Stellar Temperature & Luminosity Student Page Purpose
... 1. If the peak in the black body curve of a star is at a longer wavelength than the peak wavelength for our Sun, how does the surface temperature of that star compare to our Sun’s surface temperature? 2. Which of the following events will have the largest effect on a star’s brightness — doubling its ...
... 1. If the peak in the black body curve of a star is at a longer wavelength than the peak wavelength for our Sun, how does the surface temperature of that star compare to our Sun’s surface temperature? 2. Which of the following events will have the largest effect on a star’s brightness — doubling its ...
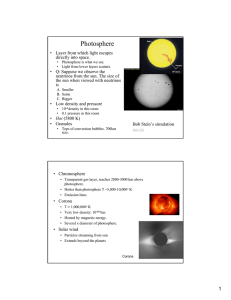
Photosphere
... • Layer from which light escapes directly into space. • Photosphere is what we see. • Light from lower layers scatters. ...
... • Layer from which light escapes directly into space. • Photosphere is what we see. • Light from lower layers scatters. ...
Astronomy 2 Relativity and Gravitation
... Now the number of H atoms in corona NH is almost exactly equal to the mass of the corona divided by the mass of a proton, 1016/1.7x10-27 . Number of Fe atoms NFe = NH x abundance by number = NH x 7 x 10-5. Number of Fe atoms with electron in upper level 2 is NFe x 10-4. Thus A21 [4 (1.5 1011) ...
... Now the number of H atoms in corona NH is almost exactly equal to the mass of the corona divided by the mass of a proton, 1016/1.7x10-27 . Number of Fe atoms NFe = NH x abundance by number = NH x 7 x 10-5. Number of Fe atoms with electron in upper level 2 is NFe x 10-4. Thus A21 [4 (1.5 1011) ...
Ordinary Stars - Edgewood High School
... As the temperature of a star increases, the peak of its radiation is shifted toward shorter (blue) wavelengths Stefan-Boltzmann Law As the temperature of a star increases, the total energy output increases as the 4th power of the temperature ...
... As the temperature of a star increases, the peak of its radiation is shifted toward shorter (blue) wavelengths Stefan-Boltzmann Law As the temperature of a star increases, the total energy output increases as the 4th power of the temperature ...
Star Gazing
... Star Gazing • Star Gazing techniques and tips: how to get the most out of looking up at the stars (powerpoint and notes on class website) ...
... Star Gazing • Star Gazing techniques and tips: how to get the most out of looking up at the stars (powerpoint and notes on class website) ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... core temperature rises to a point where fuel is used up • A carbon-oxygen core forms • Eventually the gases at a star’s surface begin to blow ...
... core temperature rises to a point where fuel is used up • A carbon-oxygen core forms • Eventually the gases at a star’s surface begin to blow ...
Powerpoint file
... • Most challenging observational technique due to proximity, contrast levels and atmospheric effects (AO, coronagraphy,..) • Candidates appeared at large (~100 AU) separations and mass determination is limited by reliability of evolutionary models (if no other information) • More robust detections ( ...
... • Most challenging observational technique due to proximity, contrast levels and atmospheric effects (AO, coronagraphy,..) • Candidates appeared at large (~100 AU) separations and mass determination is limited by reliability of evolutionary models (if no other information) • More robust detections ( ...
UNIT VIII/B: THE EARTH IN SPACE – STARS AND GALAXIES
... f. The lack of outward pressure generated by the iron-fusing core causes the outer layers to fall towards the center of the star. This implosion happens very, very quickly: it takes about 15 seconds to complete. During the collapse, the nuclei in the outer parts of the star are pushed very close tog ...
... f. The lack of outward pressure generated by the iron-fusing core causes the outer layers to fall towards the center of the star. This implosion happens very, very quickly: it takes about 15 seconds to complete. During the collapse, the nuclei in the outer parts of the star are pushed very close tog ...
