
Part 2 Answer Key
... Star Clusters are multiple star systems bound together by the force of gravity. Star Clusters can be divided into two main groups. One group is called Globular Clusters. They contain many stars and gravity holds them tightly together. They swarm just outside the galaxy and form a halo or bulge. We k ...
... Star Clusters are multiple star systems bound together by the force of gravity. Star Clusters can be divided into two main groups. One group is called Globular Clusters. They contain many stars and gravity holds them tightly together. They swarm just outside the galaxy and form a halo or bulge. We k ...
File
... 8-25 X larger than our Sun Consume their fuel very fast – die more quickly and more violently Star expands into a Supergiant which causes the core to collapse and the outer portion to explode creating a Supernova then a Neutron Star ...
... 8-25 X larger than our Sun Consume their fuel very fast – die more quickly and more violently Star expands into a Supergiant which causes the core to collapse and the outer portion to explode creating a Supernova then a Neutron Star ...
The HR Diagram
... • Where are stars most of their lives? • Where are they when they begin to die? • What are they after they use up their ...
... • Where are stars most of their lives? • Where are they when they begin to die? • What are they after they use up their ...
Other Objects in Space
... Any fragments from space that land on Earth Page 455 Figure 18 Important clues from space Made of metal and rock Hundreds fall to Earth each year! ...
... Any fragments from space that land on Earth Page 455 Figure 18 Important clues from space Made of metal and rock Hundreds fall to Earth each year! ...
Characteristics of Stars WS Questions 1-20
... do not rephrase or use complete sentences, you will automatically lose half of the points available. 1. If you could travel at the speed of light, how long would it take you to travel from Earth to the sun? ...
... do not rephrase or use complete sentences, you will automatically lose half of the points available. 1. If you could travel at the speed of light, how long would it take you to travel from Earth to the sun? ...
ppt
... If same luminosity, this means that they are about 300,000 times further away (i.e. 300,000 AU, or about 5 light years). ...
... If same luminosity, this means that they are about 300,000 times further away (i.e. 300,000 AU, or about 5 light years). ...
ppt
... was embedded in enormous shell of stars… Emmanuel Kant (1755) suggested instead that the MW is a giant disk of stars. Kant also hypothesized that space was full of other, similar disks of stars (island universes). ...
... was embedded in enormous shell of stars… Emmanuel Kant (1755) suggested instead that the MW is a giant disk of stars. Kant also hypothesized that space was full of other, similar disks of stars (island universes). ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... 17. Below sketch out the H-R diagram plotting the main stars and labeling the main sequence. ...
... 17. Below sketch out the H-R diagram plotting the main stars and labeling the main sequence. ...
Study Guide Astronomy
... Chapter 4 Section 2 Characteristics of Stars (pages 126-133) 1. Name 5 characteristics used to classify stars. ...
... Chapter 4 Section 2 Characteristics of Stars (pages 126-133) 1. Name 5 characteristics used to classify stars. ...
Chapter 30.1
... A star is a body of gases that gives off energy in the form of light & heat. Size varies Color varies based on temperature Our sun is an average star ...
... A star is a body of gases that gives off energy in the form of light & heat. Size varies Color varies based on temperature Our sun is an average star ...
Solving the Mystery of Massive Star Birth
... officially becomes a new star. We know this is how small and medium-sized stars form, but what about the most massive stars? Scientists from Japan have been trying to find out. With the help of some of the World’s most powerful telescopes, these scientists were able to peer into a large gas cloud in ou ...
... officially becomes a new star. We know this is how small and medium-sized stars form, but what about the most massive stars? Scientists from Japan have been trying to find out. With the help of some of the World’s most powerful telescopes, these scientists were able to peer into a large gas cloud in ou ...
Structure of the Universe
... What is the name our galaxy? • Milky Way- Why is it called that? • Because we are on an outer arm of the spiral (looks like a pin wheel) when you look into it, it looks like a milky cloud. ...
... What is the name our galaxy? • Milky Way- Why is it called that? • Because we are on an outer arm of the spiral (looks like a pin wheel) when you look into it, it looks like a milky cloud. ...
Name Date Period ______ 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
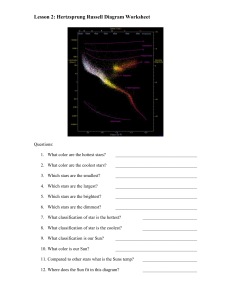
Test ticket - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... 2-2 the life cycle of stars the beginning and end of stars nuclear fusion different types of stars ...
... 2-2 the life cycle of stars the beginning and end of stars nuclear fusion different types of stars ...
The Stars
... billions of stars. To the naked eye, even the closest of these galaxies is no more than a dim, fuzzy spot. The sun is many thousands of times closer to the earth than any other star. Light from the sun takes a few minutes to reach the earth, but light from the next nearest star takes a few years t ...
... billions of stars. To the naked eye, even the closest of these galaxies is no more than a dim, fuzzy spot. The sun is many thousands of times closer to the earth than any other star. Light from the sun takes a few minutes to reach the earth, but light from the next nearest star takes a few years t ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.





















![Test ticket - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010793453_1-3f96ef5ee7d4646c2142d92e4dc3c3f6-300x300.png)
