File - Science Website
... Describe, in as much detail as you can, what forces allow a stable star to exist and how the star may eventually form a black hole. To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. ...
... Describe, in as much detail as you can, what forces allow a stable star to exist and how the star may eventually form a black hole. To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. ...
How we found about BLACK HOLES
... collapses when the fuel is finally used up. When a star collapses suddenly enough, it explodes in the process. The more massive it is, the greater the explosion. When a star explodes, it uses up all the hydrogen fuel still left in its outer layers. It does this very rapidly and the star glows up to ...
... collapses when the fuel is finally used up. When a star collapses suddenly enough, it explodes in the process. The more massive it is, the greater the explosion. When a star explodes, it uses up all the hydrogen fuel still left in its outer layers. It does this very rapidly and the star glows up to ...
Widener University
... A star has mass 2.5 Msun = 5.0 x 1030 kg, radius 2.0 Rsun = 1.4 x 109 m, and luminosity 40 Lsun = 1.6 x 1028 W. The star is initially composed of 100% H and converts all of it to He, each chain of 4H He releasing an amount of energy E = 4.3 x 10-12 J. Calculate: a) the total number of H nuclei (p ...
... A star has mass 2.5 Msun = 5.0 x 1030 kg, radius 2.0 Rsun = 1.4 x 109 m, and luminosity 40 Lsun = 1.6 x 1028 W. The star is initially composed of 100% H and converts all of it to He, each chain of 4H He releasing an amount of energy E = 4.3 x 10-12 J. Calculate: a) the total number of H nuclei (p ...
13 The Family of Stars
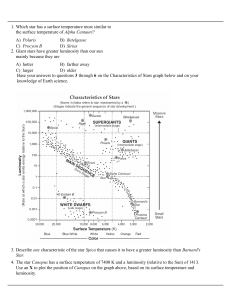
... Polaris is just about the same spectral type (G) (and thus surface temperature) as our Sun, but it is 10,000 times brighter than our Sun. This must be caused by Polaris having a larger radius than the Sun. Polaris must be 100 times larger than the Sun because R2 = 1002 = 10,000 produces a luminosity ...
... Polaris is just about the same spectral type (G) (and thus surface temperature) as our Sun, but it is 10,000 times brighter than our Sun. This must be caused by Polaris having a larger radius than the Sun. Polaris must be 100 times larger than the Sun because R2 = 1002 = 10,000 produces a luminosity ...
Project 3. Colour in Astronomy
... M50, but most of the dimmer, red stars do not. M50 lies about 3000 light-years from Earth and is about 20 light years across. Magnitude is a number that measures the brightness of a star or galaxy. In magnitude, higher numbers correspond to fainter objects, lower numbers to brighter objects; the ver ...
... M50, but most of the dimmer, red stars do not. M50 lies about 3000 light-years from Earth and is about 20 light years across. Magnitude is a number that measures the brightness of a star or galaxy. In magnitude, higher numbers correspond to fainter objects, lower numbers to brighter objects; the ver ...
Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli) Chapter 33
... position of a particular star varies by 0.00014° due to parallax. How many kilometers is this star from Earth? A) 1.2 × 1011 km B) 1.2 × 1014 km C) 1.2 × 1017 km D) 1.2 × 1020 km Answer: B Var: 1 7) The earth's orbit has a mean radius of 1.5 × 108 km. Over a six-month period, the apparent position o ...
... position of a particular star varies by 0.00014° due to parallax. How many kilometers is this star from Earth? A) 1.2 × 1011 km B) 1.2 × 1014 km C) 1.2 × 1017 km D) 1.2 × 1020 km Answer: B Var: 1 7) The earth's orbit has a mean radius of 1.5 × 108 km. Over a six-month period, the apparent position o ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
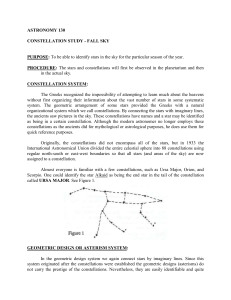
... The Greeks recognized the impossibility of attempting to learn much about the heavens without first organizing their information about the vast number of stars in some systematic system. The geometric arrangement of some stars provided the Greeks with a natural organizational system which we call co ...
... The Greeks recognized the impossibility of attempting to learn much about the heavens without first organizing their information about the vast number of stars in some systematic system. The geometric arrangement of some stars provided the Greeks with a natural organizational system which we call co ...
Conference Summary Richard Ellis (Caltech) ITALIA
... • How did the Hubble Sequence emerge at z<1 from the varied active and irregular sources at z > 2? What are the physical processes involved? Are the detailed models correct? • z > 6 the final frontier: did early galaxies reionize the Universe and what early feedback processes shape the later assembl ...
... • How did the Hubble Sequence emerge at z<1 from the varied active and irregular sources at z > 2? What are the physical processes involved? Are the detailed models correct? • z > 6 the final frontier: did early galaxies reionize the Universe and what early feedback processes shape the later assembl ...
Galactic Evolution:
... some power of the volume gas density Star formation is a self-regulated process controlled by the energetic feedback from young stars that prevents new stars from being formed. Efficiency of the process is described by a. ...
... some power of the volume gas density Star formation is a self-regulated process controlled by the energetic feedback from young stars that prevents new stars from being formed. Efficiency of the process is described by a. ...
Amanda Boyle Starstuff
... dead. Because space is cold. And very dark. While stars are not themselves alive, they produce light and heat and radiation that allows us to live. Without stars, we would have never existed, for they not only create all of the elements that make up our existence, but they also provide the very ener ...
... dead. Because space is cold. And very dark. While stars are not themselves alive, they produce light and heat and radiation that allows us to live. Without stars, we would have never existed, for they not only create all of the elements that make up our existence, but they also provide the very ener ...
Earth in Space - Learning Outcomes
... The development of what we know about the Earth, Solar System and Universe is a fascinating study in its own right. From earliest times Man has wondered at and speculated over the ‘Nature of the Heavens’. It is hardly surprising that most people (until around 1500 A.D.) thought that the Sun revolved ...
... The development of what we know about the Earth, Solar System and Universe is a fascinating study in its own right. From earliest times Man has wondered at and speculated over the ‘Nature of the Heavens’. It is hardly surprising that most people (until around 1500 A.D.) thought that the Sun revolved ...
The masses of stars
... red, and thus cool, supergiant) and Rigel a hot (blue-white) supergiant. The diameter of Betelgeuse is greater than the size of Jupiter’s orbit around the Sun; although the star’s surface temperature is much cooler than that of the Sun, at only about 3,500K, the fact that it is radiating through suc ...
... red, and thus cool, supergiant) and Rigel a hot (blue-white) supergiant. The diameter of Betelgeuse is greater than the size of Jupiter’s orbit around the Sun; although the star’s surface temperature is much cooler than that of the Sun, at only about 3,500K, the fact that it is radiating through suc ...