Jupiter-Sized Star Smallest Ever Detected
... number of stars over extended time intervals. During the past years, it has also included a search for periodic, very shallow "dips" in the brightness of stars, caused by the regular transit of small orbiting objects (small stars, brown dwarfs or Jupiter-size planets). The OGLE team has since announ ...
... number of stars over extended time intervals. During the past years, it has also included a search for periodic, very shallow "dips" in the brightness of stars, caused by the regular transit of small orbiting objects (small stars, brown dwarfs or Jupiter-size planets). The OGLE team has since announ ...
How Stars Form Powerpoint
... can have different compositions. Most important: Stars do not move along the Main Sequence! Once they reach it, they are in equilibrium and do not move until their fuel begins to run out. ...
... can have different compositions. Most important: Stars do not move along the Main Sequence! Once they reach it, they are in equilibrium and do not move until their fuel begins to run out. ...
Powerpoint of lecture 1
... Sun (Kelvin, Helmholtz, 19th century), then timescale ~ E/L where E = gravitational energy of star, L = luminosity: tKH = GM2/LR ~ 3107 yr for Sun. But geology requires much longer timescale – only nuclear fuel provides this; nuclear binding energy releases up to ~1% of rest mass energy: EN ~ 0.01M ...
... Sun (Kelvin, Helmholtz, 19th century), then timescale ~ E/L where E = gravitational energy of star, L = luminosity: tKH = GM2/LR ~ 3107 yr for Sun. But geology requires much longer timescale – only nuclear fuel provides this; nuclear binding energy releases up to ~1% of rest mass energy: EN ~ 0.01M ...
Nebulae
... • Greater mass, greater pressure and temperature in the core • If protostar less than 0.08 Msun, it can never develop the temperature and pressure to start the hydrogen fusion • Such “failed” stars end up as brown dwarfs, which shines faintly by Kelvin-Helmholtz contraction ...
... • Greater mass, greater pressure and temperature in the core • If protostar less than 0.08 Msun, it can never develop the temperature and pressure to start the hydrogen fusion • Such “failed” stars end up as brown dwarfs, which shines faintly by Kelvin-Helmholtz contraction ...
Eclipsing Binaries
... for giant, evolved stars. Giants might have a large mass, or they might have a small mass, but still they are very luminous. Also the mass of a white dwarf is not correlated to its luminosity. Something different is happening for these guys. ...
... for giant, evolved stars. Giants might have a large mass, or they might have a small mass, but still they are very luminous. Also the mass of a white dwarf is not correlated to its luminosity. Something different is happening for these guys. ...
Lecture 14: Star Formation
... Stars do not begin the protostar phase with the total mass they will have at the end. They are still accreting mass while collapsing slowly. Mass steadily increases Deuterium burning is an important energy source (even though only 1 H atom in 105 is a deuterium atom. ...
... Stars do not begin the protostar phase with the total mass they will have at the end. They are still accreting mass while collapsing slowly. Mass steadily increases Deuterium burning is an important energy source (even though only 1 H atom in 105 is a deuterium atom. ...
Homework #8 1. Problem 10.21 2. The Origin of the Main Sequence
... Stop and think. This result was derived without using any information about nuclear reactions. This means that, for the assumptions in this problem, the mass-luminosity relation does not depend in detail on the mechanism of energy generation. Part f) will hopefully help you understand how this can b ...
... Stop and think. This result was derived without using any information about nuclear reactions. This means that, for the assumptions in this problem, the mass-luminosity relation does not depend in detail on the mechanism of energy generation. Part f) will hopefully help you understand how this can b ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • At the dawn of the 20th century, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way Galaxy was the universe, and it measured only a few thousand light-years across. ...
... • At the dawn of the 20th century, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way Galaxy was the universe, and it measured only a few thousand light-years across. ...
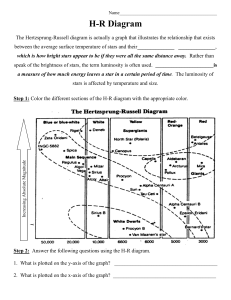
H-R Diagram Student
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
How do stars form as a function of stellar mass
... Authors: Bernadette Rodgers, Greg Doppmann, Nicole van der Bliek, Sandrine Thomas and Claudia Araya Abstract: How do stars form as a function of stellar mass? What are the effects of the immediate circumstellar environment? These are 2 fundamental questions that our study of companions to intermedia ...
