Notification form and information for notifiable infectious diseases in
... Psittacosis (ornithosis) Q fever ¨ Lab ¨ Result pending ¨ Linked to lab-confirmed case ¨ Clinical only Rheumatic fever (acute) – use separate form Result: Method: Rickettsial infection (typhus) Species: Ross River virus infection FOLLOW-UP (tick one or more) Rotavirus infection Rubella ¨ No ...
... Psittacosis (ornithosis) Q fever ¨ Lab ¨ Result pending ¨ Linked to lab-confirmed case ¨ Clinical only Rheumatic fever (acute) – use separate form Result: Method: Rickettsial infection (typhus) Species: Ross River virus infection FOLLOW-UP (tick one or more) Rotavirus infection Rubella ¨ No ...
Kineta`s Novel Broad Spectrum Antivirals Trigger Effective Natural
... discussed in a talk by Kristin Bedard, PhD, Director and Head of Virology, at the Novel Antiviral Therapies for Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses: Bench to Beside Conference in Austin. “Kineta’s molecules function by triggering host innate antiviral immunity rather than focusing on a specific ...
... discussed in a talk by Kristin Bedard, PhD, Director and Head of Virology, at the Novel Antiviral Therapies for Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses: Bench to Beside Conference in Austin. “Kineta’s molecules function by triggering host innate antiviral immunity rather than focusing on a specific ...
Adult clinical infectious diseases helpline
... (Free from any TELKOM Line) *Standard cellular rates apply to calls from cell phones ...
... (Free from any TELKOM Line) *Standard cellular rates apply to calls from cell phones ...
What is a virus
... A capsid, and a core of nucleic acid, either DNA or RNA What is a capsid and what does it do? A capsid is a virus’s outer protein coat. The proteins in the capsid “trick” a cell into allowing the virus inside. What are some diseases caused by viruses? Polio, measles, mumps, influenza, yellow fever, ...
... A capsid, and a core of nucleic acid, either DNA or RNA What is a capsid and what does it do? A capsid is a virus’s outer protein coat. The proteins in the capsid “trick” a cell into allowing the virus inside. What are some diseases caused by viruses? Polio, measles, mumps, influenza, yellow fever, ...
Reading Chapter 27 NERVOUS SYSTEM Neurons
... they are coated with antibodies. The antibody enhances the infectivity of the virus by providing new receptors for the virus, promotes uptake into cells The difference between alphavirus and flavivirus: the organization of their genomes and the mechanisms of protein synthesis. Both cause lytic or pe ...
... they are coated with antibodies. The antibody enhances the infectivity of the virus by providing new receptors for the virus, promotes uptake into cells The difference between alphavirus and flavivirus: the organization of their genomes and the mechanisms of protein synthesis. Both cause lytic or pe ...
Glyconutritional Research and Four Prevalent Types of Infectious
... Hepatitis: One of the most deadly groups of viruses is the hepatitis family, which includes A,B, and C. These viruses attack liver tissue, leading to cirrhosis and liver cancer. The body’s main defense against the hepatitis virus is the production of interferons. These are proteins responsible for a ...
... Hepatitis: One of the most deadly groups of viruses is the hepatitis family, which includes A,B, and C. These viruses attack liver tissue, leading to cirrhosis and liver cancer. The body’s main defense against the hepatitis virus is the production of interferons. These are proteins responsible for a ...
1. DNA Viral Pathogens
... • transmitted parenterally (blood transfusion, injected drugs) • incubation period can be up to 20 years! • ~85% of infections become chronic • cirrhosis, liver cancer, even death are common outcomes ...
... • transmitted parenterally (blood transfusion, injected drugs) • incubation period can be up to 20 years! • ~85% of infections become chronic • cirrhosis, liver cancer, even death are common outcomes ...
Mirco-organisims Many living organisms such as plants, animals
... several years. During this period though the virus continues to grow in special white blood cells in the body. Eventually the huge numbers of virus particles produced destroys these cells quicker than the immune system can produce them. These white blood cells are essential for the normal function o ...
