class 4, S11 (ch. 2c and 3)Jan20
... Hallmarks of Good Science • Science seeks explanations that rely solely on natural causes. • Science progresses by creating and testing models of nature that explain observations as simply as possible: Occam’s Razor • A scientific model must make testable predictions that could force us to revise o ...
... Hallmarks of Good Science • Science seeks explanations that rely solely on natural causes. • Science progresses by creating and testing models of nature that explain observations as simply as possible: Occam’s Razor • A scientific model must make testable predictions that could force us to revise o ...
Lecture 1 - University of Cape Town
... HII regions • The gas here is ionized and hot (10,000 K is typical) – usually as a result of intense irradiation from a massive young star. • The radiation comes from electrons accelerated (diverted) as they come close to a positive ion. ...
... HII regions • The gas here is ionized and hot (10,000 K is typical) – usually as a result of intense irradiation from a massive young star. • The radiation comes from electrons accelerated (diverted) as they come close to a positive ion. ...
Earth in Space 19-1
... because it receives sunlight more directly than the poles. Without the tilt Earth would not have seasons. Summer and winter are not affected by changes in Earth's distance from the sun. In fact, when the Northern Hemisphere is having summer, Earth is at its greatest distance from the sun. ...
... because it receives sunlight more directly than the poles. Without the tilt Earth would not have seasons. Summer and winter are not affected by changes in Earth's distance from the sun. In fact, when the Northern Hemisphere is having summer, Earth is at its greatest distance from the sun. ...
Astronomical Distances
... your measuring instruments? Answer: You resort to using GEOMETRY to find the distance. ...
... your measuring instruments? Answer: You resort to using GEOMETRY to find the distance. ...
Milky Way galaxy - Uplift North Hills Prep
... theoretical framework to understand the observed universe, its origin, and its future. foundation: Einstein’s general theory of relativity and its theory of gravitation—for in the large-scale structure of the universe, gravity is the dominant force. ...
... theoretical framework to understand the observed universe, its origin, and its future. foundation: Einstein’s general theory of relativity and its theory of gravitation—for in the large-scale structure of the universe, gravity is the dominant force. ...
Minerals
... hemisphere is tilted toward the sun so we are experiencing summer. Around December 21, the sun’s rays are direct on the Tropic of Capricorn, 23 ½ o South and the northern hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, so we are experiencing winter. Around September 21 and March 21 the sun’s rays are direct ...
... hemisphere is tilted toward the sun so we are experiencing summer. Around December 21, the sun’s rays are direct on the Tropic of Capricorn, 23 ½ o South and the northern hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, so we are experiencing winter. Around September 21 and March 21 the sun’s rays are direct ...
PHYS299B_Final_HudsonJustin
... • With the raw data that would have been collected, we would have produced a light curve as seen to the bottom picture. • What this light curve shows is that the deepest dips in brightness during the phase is when the brightest star is blocked by the other creating the eclipsing effect like when Ear ...
... • With the raw data that would have been collected, we would have produced a light curve as seen to the bottom picture. • What this light curve shows is that the deepest dips in brightness during the phase is when the brightest star is blocked by the other creating the eclipsing effect like when Ear ...
Astronomy Club of Asheville July 2016 Sky Events
... Mars, although rapidly fading, remains in great viewing position this month – high in the sky for most of the night in the constellation Libra. The planet Saturn can be found within the boundaries of the constellation Ophiuchus, the Serpent Holder, all month, and it’s a great time to observe it ...
... Mars, although rapidly fading, remains in great viewing position this month – high in the sky for most of the night in the constellation Libra. The planet Saturn can be found within the boundaries of the constellation Ophiuchus, the Serpent Holder, all month, and it’s a great time to observe it ...
Introduction Notes - Sunflower Astronomy
... Get into groups of three and revise the IAU definition of a planet by considering some or all of the problems that were listed. On the worksheet provided write an alternate definition for a planet. Everyone turns in a copy of the worksheet. Time: 10 minutes. Beyond The Solar System Nearest star to t ...
... Get into groups of three and revise the IAU definition of a planet by considering some or all of the problems that were listed. On the worksheet provided write an alternate definition for a planet. Everyone turns in a copy of the worksheet. Time: 10 minutes. Beyond The Solar System Nearest star to t ...
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Black Holes
... as plutonium-244, 244Pu, (81 million years). The short-lived isotopes are particularly interesting. If they formed in an exploding star, that explosion might have triggered the collapse of the huge interstellar cloud in which the ...
... as plutonium-244, 244Pu, (81 million years). The short-lived isotopes are particularly interesting. If they formed in an exploding star, that explosion might have triggered the collapse of the huge interstellar cloud in which the ...
SNC 1D Astonomy
... Patterns in the Night Sky • Many groups of stars seem to form patterns called constellations. • They appear to lie very close to each other at exactly the same distance from Earth. • They look close together because they lie on the same line of sight. • They may actually be many light years apart! ...
... Patterns in the Night Sky • Many groups of stars seem to form patterns called constellations. • They appear to lie very close to each other at exactly the same distance from Earth. • They look close together because they lie on the same line of sight. • They may actually be many light years apart! ...
