1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light... limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of...
... limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer potential model, with a value of a = 100 kpc, together with the Viral t ...
... limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer potential model, with a value of a = 100 kpc, together with the Viral t ...
Main Sequence Star What is happening in the core? How does the
... Main Sequence Star What is happening in the core? How does the star support itself? ...
... Main Sequence Star What is happening in the core? How does the star support itself? ...
STARS and GALAXIES
... • A large ball of gas held together by gravity that produces tremendous amounts of heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer emit radiation (no light). ...
... • A large ball of gas held together by gravity that produces tremendous amounts of heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer emit radiation (no light). ...
CH27.2 Stellar Evolution
... NONE are yet known to exist…..our universe isn’t thought to be old enough for this to happen yet! ...
... NONE are yet known to exist…..our universe isn’t thought to be old enough for this to happen yet! ...
Click here for Jeopardychap16
... Give correct order of Evolution of sun-like star From young to old: ...
... Give correct order of Evolution of sun-like star From young to old: ...
homework assignment 3
... Due Monday, April 22, 2013 at 5 p.m., either electronically or on paper. 1. Most astronomy textbooks use planets orbiting the Sun to illustrate the relevance of Kepler’s third law of planetary motion. In a class on stars and galaxies, describe a more relevant example of Kepler’s third law (i.e., whe ...
... Due Monday, April 22, 2013 at 5 p.m., either electronically or on paper. 1. Most astronomy textbooks use planets orbiting the Sun to illustrate the relevance of Kepler’s third law of planetary motion. In a class on stars and galaxies, describe a more relevant example of Kepler’s third law (i.e., whe ...
Properties of Main Sequence Stars
... Determine approximate values of the luminosity, temperature, mass and radius of an O5 and M5 main sequence star using the HR diagram on the accompanying page or use the HR diagrams in the text (Unit 59). ...
... Determine approximate values of the luminosity, temperature, mass and radius of an O5 and M5 main sequence star using the HR diagram on the accompanying page or use the HR diagrams in the text (Unit 59). ...
Holography
... the day than at night? 2. Will the converging lens focus blue light or red light at a closer distance to the lens? Explain. 3. Assume that you have the thinnest film that strongly reflects red light. Would you need to make the film thinner or thicker to completely reflect blue light? Explain. 4. If ...
... the day than at night? 2. Will the converging lens focus blue light or red light at a closer distance to the lens? Explain. 3. Assume that you have the thinnest film that strongly reflects red light. Would you need to make the film thinner or thicker to completely reflect blue light? Explain. 4. If ...
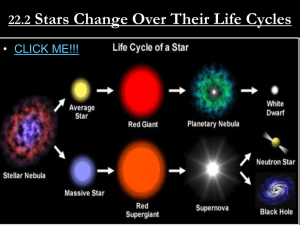
22.2 Stars Change Over Their Life Cycles
... All stars are balls of glowing gas that produce or have produced energy by fusion ...
... All stars are balls of glowing gas that produce or have produced energy by fusion ...
STARS- hot glowing sphere of gas that produces energy by
... STAR- hot glowing sphere of gas that produces energy by fusion 1] Light year—distance light travels in a year (9.5 trillion km, 6 trillion miles) 2] Star brightness A) Actual brightness- brightness right next to a star B) Apparent brightness—brightness as seen from earth 3] Formation of stars A) Neb ...
... STAR- hot glowing sphere of gas that produces energy by fusion 1] Light year—distance light travels in a year (9.5 trillion km, 6 trillion miles) 2] Star brightness A) Actual brightness- brightness right next to a star B) Apparent brightness—brightness as seen from earth 3] Formation of stars A) Neb ...
Dyson Spheres around White Dwarfs arXiv:1503.04376
... A Dyson Sphere represents a particular realization of the Kardashev Type II stage, the obvious way to ”catch” all the power of a star. Dyson [1] in the original paper2 points out that such a sphere would have to emit thermal radiation with total power3 equal to that of the star. Since it would look ...
... A Dyson Sphere represents a particular realization of the Kardashev Type II stage, the obvious way to ”catch” all the power of a star. Dyson [1] in the original paper2 points out that such a sphere would have to emit thermal radiation with total power3 equal to that of the star. Since it would look ...
Equations of Stellar Structure Stellar structure and evolution can be
... transporting energy from its interior to its surface. For convenience, we will express the temperature stratification of the star in terms of the temperature gradient ...
... transporting energy from its interior to its surface. For convenience, we will express the temperature stratification of the star in terms of the temperature gradient ...
The Inverse Square Law and Surface Area
... • Stars which have the same surface temperature ( and spectral characteristics) as the sun all have the same power output • We can readily calculate the power output of nearby stars and classify their power output and compare them with more distant stars The following very bright objects of known lu ...
... • Stars which have the same surface temperature ( and spectral characteristics) as the sun all have the same power output • We can readily calculate the power output of nearby stars and classify their power output and compare them with more distant stars The following very bright objects of known lu ...