Previous Discussion Section Notes
... • Controls include regulation of synthesis and degradation of the receptor by multiple mechanisms; covalent modification, association with other regulatory proteins, and/or relocalization within the cell. • Modulating inputs may come from other receptors, directly or indirectly. • Receptors are alwa ...
... • Controls include regulation of synthesis and degradation of the receptor by multiple mechanisms; covalent modification, association with other regulatory proteins, and/or relocalization within the cell. • Modulating inputs may come from other receptors, directly or indirectly. • Receptors are alwa ...
Sedative - Hypnotics
... - inactive metabolites w/ few exceptions *Phenobarbital – 20 – 30% excreted unchanged; elimination half-life of 4 – 5 days multiple dosing cumulative CNS effects biodisposition affected by hepatic changes due to: old age, diseases, microsomal enzyme activity ...
... - inactive metabolites w/ few exceptions *Phenobarbital – 20 – 30% excreted unchanged; elimination half-life of 4 – 5 days multiple dosing cumulative CNS effects biodisposition affected by hepatic changes due to: old age, diseases, microsomal enzyme activity ...
Indirect Pharmacodynamic Models for Tolerance
... Two patients died and no one entered the 2nd cycle due to drug related toxicity such as GI bleeding. PK profiles for IL12 were comparable to those observed in Phase I study. Leonard et al., Blood, 1997 ...
... Two patients died and no one entered the 2nd cycle due to drug related toxicity such as GI bleeding. PK profiles for IL12 were comparable to those observed in Phase I study. Leonard et al., Blood, 1997 ...
Slide 1
... ◦ Marijuana smoke contains many of the same tars and carcinogenic compounds as cigarettes but in greater quantity (more benzopyrene ◦ single mj may be more harmful then because…… ...
... ◦ Marijuana smoke contains many of the same tars and carcinogenic compounds as cigarettes but in greater quantity (more benzopyrene ◦ single mj may be more harmful then because…… ...
What is schizophrenia
... Sulpiride selectively inhibit D2receptors in the mesolimbic and mesocortical areas of the brain. Sulpiride ,Clozapine and risperidone have low risk of extrapyramidal adverse reaction. ...
... Sulpiride selectively inhibit D2receptors in the mesolimbic and mesocortical areas of the brain. Sulpiride ,Clozapine and risperidone have low risk of extrapyramidal adverse reaction. ...
Interactions Among Organisms
... The Biosphere – All the area on the surface of earth and in the atmosphere that supports life. Ecosystem – A group of organisms living together and the environment around them. Community – All of the interacting populations in an area Population – All of the organisms of the same species living in a ...
... The Biosphere – All the area on the surface of earth and in the atmosphere that supports life. Ecosystem – A group of organisms living together and the environment around them. Community – All of the interacting populations in an area Population – All of the organisms of the same species living in a ...
Mechanism of Drug Action and Drug Targets Receptors
... In this lecture, the diversity of receptors for and responses to a single kind of neurotransmitter is illustrated by acetylcholine. Synapses in which acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter are termed cholinergic synapses. Acetylcholine receptors that cause excitatory responses lasting only milliseco ...
... In this lecture, the diversity of receptors for and responses to a single kind of neurotransmitter is illustrated by acetylcholine. Synapses in which acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter are termed cholinergic synapses. Acetylcholine receptors that cause excitatory responses lasting only milliseco ...
AB_tox_07ho
... irreversible, not dose-related, may appear months after drug dc’ed frequently fatal--if not, high incidence of leukemia in survivors ...
... irreversible, not dose-related, may appear months after drug dc’ed frequently fatal--if not, high incidence of leukemia in survivors ...
Pharmacodynamics
... An agent which activates the receptor to produce an effect similar to that of physiological signal molecule ...
... An agent which activates the receptor to produce an effect similar to that of physiological signal molecule ...
Jennifer Sims-Early safety assessment of biologicals
... • Biologics generally demonstrate high specificity for target • Assessment of binding to homologous targets – ...
... • Biologics generally demonstrate high specificity for target • Assessment of binding to homologous targets – ...
Ecology Unit Organization
... population. The cooperation and competition between individuals contributes to these different properties. Species-specific and environmental catastrophes, geological events, the sudden influx/depletion of abiotic resources or increased human activities affect species distribution and abundance. Exa ...
... population. The cooperation and competition between individuals contributes to these different properties. Species-specific and environmental catastrophes, geological events, the sudden influx/depletion of abiotic resources or increased human activities affect species distribution and abundance. Exa ...
Q10 Compare and contrast the mechanism of
... Indirect effects include release of ACh at cardiac muscarinic receptors resulting in bradycardia and further increase in the refractory period of the AV node. The slowing in conduction improves tachyarrhythmia ...
... Indirect effects include release of ACh at cardiac muscarinic receptors resulting in bradycardia and further increase in the refractory period of the AV node. The slowing in conduction improves tachyarrhythmia ...
Local anesthetics
... treatment for central myotonia (肌强直)caused by cerebral accident(脑血管意外) or spinal cord injury(脊髓损伤) ...
