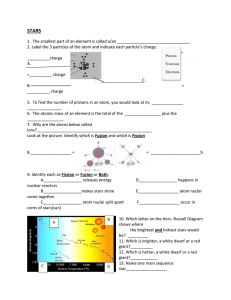
The Pulsar “Lighthouse”
... • Degenerate pressure of neutrons can support stars only up to 3M • For M > 3M: Further collapse Î black hole • Mass is so concentrated that light cannot escape. • One way to think about it: – vescape = 2GM/R becomes greater than speed of light. – So photons can’t escape. • Black holes now known o ...
... • Degenerate pressure of neutrons can support stars only up to 3M • For M > 3M: Further collapse Î black hole • Mass is so concentrated that light cannot escape. • One way to think about it: – vescape = 2GM/R becomes greater than speed of light. – So photons can’t escape. • Black holes now known o ...
Patterns in the night sky - Laureate International College
... the Sun which means that they move in an orbit around the sun. Most planets also have moons that orbit around them. The sun, planets, moon, and other objects that orbit the sun make up the solar system. ...
... the Sun which means that they move in an orbit around the sun. Most planets also have moons that orbit around them. The sun, planets, moon, and other objects that orbit the sun make up the solar system. ...
A Universe of Dwarfs and Giants
... classed as proper stars. A star must produce its own light. These objects are either very dim or even black when looked at in visible light. The little they radiate is mainly infra-red light. Brown dwarfs can be thought of as failed stars; much bigger than a planet but just not big enough to make it ...
... classed as proper stars. A star must produce its own light. These objects are either very dim or even black when looked at in visible light. The little they radiate is mainly infra-red light. Brown dwarfs can be thought of as failed stars; much bigger than a planet but just not big enough to make it ...
stars - Legacy High School
... 18. When nuclear fusion is occurring in a star, the element_____________ fuses to form______________. 19. When objects are moving away, the spectrum lines are displaced toward longer wavelengths of light, this is called a ______________shift. 20. When objects are toward earth, the spectrum lines are ...
... 18. When nuclear fusion is occurring in a star, the element_____________ fuses to form______________. 19. When objects are moving away, the spectrum lines are displaced toward longer wavelengths of light, this is called a ______________shift. 20. When objects are toward earth, the spectrum lines are ...
STELLAR EVOLUTION
... undergo repeated novae explosions, or disintegrate as a supernova. Almost all evolutionary processes in stars take much longer than a human lifetime; we cannot watch a star evolve from birth to death. A few exceptions are supernova and nova explosions, which happen in hours and days. ...
... undergo repeated novae explosions, or disintegrate as a supernova. Almost all evolutionary processes in stars take much longer than a human lifetime; we cannot watch a star evolve from birth to death. A few exceptions are supernova and nova explosions, which happen in hours and days. ...
Study Guide for the Final Astronomy Exam
... A) Material in Questions for Review #1 to 4 is fair game. Understand the answers to these questions. B) State the significance of the universal gravitational constant being such a small number. C) Explain the inverse square law nature of gravity. 5) Unit 32 to 34: Planetary Science A) In a written e ...
... A) Material in Questions for Review #1 to 4 is fair game. Understand the answers to these questions. B) State the significance of the universal gravitational constant being such a small number. C) Explain the inverse square law nature of gravity. 5) Unit 32 to 34: Planetary Science A) In a written e ...
Planetary Configurations
... • Recall escape speed: • The Sch. Radius (RS) is the distance at which vesc=c for a BH: ...
... • Recall escape speed: • The Sch. Radius (RS) is the distance at which vesc=c for a BH: ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance Spectroscopy
... • Largest stars on main sequence fall on the top left • At the same size, hotter stars are more luminous than cooler ones • At the same temperature, larger stars are more luminous than smaller ones ...
... • Largest stars on main sequence fall on the top left • At the same size, hotter stars are more luminous than cooler ones • At the same temperature, larger stars are more luminous than smaller ones ...
KOI-54 Claude Plymate There is a star system about 45 light years
... be 90 and 91 times their orbital period. Apparently, these modes are natural resonance periods for the two stars. The stars are nearly but not exactly identical with slightly different resonance periods. Every time the stars swing by each other (pariastron) they get a kick that excites their natural ...
... be 90 and 91 times their orbital period. Apparently, these modes are natural resonance periods for the two stars. The stars are nearly but not exactly identical with slightly different resonance periods. Every time the stars swing by each other (pariastron) they get a kick that excites their natural ...
PHY 150
... As Figure 19-19 shows, there are two types of Cepheid variables. Type I Cepheids are metal-rich stars of Population I, while Type II Cepheids are metal-poor stars of Population II. (A) Which type of Cepheid variables would you expect to be found in globular clusters? Which type would you expect to b ...