... several years. During this period though the virus continues to grow in special white blood cells in the body. Eventually the huge numbers of virus particles produced destroys these cells quicker than the immune system can produce them. These white blood cells are essential for the normal function o ...
Rev Esp Quimioter 2017, Mar 8
... to discharge patients (“hidden bacteraemia”). The highest number of confirmed bacteraemias comes from the samples of patients with urinary tract infections, followed by community-acquired pneumonia. The suspicion and detection of bacteraemia have an important diagnostic and prognostic significance a ...
... to discharge patients (“hidden bacteraemia”). The highest number of confirmed bacteraemias comes from the samples of patients with urinary tract infections, followed by community-acquired pneumonia. The suspicion and detection of bacteraemia have an important diagnostic and prognostic significance a ...
The Facts on Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease - Coolwinds Pre
... HFMD is contagious and often causes illness within 3 to 7 days after exposure to an infected person. ...
... HFMD is contagious and often causes illness within 3 to 7 days after exposure to an infected person. ...
Signs and Symptoms of HIV DiseaseThree stages
... Signs and Symptoms of HIV Disease HIV (HUMAN IMMUMODIFICIENCY VIRUS) Three stages: (All test positive) ASYMPTOMATIC STAGE No physically apparent symptoms HAZARDS: unknowing infection to others Activation of condition through vaccines SYMPTOMATIC STAGE Some symptoms, less severe than the classic AIDS ...
... Signs and Symptoms of HIV Disease HIV (HUMAN IMMUMODIFICIENCY VIRUS) Three stages: (All test positive) ASYMPTOMATIC STAGE No physically apparent symptoms HAZARDS: unknowing infection to others Activation of condition through vaccines SYMPTOMATIC STAGE Some symptoms, less severe than the classic AIDS ...
Mikrobiology - GEOCITIES.ws
... oportunistic flora - normally living in organism, but in some special ocasions can became a patogen - E. coli transcient flora - periodically occurs in organism, but as patogen act just in some special locations - S. pneumoniae Infectious disease - caused by microorganism or by it´s toxin Factors of ...
... oportunistic flora - normally living in organism, but in some special ocasions can became a patogen - E. coli transcient flora - periodically occurs in organism, but as patogen act just in some special locations - S. pneumoniae Infectious disease - caused by microorganism or by it´s toxin Factors of ...
College of Medicine Microbiology
... transmitted by blood transfusion. Injection of needles during intravenous drug use or indwelling catheter, have role in transmission. Sexual intercourse: certain pathogenic microorganisms can be transmitted by sexual contact in homosexual or heterosexual persons. Vertical transmission: The pathoge ...
... transmitted by blood transfusion. Injection of needles during intravenous drug use or indwelling catheter, have role in transmission. Sexual intercourse: certain pathogenic microorganisms can be transmitted by sexual contact in homosexual or heterosexual persons. Vertical transmission: The pathoge ...
MEASLES (RUBEOLA) VIRUS
... Postinfectious encephalitis is believed to be immune mediated, occurs after rash. ...
... Postinfectious encephalitis is believed to be immune mediated, occurs after rash. ...
Biology: Immune System Study Guide
... 4. Bacteria that break down the nutrients in dead matter into simpler substances that are taken up by plant roots are called _______________________. 5. What are some human uses for bacteria? 6. The outer protein coat of a virus is called a ___________________. 7. All viruses are made of proteins an ...
... 4. Bacteria that break down the nutrients in dead matter into simpler substances that are taken up by plant roots are called _______________________. 5. What are some human uses for bacteria? 6. The outer protein coat of a virus is called a ___________________. 7. All viruses are made of proteins an ...
Viral Diarrhoea and Vomiting - Worcestershire Health Services
... Yes. Anyone can get it. Some viruses tend to cause diarrhoea among people in specific age groups. Rotavirus infection is the most common cause of diarrhoea in infants and young children under 5 years old. Norwalk like viruses are more likely to cause diarrhoea in older children and adults. Infection ...
... Yes. Anyone can get it. Some viruses tend to cause diarrhoea among people in specific age groups. Rotavirus infection is the most common cause of diarrhoea in infants and young children under 5 years old. Norwalk like viruses are more likely to cause diarrhoea in older children and adults. Infection ...
