacterial infection that affects lungs, but it may also affect bones, brain, kidneys, and lymph nodes. • Disseminated type spreads from lungs to other body organs via circulatory or lymphatic ...
The Chain of Infection
... -the person that the pathogen enters A susceptible person is someone at higher risk for developing an infection ...
... -the person that the pathogen enters A susceptible person is someone at higher risk for developing an infection ...
Blood and Bloody Fluid Exposures
... Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Ebola is a highly contagious viral disease. The disease is transmitted via body fluids such as blood, sweat, saliva or tears. Those caring for sufferers are therefore susceptible to the Ebola virus, which can spread to health staff and family members, if appropriate infecti ...
... Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Ebola is a highly contagious viral disease. The disease is transmitted via body fluids such as blood, sweat, saliva or tears. Those caring for sufferers are therefore susceptible to the Ebola virus, which can spread to health staff and family members, if appropriate infecti ...
HIV Associated TB: A Major Public Health Challenge Mitzi Nisbet
... Co-infection with tuberculosis (TB) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) poses a tremendous challenge to TB control, especially in resource-limited settings. Among the estimated 8.7 million new TB cases in 2011, 1.1 million (13%) had HIV infection. Co-infection with HIV leads to challenges in both ...
... Co-infection with tuberculosis (TB) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) poses a tremendous challenge to TB control, especially in resource-limited settings. Among the estimated 8.7 million new TB cases in 2011, 1.1 million (13%) had HIV infection. Co-infection with HIV leads to challenges in both ...
A List of Notifiable Scheduled Infectious Diseases (as
... Acute poliomyelitis Amoebic dysentery Anthrax Bacillary dysentery Botulism Chickenpox Chikungunya fever Cholera Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease Dengue fever Diphtheria Enterovirus 71 infection Food poisoning Haemophilus influenzae ...
... Acute poliomyelitis Amoebic dysentery Anthrax Bacillary dysentery Botulism Chickenpox Chikungunya fever Cholera Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease Dengue fever Diphtheria Enterovirus 71 infection Food poisoning Haemophilus influenzae ...
PPT
... = (infectivity) (contacts per day) (infection duration) Sometimes referred to at Ro the reproductivity number (The number of new infections) / (a single infected person) ...
... = (infectivity) (contacts per day) (infection duration) Sometimes referred to at Ro the reproductivity number (The number of new infections) / (a single infected person) ...
Click here - NHS Highland
... Also known HBV or Hep B is a virus which may in some people not cause any symptoms but may in others cause flu like illness, tiredness, joint pains and loss of appetite. In more severe cases it causes abdominal pain and jaundice. Infection may result in illness for a few weeks whilst in others, dama ...
... Also known HBV or Hep B is a virus which may in some people not cause any symptoms but may in others cause flu like illness, tiredness, joint pains and loss of appetite. In more severe cases it causes abdominal pain and jaundice. Infection may result in illness for a few weeks whilst in others, dama ...
CANINE DISTEMPER REVISITED
... The distribution is worldwide and domestic dogs are considered important reservoirs. The highest incidence of disease is found in young (2-6 months old) unvaccinated dogs. All body secretions and excretions of infected animals are infectious. Transmission is primarily via inhalation of aerosolized b ...
... The distribution is worldwide and domestic dogs are considered important reservoirs. The highest incidence of disease is found in young (2-6 months old) unvaccinated dogs. All body secretions and excretions of infected animals are infectious. Transmission is primarily via inhalation of aerosolized b ...
Human cytomegalovirus

Human cytomegalovirus is a species of the Cytomegalovirus genus of viruses, which in turn is a member of the viral family known as Herpesviridae or herpesviruses. It is typically abbreviated as HCMV or, commonly but more ambiguously, as CMV. It is also known as human herpesvirus-5 (HHV-5). Within Herpesviridae, HCMV belongs to the Betaherpesvirinae subfamily, which also includes cytomegaloviruses from other mammals.Although they may be found throughout the body, HCMV infections are frequently associated with the salivary glands. HCMV infection is typically unnoticed in healthy people, but can be life-threatening for the immunocompromised, such as HIV-infected persons, organ transplant recipients, or newborn infants. After infection, HCMV remains latent within the body throughout life and can be reactivated at any time. Eventually, it may cause mucoepidermoid carcinoma and possibly other malignancies such as prostate cancer.HCMV is found throughout all geographic locations and socioeconomic groups, and infects between 60% and 70% of adults in industrialized countries and almost 100% in emerging countries.Of all herpes viruses, HCMV harbors the most genes dedicated to altering (evading) innate and adaptive immunity in the host and represents a life-long burden of antigenic T cell surveillance and immune dysfunction.Commonly it is indicated by the presence of antibodies in the general population. Seroprevalence is age-dependent: 58.9% of individuals aged 6 and older are infected with CMV while 90.8% of individuals aged 80 and older are positive for HCMV. HCMV is also the virus most frequently transmitted to a developing fetus.HCMV infection is more widespread in developing countries and in communities with lower socioeconomic status and represents the most significant viral cause of birth defects in industrialized countries. Congenital HCMV is the leading infectious cause of deafness, learning disabilities, and intellectual disability in childrenCMV also ""seems to have a large impact on immune parameters in later life and may contribute to increased morbidity and eventual mortality.""