... treatment for central myotonia (肌强直)caused by cerebral accident(脑血管意外) or spinal cord injury(脊髓损伤) ...
Mainly 15-45 age range, but increasing in kids!
... Stimulant for ADHD (attention deficit hyperactive disorder) NH ...
... Stimulant for ADHD (attention deficit hyperactive disorder) NH ...
Section A: Answer four of the following five questions. Each question
... Reactions who biological characteristics can be predicted based on chemical structure of the drug Reaction predictable from the known pharmacology of the drug, usually dose-dependent Reaction not predictable from the known pharmacology of the drug, usually independent of its primary biological effec ...
... Reactions who biological characteristics can be predicted based on chemical structure of the drug Reaction predictable from the known pharmacology of the drug, usually dose-dependent Reaction not predictable from the known pharmacology of the drug, usually independent of its primary biological effec ...
This page
... • Progestin “mini-pills” are used to treat endometriosis (overgrowth of the lining of the uterus) but are not routinely used for contraception because they are less effective than estrogen-progestin contraceptives. o An exception to this is that progestin mini-pills are sometimes used by women who a ...
... • Progestin “mini-pills” are used to treat endometriosis (overgrowth of the lining of the uterus) but are not routinely used for contraception because they are less effective than estrogen-progestin contraceptives. o An exception to this is that progestin mini-pills are sometimes used by women who a ...
Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics of Alcohol and Opioids
... • Ethanol metabolism produces reduced NAD (NADH) • NADH reduces ability of liver to produce UDPglucuronic acid, necessary for glucuronidation of morphine and other drugs ...
... • Ethanol metabolism produces reduced NAD (NADH) • NADH reduces ability of liver to produce UDPglucuronic acid, necessary for glucuronidation of morphine and other drugs ...
Tutorial Kit (Applied Biology and Biotechnology-300 L)
... Thus, many drugs may be metabolized before adequate plasma concentrations are reached. ...
... Thus, many drugs may be metabolized before adequate plasma concentrations are reached. ...
The Atypical Antipsychotics
... temperature-regulating mechanisms and can produce poikilothermia (body temperature varies with the environment). In the pituitary, neuroleptics block D2 receptors, leading to an increase in prolactin release. Atypical neuroleptics are less likely to produce prolactin elevations. Sedation occurs with ...
... temperature-regulating mechanisms and can produce poikilothermia (body temperature varies with the environment). In the pituitary, neuroleptics block D2 receptors, leading to an increase in prolactin release. Atypical neuroleptics are less likely to produce prolactin elevations. Sedation occurs with ...
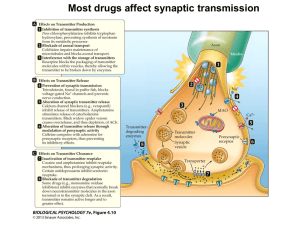
Fig 4.9a Synaptic Transmission
... – Neurons change because of drug exposure • neuroplasticity to drug and its effects – at dendrites, pre & post synapse, receptors – changes to anatomy and chemistry ...
... – Neurons change because of drug exposure • neuroplasticity to drug and its effects – at dendrites, pre & post synapse, receptors – changes to anatomy and chemistry ...
Narcotic analgesics
... (thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system). Opioid receptors are grouped into the following four classes: 1- Mu- found in pain-regulating areas of the brain; contribute to analgesia, euphoria, respiratory depression, physical dependence and hypothermic actions. 2- Kappa- found in the cerebral cortex an ...
... (thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system). Opioid receptors are grouped into the following four classes: 1- Mu- found in pain-regulating areas of the brain; contribute to analgesia, euphoria, respiratory depression, physical dependence and hypothermic actions. 2- Kappa- found in the cerebral cortex an ...
Toxicodynamics

Toxicodynamics, termed pharmacodynamics in pharmacology, describes the dynamic interactions of a toxicant with a biological target and its biological effects. A biological target, also known as the site of action, can be binding proteins, ion channels, DNA, or a variety of other receptors. When a toxicant enters an organism, it can interact with these receptors and produce structural or functional alterations. The mechanism of action of the toxicant, as determined by a toxicant’s chemical properties, will determine what receptors are targeted and the overall toxic effect at the cellular level and organismal level.Toxicants have been grouped together according to their chemical properties by way of quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSARs), which allows prediction of toxic action based on these properties. endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and carcinogens are examples of classes of toxicants that can act as QSARs. EDCs mimic or block transcriptional activation normally caused by natural steroid hormones. These types of chemicals can act on androgen receptors, estrogen receptors and thyroid hormone receptors. This mechanism can include such toxicants as dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDE) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Another class of chemicals, carcinogens, are substances that cause cancer and can be classified as genotoxic or nongenotoxic carcinogens. These categories include toxicants such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). The process of toxicodynamics can be useful for application in environmental risk assessment by implementing toxicokinetic-toxicodynamic (TKTD) models. TKTD models include phenomenas such as time-varying exposure, carry-over toxicity, organism recovery time, effects of mixtures, and extrapolation to untested chemicals and species. Due to their advantages, these types of models may be more applicable for risk assessment than traditional modeling approaches.