Constellation Information
... This is a winter landmark everyone ought to know. Orion is the boldest and brightest of all the constellations. The three belt stars and two other (Bellatrix and Saiph) shine about as bright as the stars of the Big Dipper. But added to these are two that are even brighter: blue-white Rigel, marking ...
... This is a winter landmark everyone ought to know. Orion is the boldest and brightest of all the constellations. The three belt stars and two other (Bellatrix and Saiph) shine about as bright as the stars of the Big Dipper. But added to these are two that are even brighter: blue-white Rigel, marking ...
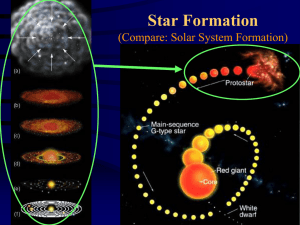
Life Cycle of a Star Notes
... together to form heavier elements such as helium and release energy. If enough matter is left behind, this may be so dense, and its gravitational field so strong that nothing can escape from it, not even light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is then called a black hole. We cannot see ...
... together to form heavier elements such as helium and release energy. If enough matter is left behind, this may be so dense, and its gravitational field so strong that nothing can escape from it, not even light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is then called a black hole. We cannot see ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Universe is expanding Doppler shift—light changes as it moves toward or away from an object Starlight moving toward Earth shifts to blue-violet end of spectrum Starlight moving away from Earth shifts to red end of spectrum All galaxies outside the Local Group indicate a red shift in their spec ...
... Universe is expanding Doppler shift—light changes as it moves toward or away from an object Starlight moving toward Earth shifts to blue-violet end of spectrum Starlight moving away from Earth shifts to red end of spectrum All galaxies outside the Local Group indicate a red shift in their spec ...
Stars Part 2 - westscidept
... • Absolute magnitude is a measure of how bright a star would be if the star were 32.6 light-years away from Earth. • The absolute magnitude of the sun is +4.8. But because the sun is so close to Earth, its apparent magnitude is -26.8, which makes it the brightest object in the sky. ...
... • Absolute magnitude is a measure of how bright a star would be if the star were 32.6 light-years away from Earth. • The absolute magnitude of the sun is +4.8. But because the sun is so close to Earth, its apparent magnitude is -26.8, which makes it the brightest object in the sky. ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature? - d
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own HertzsprungRussell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own HertzsprungRussell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
H-R Diagram Student
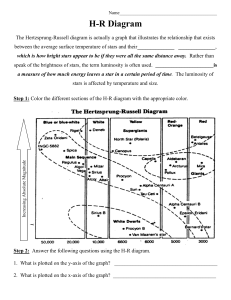
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
Astrophysics Presentation
... If it is moving we hear a higher frequency in front of the truck and a lower frequency once it passes us. ...
... If it is moving we hear a higher frequency in front of the truck and a lower frequency once it passes us. ...
Review Quiz No. 22
... the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a white dwarf. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a neutron star. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a black hole. a neutron star is tidally disrupted by a ...
... the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a white dwarf. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a neutron star. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a black hole. a neutron star is tidally disrupted by a ...
Stellar Physics Lecture 1
... – The narrow band of stars scattered close to the solid line. – Most stars occur along this band – an indication that this is where stars spend most of their lives. For this reason, it is known as the Main Sequence. ...
... – The narrow band of stars scattered close to the solid line. – Most stars occur along this band – an indication that this is where stars spend most of their lives. For this reason, it is known as the Main Sequence. ...
Stars: Other Suns
... • Measure directly only with binary systems of stars (lots!) • Revolve around center of mass • Apply Kepler’s 3rd law to get sum of masses from orbital period, separation (need distance!) ...
... • Measure directly only with binary systems of stars (lots!) • Revolve around center of mass • Apply Kepler’s 3rd law to get sum of masses from orbital period, separation (need distance!) ...
The life cycle of a star
... When extremely large stars die, the resulting core is called a neutron star An extremely dense star made of neutrons ...
... When extremely large stars die, the resulting core is called a neutron star An extremely dense star made of neutrons ...
Stars - Madison County Schools
... – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 12
... (given an appropriate graph) and combine this with its apparent magnitude and the distance-magnitude equation to determine how far it is from Earth. 7. Briefly describe the conditions necessary for mass transfer to occur in a binary star system. 1. Prototstars become pre-main-sequence stars when the ...
... (given an appropriate graph) and combine this with its apparent magnitude and the distance-magnitude equation to determine how far it is from Earth. 7. Briefly describe the conditions necessary for mass transfer to occur in a binary star system. 1. Prototstars become pre-main-sequence stars when the ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Cloud contracts/warms, begins radiating; almost all radiated energy escapes • Cloud becomes dense opaque to radiation radiated energy trapped core heats up ...
... • Cloud contracts/warms, begins radiating; almost all radiated energy escapes • Cloud becomes dense opaque to radiation radiated energy trapped core heats up ...
Review for Exam 2
... 5) How long does it take for stars and planets to be born? 6) What is a brown dwarf? How does it change over 6me? 7) What is the boundary in mass between stars and brown dwarfs? 8) What 3 ...
... 5) How long does it take for stars and planets to be born? 6) What is a brown dwarf? How does it change over 6me? 7) What is the boundary in mass between stars and brown dwarfs? 8) What 3 ...
H-R Diagram - SFA Physics
... stars in the night sky. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 onto Figure 2. ...
... stars in the night sky. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 onto Figure 2. ...
April 1st
... • Not enough mass for fusion • Minimum mass of gas need for fusion is 0.08 solar masses (80 times the mass of Jupiter) ...
... • Not enough mass for fusion • Minimum mass of gas need for fusion is 0.08 solar masses (80 times the mass of Jupiter) ...
Lecture 17: General Relativity and Black Holes
... for interstellar extinction by dust. True or false 3. The Herschels attempted to determine the galaxy's structure by (a) looking for dust clouds with their telescope (b) locating the galactic center. (c) correct systematically counting stars in each direction (d) observing globular star clusters (e) ...
... for interstellar extinction by dust. True or false 3. The Herschels attempted to determine the galaxy's structure by (a) looking for dust clouds with their telescope (b) locating the galactic center. (c) correct systematically counting stars in each direction (d) observing globular star clusters (e) ...
Space Science Unit
... • The largest stars, larger than the giant stars • Their diameters are 1,000 times that of our Sun • A star this size would extend past Mars from where our Sun is now if compared to our Sun’s current size • Due to their size, they are the shortest lived stars and die off quickly ...
... • The largest stars, larger than the giant stars • Their diameters are 1,000 times that of our Sun • A star this size would extend past Mars from where our Sun is now if compared to our Sun’s current size • Due to their size, they are the shortest lived stars and die off quickly ...
The Sun and Beyond - Valhalla High School
... The Milky Way- our home galaxy Milky Way Local GroupThe Milky Way is not an island universe, but a member of a small cluster of galaxies called the Local Group. The Local Group contains about 3 dozen known galaxies, clumped in two subgroups around two massive spiral galaxies -the Milky Way, a ...
... The Milky Way- our home galaxy Milky Way Local GroupThe Milky Way is not an island universe, but a member of a small cluster of galaxies called the Local Group. The Local Group contains about 3 dozen known galaxies, clumped in two subgroups around two massive spiral galaxies -the Milky Way, a ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.