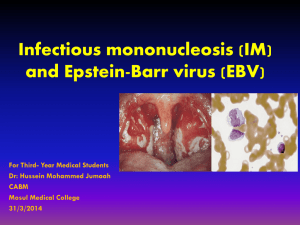
Infectious mononucleosis (IM) and Epstein
... In developing countries, subclinical infection in childhood is virtually universal. In developed countries, primary infection may be delayed until early adult life. The virus is acquired from asymptomatic excreters via saliva, by droplet infection, or by kissing. EBV is not highly contagious ,isolat ...
... In developing countries, subclinical infection in childhood is virtually universal. In developed countries, primary infection may be delayed until early adult life. The virus is acquired from asymptomatic excreters via saliva, by droplet infection, or by kissing. EBV is not highly contagious ,isolat ...
Civil war conditions created a perfect environment for dysentery and
... 5. When you pour hydrogen peroxide on a bloody abrasion, it bubbles. The bubbles give off oxygen. What type of microbe would potentially be destroyed by the use of hydrogen peroxide – aerobic or anerobic? ______________________________________________________________ 6. Bacteria are classified by sh ...
... 5. When you pour hydrogen peroxide on a bloody abrasion, it bubbles. The bubbles give off oxygen. What type of microbe would potentially be destroyed by the use of hydrogen peroxide – aerobic or anerobic? ______________________________________________________________ 6. Bacteria are classified by sh ...
MenACWY Information Pack
... Spreads through close persistent contact – e.g. Living in the same house, intimate kissing, sneezing, coughing ...
... Spreads through close persistent contact – e.g. Living in the same house, intimate kissing, sneezing, coughing ...
Hemobartonellosis in Cats
... Hemobartonella felis (newly renamed Mycoplasma haemophilus) is transferred via blood-sucking insects or by entry into the body through the mouth, in bite wounds, or through blood transfusions. The parasites are active in the blood 2-17 days after infection and can remain active for 3-8 weeks. The ca ...
... Hemobartonella felis (newly renamed Mycoplasma haemophilus) is transferred via blood-sucking insects or by entry into the body through the mouth, in bite wounds, or through blood transfusions. The parasites are active in the blood 2-17 days after infection and can remain active for 3-8 weeks. The ca ...
Human cytomegalovirus

Human cytomegalovirus is a species of the Cytomegalovirus genus of viruses, which in turn is a member of the viral family known as Herpesviridae or herpesviruses. It is typically abbreviated as HCMV or, commonly but more ambiguously, as CMV. It is also known as human herpesvirus-5 (HHV-5). Within Herpesviridae, HCMV belongs to the Betaherpesvirinae subfamily, which also includes cytomegaloviruses from other mammals.Although they may be found throughout the body, HCMV infections are frequently associated with the salivary glands. HCMV infection is typically unnoticed in healthy people, but can be life-threatening for the immunocompromised, such as HIV-infected persons, organ transplant recipients, or newborn infants. After infection, HCMV remains latent within the body throughout life and can be reactivated at any time. Eventually, it may cause mucoepidermoid carcinoma and possibly other malignancies such as prostate cancer.HCMV is found throughout all geographic locations and socioeconomic groups, and infects between 60% and 70% of adults in industrialized countries and almost 100% in emerging countries.Of all herpes viruses, HCMV harbors the most genes dedicated to altering (evading) innate and adaptive immunity in the host and represents a life-long burden of antigenic T cell surveillance and immune dysfunction.Commonly it is indicated by the presence of antibodies in the general population. Seroprevalence is age-dependent: 58.9% of individuals aged 6 and older are infected with CMV while 90.8% of individuals aged 80 and older are positive for HCMV. HCMV is also the virus most frequently transmitted to a developing fetus.HCMV infection is more widespread in developing countries and in communities with lower socioeconomic status and represents the most significant viral cause of birth defects in industrialized countries. Congenital HCMV is the leading infectious cause of deafness, learning disabilities, and intellectual disability in childrenCMV also ""seems to have a large impact on immune parameters in later life and may contribute to increased morbidity and eventual mortality.""