January 2013 - astronomy for beginners
... where there is a vertical line of stars forming his sword electron jumps back to its original orbit and emits a flash of (hanging from his belt). About half way down the line light. The colour of this light is unique to the type of atom of stars making up Orion’s sword is a hazy patch that that has ...
... where there is a vertical line of stars forming his sword electron jumps back to its original orbit and emits a flash of (hanging from his belt). About half way down the line light. The colour of this light is unique to the type of atom of stars making up Orion’s sword is a hazy patch that that has ...
- Schoolnet
... 62. The Moon revolves around Earth once every 29.5 days. It takes the Moon the same amount of time for it to complete one rotation. Because of this phenomenon, the same side of the Moon always faces Earth. Which best explains what makes the timing of the revolution and rotation of the Moon equal? A. ...
... 62. The Moon revolves around Earth once every 29.5 days. It takes the Moon the same amount of time for it to complete one rotation. Because of this phenomenon, the same side of the Moon always faces Earth. Which best explains what makes the timing of the revolution and rotation of the Moon equal? A. ...
CH 12
... done by Cavendish's time by as librarian in Alexandria called Eratosthenes (around 200 BC). Eratosthenes knew that ot a particular day every year sunlight reached the bottom of a very deep well in Syene (modern Aswan). He also knew the distance between Alexandria and Syene. From this information he ...
... done by Cavendish's time by as librarian in Alexandria called Eratosthenes (around 200 BC). Eratosthenes knew that ot a particular day every year sunlight reached the bottom of a very deep well in Syene (modern Aswan). He also knew the distance between Alexandria and Syene. From this information he ...
Study Guide for 3RD Astronomy Exam
... State or identify what additional information can be obtained from and eclipsing binaries besides the combined mass of the stars. Determine the combined mass of a binary star system using ...
... State or identify what additional information can be obtained from and eclipsing binaries besides the combined mass of the stars. Determine the combined mass of a binary star system using ...
Astronomy and Astrophysics (ASTRO) Iowa State University – 2013-2014 1
... For the nonscientist. Observational aspects of stellar astronomy: motions, distances, sizes, spectra; types of stars; variability; binary systems. Stellar evolution: the birth, life, and death of stars, including supernovae, neutron stars, and black holes. The Milky Way Galaxy: clouds of matter in s ...
... For the nonscientist. Observational aspects of stellar astronomy: motions, distances, sizes, spectra; types of stars; variability; binary systems. Stellar evolution: the birth, life, and death of stars, including supernovae, neutron stars, and black holes. The Milky Way Galaxy: clouds of matter in s ...
Celestial Navigation in 60 min
... We found a mathematical relation between what we know (delta, GHA, h) and what we are looking for (latitude, longitude). With 2 observations, we get a system of 2 equations with 2 unknowns that we are able to solve. The celestial navigation problem is thus resolved. What? You don't like my equation ...
... We found a mathematical relation between what we know (delta, GHA, h) and what we are looking for (latitude, longitude). With 2 observations, we get a system of 2 equations with 2 unknowns that we are able to solve. The celestial navigation problem is thus resolved. What? You don't like my equation ...
Deep Space Mystery Note Form 3
... Type II Type II Binary stars are when there are two stars and they revolve around each other. In these systems supernovas occur also. Stars up to eight times the mass of our sun usually evolve into white dwarfs. A star that is condensed to this size has a very strong gravitational pull. ...
... Type II Type II Binary stars are when there are two stars and they revolve around each other. In these systems supernovas occur also. Stars up to eight times the mass of our sun usually evolve into white dwarfs. A star that is condensed to this size has a very strong gravitational pull. ...
Today in Astronomy 142: observations of stars
... between the evolving matter and radiation fields. Observations from ground-based, balloon-borne, and satellite instruments show the CMB to agree with a blackbody spectrum (dotted line) across 3 decades of frequency and 4 orders of magnitude in intensity. This agreement with a blackbody spectrum indi ...
... between the evolving matter and radiation fields. Observations from ground-based, balloon-borne, and satellite instruments show the CMB to agree with a blackbody spectrum (dotted line) across 3 decades of frequency and 4 orders of magnitude in intensity. This agreement with a blackbody spectrum indi ...
Oct 2011 - Bays Mountain Park
... of Aries and the more elusive Cetus in the east as darkness falls. At magnitude -2.9 it is unmistakable to the naked eye in the fairly blank area between the Ram and the Sea Monster. Jupiter is especially nice this month since it reaches opposition or opposite the Sun in the sky the night of October ...