RFS_multiple_choice_Dec8_Key
... navigator Ferdinand Magellan and his crew "discovered" 2 irregularlyshaped objects, which were cloud-like in appearance, in the night-sky of the Southern Hemisphere. These later came to be known as the 2 "Magellanic Clouds", the larger and the smaller being called "Large Magellanic Cloud" (LMC) and ...
... navigator Ferdinand Magellan and his crew "discovered" 2 irregularlyshaped objects, which were cloud-like in appearance, in the night-sky of the Southern Hemisphere. These later came to be known as the 2 "Magellanic Clouds", the larger and the smaller being called "Large Magellanic Cloud" (LMC) and ...
PHY 133 - GEOCITIES.ws
... (interesting aside – the fact that a circle has 360 degrees is related to the fact that the Babylonians thought there were 360 days in a year, and so each day represented another step in the sun’s motion through the stars. After 360 days, it had made it nearly full circle) You see, the SUN and the S ...
... (interesting aside – the fact that a circle has 360 degrees is related to the fact that the Babylonians thought there were 360 days in a year, and so each day represented another step in the sun’s motion through the stars. After 360 days, it had made it nearly full circle) You see, the SUN and the S ...
The Universe Inside of You: Where do the atoms in your body come
... Another Way To Make Au: The r-Process Capture neutrons very quickly - “rapid” compared to the time it takes to beta-decay. So many neutrons are captured that we push the “path” far from the stable isotopes. No information on nuclear properties of thousands of nuclei that participate in this process ...
... Another Way To Make Au: The r-Process Capture neutrons very quickly - “rapid” compared to the time it takes to beta-decay. So many neutrons are captured that we push the “path” far from the stable isotopes. No information on nuclear properties of thousands of nuclei that participate in this process ...
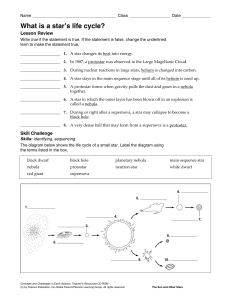
What is a star`s life cycle?
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
Earth in space
... • explaining day & night, seasons, Moon’s phases, motion of stars & planets, solar & lunar eclipses, scaling planets and orbits • some big ideas – relative motion, space, time, gravity ...
... • explaining day & night, seasons, Moon’s phases, motion of stars & planets, solar & lunar eclipses, scaling planets and orbits • some big ideas – relative motion, space, time, gravity ...
Cosmic Distance Ladder
... • Reliable measurements, those with errors of 10% or less, can only be achieved at stellar distances of no more than about 100 pc. • Space-based telescopes are not limited by this effect and can accurately measure distances to objects beyond the limit of ground-based observations. • E.g. Hipparcos 0 ...
... • Reliable measurements, those with errors of 10% or less, can only be achieved at stellar distances of no more than about 100 pc. • Space-based telescopes are not limited by this effect and can accurately measure distances to objects beyond the limit of ground-based observations. • E.g. Hipparcos 0 ...
Astronomy 114 Problem Set # 6 Due: 11 Apr 2007 SOLUTIONS 1
... 4/3π(104m)3 The density of matter in a neutron and the density of matter in a neutron star are similar. The density of the neutron star is higher because the gravitational pull can compress the nuclear fluid somewhat even though it is degenerate matter. ...
... 4/3π(104m)3 The density of matter in a neutron and the density of matter in a neutron star are similar. The density of the neutron star is higher because the gravitational pull can compress the nuclear fluid somewhat even though it is degenerate matter. ...
STARS
... class I) of spectral type K-M. They are the largest stars in the universe in terms of Volume, although they are not the most massive. • Stars with more than about 10 solar masses after burning their hydrogen become red supergiants during their helium-burning phase. These stars have very cool surface ...
... class I) of spectral type K-M. They are the largest stars in the universe in terms of Volume, although they are not the most massive. • Stars with more than about 10 solar masses after burning their hydrogen become red supergiants during their helium-burning phase. These stars have very cool surface ...
PS 224: Astronomy Fall 2014 Midterm (October 16, 2014)
... 4) In order for us to understand how the solar system got to be that way it is, we must identify the major solar system patterns that our formation theory must explain. Name five patterns of motion or planetary arrangement/location that our theory should be able to explain. ...
... 4) In order for us to understand how the solar system got to be that way it is, we must identify the major solar system patterns that our formation theory must explain. Name five patterns of motion or planetary arrangement/location that our theory should be able to explain. ...
Maps & Projections - New York Science Teacher
... List differences between latitude and longitude Why are there time zones on Earth? If it 2pm in New York State and California is 45 degrees west, what time is it in California? ...
... List differences between latitude and longitude Why are there time zones on Earth? If it 2pm in New York State and California is 45 degrees west, what time is it in California? ...
Solar System scale model
... The Solar System is often portrayed as a line of planets, closely packed to each other. But this picture is misleading! There is a lot of space in space! Astronomical distances are measured in km and in Astronomical Units (AU). 1 AU is 149,600,000km and is the same distance between the Sun and the E ...
... The Solar System is often portrayed as a line of planets, closely packed to each other. But this picture is misleading! There is a lot of space in space! Astronomical distances are measured in km and in Astronomical Units (AU). 1 AU is 149,600,000km and is the same distance between the Sun and the E ...