... As Figure 19-19 shows, there are two types of Cepheid variables. Type I Cepheids are metal-rich stars of Population I, while Type II Cepheids are metal-poor stars of Population II. (A) Which type of Cepheid variables would you expect to be found in globular clusters? Which type would you expect to b ...
Name Date ______ Period _____ Earth Science Chapter 25 Study
... Stars that radiate short pulses of radio energy are called ____________________. The most dense stars known to exist are called ___________. The average star spends ____________________ percent of its life as a hydrogen-burning, main-sequence star. The sun is positioned about ____________________ of ...
... Stars that radiate short pulses of radio energy are called ____________________. The most dense stars known to exist are called ___________. The average star spends ____________________ percent of its life as a hydrogen-burning, main-sequence star. The sun is positioned about ____________________ of ...
Stars - Clover Sites
... moon. Show positions and area events for eclipses of the sun and moon. One may demonstrate by using an orange, walnut, and marble, or similar objects, to show positions and movements of the earth, sun, and moon when there is an eclipse of the sun and when there is an eclipse of the moon. ...
... moon. Show positions and area events for eclipses of the sun and moon. One may demonstrate by using an orange, walnut, and marble, or similar objects, to show positions and movements of the earth, sun, and moon when there is an eclipse of the sun and when there is an eclipse of the moon. ...
Codes of Life
... neutron star having a mass three times the Sun but with a diameter of only 20 kilometres! • A teaspoon of matter from a neutron star would have a mass of a billion tonnes! ...
... neutron star having a mass three times the Sun but with a diameter of only 20 kilometres! • A teaspoon of matter from a neutron star would have a mass of a billion tonnes! ...
1 Ay 124 Winter 2014 – HOMEWORK #2 Problem 1
... Due Friday, Jan 31, 2014 by 5pm, in Steidel’s mailbox in 249 Cahill ...
... Due Friday, Jan 31, 2014 by 5pm, in Steidel’s mailbox in 249 Cahill ...
The Milky Way – A Classic Galaxy
... • Hubble found globulars in Andromeda; they were roughly spherically distributed, and centered on the center of the galaxy. • In our own sky, we’d known for over a hundred years that globulars are strongly concentrated in the summer sky; hardly any in the winter sky. Ergo We must be far from the ce ...
... • Hubble found globulars in Andromeda; they were roughly spherically distributed, and centered on the center of the galaxy. • In our own sky, we’d known for over a hundred years that globulars are strongly concentrated in the summer sky; hardly any in the winter sky. Ergo We must be far from the ce ...
Hertzsprung Russell diagram
... line in the diagram) and this is called the Main Sequence. Stars that lie in this area are called main sequence stars – the Sun is a main sequence star. In a way stars that lie on the main sequence are ‘normal’ stars while those that lie to one side or other of this area are ‘unusual’ stars – these ...
... line in the diagram) and this is called the Main Sequence. Stars that lie in this area are called main sequence stars – the Sun is a main sequence star. In a way stars that lie on the main sequence are ‘normal’ stars while those that lie to one side or other of this area are ‘unusual’ stars – these ...
INV 12B MOTION WITH CHANGING SPEED DRY LAB DATA
... 3. How does the sun compare to the other stars on the main sequence? (Hint: The sun’s color is …..What part of the main sequence is it in – upper left, lower left, etc.?) ...
... 3. How does the sun compare to the other stars on the main sequence? (Hint: The sun’s color is …..What part of the main sequence is it in – upper left, lower left, etc.?) ...
Stellar evolution, I
... the cloud is 0.46 parsecs, the cloud contains 1 solar mass of material and the time scale for collapse is 5 million years. ...
... the cloud is 0.46 parsecs, the cloud contains 1 solar mass of material and the time scale for collapse is 5 million years. ...
Lecture 10: The Milky Way
... We only have parallax distance measurements out to about 100pc (Gaia will take us much further in the next few years). This gives us the absolute luminosities of low-mass stars, and using binary systems we can calibrate our models to true masses and radii (see earlier). The trouble is that within 10 ...
... We only have parallax distance measurements out to about 100pc (Gaia will take us much further in the next few years). This gives us the absolute luminosities of low-mass stars, and using binary systems we can calibrate our models to true masses and radii (see earlier). The trouble is that within 10 ...
Useful Things to Study (#2)
... What does this mean? M = m + 5 - 5 log d? (The apparent magnitudes have to be corrected for any effects of interstellar dimming due to dust. Otherwise your distances aren’t right.) Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. What’s it a plot of? Where are the main sequence stars? White dwarfs, red giants, supergia ...
... What does this mean? M = m + 5 - 5 log d? (The apparent magnitudes have to be corrected for any effects of interstellar dimming due to dust. Otherwise your distances aren’t right.) Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. What’s it a plot of? Where are the main sequence stars? White dwarfs, red giants, supergia ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.