... of Aries and the more elusive Cetus in the east as darkness falls. At magnitude -2.9 it is unmistakable to the naked eye in the fairly blank area between the Ram and the Sea Monster. Jupiter is especially nice this month since it reaches opposition or opposite the Sun in the sky the night of October ...
The Primordial Abundance of $^ 6$ Li and $^ 9$ be
... 1993, where log N(Li) = log(Li/H) + 12). The primordial 4 He abundance is restricted to the range 0.237 ≤ Yp ≤ 0.247. Various alternative to SBBN have been proposed, some of which predict significantly different values for the primordial 6 Li, 7 Li and ...
... 1993, where log N(Li) = log(Li/H) + 12). The primordial 4 He abundance is restricted to the range 0.237 ≤ Yp ≤ 0.247. Various alternative to SBBN have been proposed, some of which predict significantly different values for the primordial 6 Li, 7 Li and ...
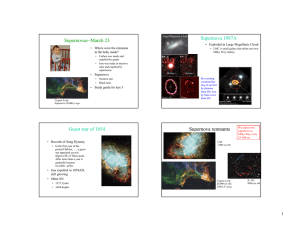
Supernovae March 23 − Supernova 1987A
... Degeneracy pressure prevents temperature from rising. Carbon burning. That is wrong; the sun will become a supernova. ...
... Degeneracy pressure prevents temperature from rising. Carbon burning. That is wrong; the sun will become a supernova. ...
Precession of the Equinox - Binary Research Institute
... position by about 4 minutes per day due to the earth’s annual orbit around the sun. This is not precession but it is a similar observed motion that is easy to notice from night to night or month to month. Precession however proceeds so slowly, about one degree per 72 years, that it takes very patien ...
... position by about 4 minutes per day due to the earth’s annual orbit around the sun. This is not precession but it is a similar observed motion that is easy to notice from night to night or month to month. Precession however proceeds so slowly, about one degree per 72 years, that it takes very patien ...
Why Star Positions?
... that their angular proper motions are very small. The star’s space velocity is an important quantity for astronomers, but determining it from the angular motion needs a knowledge of the star’s distance. A star’s distance is difficult to determine, and doing so requires a special trick which I will d ...
... that their angular proper motions are very small. The star’s space velocity is an important quantity for astronomers, but determining it from the angular motion needs a knowledge of the star’s distance. A star’s distance is difficult to determine, and doing so requires a special trick which I will d ...
Lab Activity on the Causes of the Seasons
... F. Attributes of the Arctic and Antarctic Circles: • At 66.5° North latitude (the Arctic Circle), the sun never sets on the summer solstice (around June 21); on all other days, the sun does go down at least for a little while. Everywhere north of the Arctic Circle, there are even more days when the ...
... F. Attributes of the Arctic and Antarctic Circles: • At 66.5° North latitude (the Arctic Circle), the sun never sets on the summer solstice (around June 21); on all other days, the sun does go down at least for a little while. Everywhere north of the Arctic Circle, there are even more days when the ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4
... Galactic cluster • Group of galaxies • Some contain thousands of galaxies ...
... Galactic cluster • Group of galaxies • Some contain thousands of galaxies ...
2 Coordinate systems
... unknown it usually suffices to use two coordinates. On the other hand, since the Earth rotates around it’s own axis as well as around the Sun the positions of stars and planets is continually changing, and the measurment of when an object is in a certain place is as important as deciding where it is ...
... unknown it usually suffices to use two coordinates. On the other hand, since the Earth rotates around it’s own axis as well as around the Sun the positions of stars and planets is continually changing, and the measurment of when an object is in a certain place is as important as deciding where it is ...
Historical astronomy How Johannes Kepler Johannes
... resulted in the first book on crystallography, De nive sexangula. After Galileo’s telescopic discoveries in 1610, Kepler described how the revolutionary new instrument worked. He also introduced improvements, including one that increased the field of view. His design came into wide use by the middle ...
... resulted in the first book on crystallography, De nive sexangula. After Galileo’s telescopic discoveries in 1610, Kepler described how the revolutionary new instrument worked. He also introduced improvements, including one that increased the field of view. His design came into wide use by the middle ...
Export To Word
... Gravity and energy influence the development and life cycles of galaxies, including our own Milky Way Galaxy, stars, the planetary systems, Earth, and residual material left from the formation of the Solar System. Humankind’s need to explore continues to lead to the development of knowledge and un ...
... Gravity and energy influence the development and life cycles of galaxies, including our own Milky Way Galaxy, stars, the planetary systems, Earth, and residual material left from the formation of the Solar System. Humankind’s need to explore continues to lead to the development of knowledge and un ...