... Authors: Bernadette Rodgers, Greg Doppmann, Nicole van der Bliek, Sandrine Thomas and Claudia Araya Abstract: How do stars form as a function of stellar mass? What are the effects of the immediate circumstellar environment? These are 2 fundamental questions that our study of companions to intermedia ...
hubble amazing universe worksheet
... 9. Hubble even showed a star about to die! As a star runs out of ______________, it expands, and it is released into space. 10. Someday, our own star will expand and engulf the earth. Luckily, this will happen in ________________billion years. 11. Some stars are 100 times more massive that our sun. ...
... 9. Hubble even showed a star about to die! As a star runs out of ______________, it expands, and it is released into space. 10. Someday, our own star will expand and engulf the earth. Luckily, this will happen in ________________billion years. 11. Some stars are 100 times more massive that our sun. ...
Practice questions for Stars File
... Life cycle of large and massive stars 1. Describe the difference in the stages of the life cycle for a large and massive star compared to an average star 2. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a black hole 3. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a neutron star 4. E ...
... Life cycle of large and massive stars 1. Describe the difference in the stages of the life cycle for a large and massive star compared to an average star 2. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a black hole 3. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a neutron star 4. E ...
File - Mr. Goodyear Astronomy
... star creating other elements in star increasing fusion process. - This increase energy causes an explosion-like occurrence. This cause star to lose large quantities of mass. - Also during this time period star sheds off excess gas envelopes, which appears as a ring around star when viewed from a dis ...
... star creating other elements in star increasing fusion process. - This increase energy causes an explosion-like occurrence. This cause star to lose large quantities of mass. - Also during this time period star sheds off excess gas envelopes, which appears as a ring around star when viewed from a dis ...
microwaves - TeacherWeb
... Near Infrared radiation is also used to image the internal structures of the sinuses during surgery. This reduces exposure to radiation during CT scans and reduces the risk of injury to the brain and eyes during surgery. ...
... Near Infrared radiation is also used to image the internal structures of the sinuses during surgery. This reduces exposure to radiation during CT scans and reduces the risk of injury to the brain and eyes during surgery. ...
Specific Word Instruction Possible Sentences
... stronomy is the study of the planets, stars, and galaxies. People have been watching the movement of the sun, moon, planets, and stars since ancient times. So astronomy is a very, very old science. From early times, people tried to make models of the universe. For many years, no one wanted to believ ...
... stronomy is the study of the planets, stars, and galaxies. People have been watching the movement of the sun, moon, planets, and stars since ancient times. So astronomy is a very, very old science. From early times, people tried to make models of the universe. For many years, no one wanted to believ ...
File - Etna FFA Agriculture
... different types of stars: Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. ...
... different types of stars: Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. ...
bYTEBoss lesson 3 life of star
... different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that there are black holes at the centre of galaxies. If ligh ...
... different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that there are black holes at the centre of galaxies. If ligh ...
Astronomy 242: Review Questions #1 Distributed: February 10
... (a) Using the information in this diagram, estimate the range of surface gravities g for stars along the Main Sequence. Which end of the main sequence has the highest surface gravities? (b) Typical white dwarf stars have masses Mwd ≃ 1M⊙ . How do the surface gravities of white dwarf stars compare to ...
... (a) Using the information in this diagram, estimate the range of surface gravities g for stars along the Main Sequence. Which end of the main sequence has the highest surface gravities? (b) Typical white dwarf stars have masses Mwd ≃ 1M⊙ . How do the surface gravities of white dwarf stars compare to ...
The Adventures of π-Man: Measuring the Universe
... reverse. If the curvature of space is negative, then the universe is infinite and its expansion will continue unimpeded forever. If the universe is Euclidean (curvature = 0), then the universe will also continue to expand, but at an ever-slowing rate. (This model was drastically complicated, however ...
... reverse. If the curvature of space is negative, then the universe is infinite and its expansion will continue unimpeded forever. If the universe is Euclidean (curvature = 0), then the universe will also continue to expand, but at an ever-slowing rate. (This model was drastically complicated, however ...
ASTR 1020 – Spring 2017 – Prof. Magnani Answer Key – Homework 5
... The way to get heat out of an interstellar cloud is for the particles that make up to cloud to collide with each other. In a collision between two particles (atoms or molecules or ions), one of the colliding partners loses some kinetic energy and the other picks it up. However, the gain in energy co ...
... The way to get heat out of an interstellar cloud is for the particles that make up to cloud to collide with each other. In a collision between two particles (atoms or molecules or ions), one of the colliding partners loses some kinetic energy and the other picks it up. However, the gain in energy co ...