Stars
... Barnard’s Star’s motion, which can only be explained as the gravitational attraction of an unseen companion, probably a gas giant planet several times larger than Jupiter. We cannot see this planet directly because the star is too bright to make out the much dimmer planet, but the tale-tell tug on t ...
... Barnard’s Star’s motion, which can only be explained as the gravitational attraction of an unseen companion, probably a gas giant planet several times larger than Jupiter. We cannot see this planet directly because the star is too bright to make out the much dimmer planet, but the tale-tell tug on t ...
PS#3
... Lsun is 4x1026 W, so this is about 0.001 times the Sun’s luminosity 4. A radio transmitter on a spacecraft emits a signal at a frequency of 10 Hz. At Earth the signal is received and noted to be at 99,970,000Hz. How fast is the spacecraft moving? Is it receding or approaching? ...
... Lsun is 4x1026 W, so this is about 0.001 times the Sun’s luminosity 4. A radio transmitter on a spacecraft emits a signal at a frequency of 10 Hz. At Earth the signal is received and noted to be at 99,970,000Hz. How fast is the spacecraft moving? Is it receding or approaching? ...
Luminosity - UCF Physics
... thousands of stellar spectra. Established a classification scheme based on Hydrogen lines…. The types were alphabetical….letters were assigned in declining strength of the H-lines ...
... thousands of stellar spectra. Established a classification scheme based on Hydrogen lines…. The types were alphabetical….letters were assigned in declining strength of the H-lines ...
Stages - A Summary - University of Dayton
... will stay for over 90% of its life, virtually unchanged externally. [Note : Stars of different masses experience similar evolutionary tracks on the H-R Diagram, but end up at different points on the ZAMS; recall that mass => gravity => squeezing => core T => fusion E => luminosity.] Although lowmass ...
... will stay for over 90% of its life, virtually unchanged externally. [Note : Stars of different masses experience similar evolutionary tracks on the H-R Diagram, but end up at different points on the ZAMS; recall that mass => gravity => squeezing => core T => fusion E => luminosity.] Although lowmass ...
Distance - courses.psu.edu
... 3. a) A star with the Sun's luminosity, but located 2 AU from Earth instead of 1 AU, would appear how bright relative to the Sun? b) A star with the Sun's luminosity, but located 20 AU from Earth instead of 1 AU, would appear how bright relative to the Sun? 4. Jupiter's moon Europa, which effectivel ...
... 3. a) A star with the Sun's luminosity, but located 2 AU from Earth instead of 1 AU, would appear how bright relative to the Sun? b) A star with the Sun's luminosity, but located 20 AU from Earth instead of 1 AU, would appear how bright relative to the Sun? 4. Jupiter's moon Europa, which effectivel ...
Chapter 10 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
... Circumference of NS = 2 (radius) ~ 60 km Spin rate of fast pulsars ~ 1000 cycles per second Surface rotation velocity ~ 60,000 km/s ~ 20% speed of light ~ escape velocity from NS Anything else would be torn to pieces! ...
... Circumference of NS = 2 (radius) ~ 60 km Spin rate of fast pulsars ~ 1000 cycles per second Surface rotation velocity ~ 60,000 km/s ~ 20% speed of light ~ escape velocity from NS Anything else would be torn to pieces! ...
Dynamics of nuclear burning during type-I X-ray bursts 1. 2. 3.
... 1. The model of burning front propagation based on geostrophic circulations is tested by full hydro numerical simulations. 2. Burning on sphere either starts on the equator or propagates to the equator and then in the form of “walls-of-fire” to the poles. Initial asymmetries are efficiently erased. ...
... 1. The model of burning front propagation based on geostrophic circulations is tested by full hydro numerical simulations. 2. Burning on sphere either starts on the equator or propagates to the equator and then in the form of “walls-of-fire” to the poles. Initial asymmetries are efficiently erased. ...