3 - College of Arts and Sciences
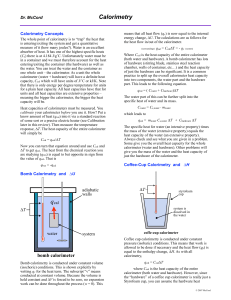
... Something is gaining Heat While Something else looses Heat. If you know one of these then you know the other ...
... Something is gaining Heat While Something else looses Heat. If you know one of these then you know the other ...
Document
... • If HEAT IS ADDED to the system (gas) è Q > 0 • If HEAT IS RELEASED by the system (gas) è Q < 0 W is the work • If WORK IS DONE ON the system (gas) è gas compresses è W > 0 • If WORK IS DONE BY the system (gas) è gas expands è W < 0 ...
... • If HEAT IS ADDED to the system (gas) è Q > 0 • If HEAT IS RELEASED by the system (gas) è Q < 0 W is the work • If WORK IS DONE ON the system (gas) è gas compresses è W > 0 • If WORK IS DONE BY the system (gas) è gas expands è W < 0 ...
Heat Transfer
... Heat circulates through liquids and gases by convection, which is the movement of heated particles from one place to another. Convection cannot take place in solids because the molecules that make up a solid are fixed in place. Liquids and gases are fluids, and their molecules can slide around. In ...
... Heat circulates through liquids and gases by convection, which is the movement of heated particles from one place to another. Convection cannot take place in solids because the molecules that make up a solid are fixed in place. Liquids and gases are fluids, and their molecules can slide around. In ...
Science 9th grade LEARNING OBJECT How is heat transferred
... SKILL 3. Assess the process of heat transfer by means of convection. SKILL 4. Explain the formation of gusts in the atmosphere. Convection in the atmosphere Convection is a process that occurs naturally in the atmosphere; in the morning the Sun heats up the surface of the Earth, which transfers heat ...
... SKILL 3. Assess the process of heat transfer by means of convection. SKILL 4. Explain the formation of gusts in the atmosphere. Convection in the atmosphere Convection is a process that occurs naturally in the atmosphere; in the morning the Sun heats up the surface of the Earth, which transfers heat ...
Consequences of the relation between temperature, heat, and
... Heat capacities can be very different between materials with similar bonding (e.g. two metals Au and Fe), materials with the same atomic constituents but different atomic arrangements (e.g. diamond and graphite), and between the same material in different states of aggregation (e.g. liquid water vs. ...
... Heat capacities can be very different between materials with similar bonding (e.g. two metals Au and Fe), materials with the same atomic constituents but different atomic arrangements (e.g. diamond and graphite), and between the same material in different states of aggregation (e.g. liquid water vs. ...
heat processes
... only enthalpy flow changes. Moving for example the composite curve of cold streams to the right increases temperature difference between the streams (heat transfer surface of the heat exchangers transferring enthalpy from hot to cold streams will be smaller), but at the same time demands on hot and ...
... only enthalpy flow changes. Moving for example the composite curve of cold streams to the right increases temperature difference between the streams (heat transfer surface of the heat exchangers transferring enthalpy from hot to cold streams will be smaller), but at the same time demands on hot and ...
Lecture 4: 09.16.05 Temperature, heat, and entropy
... •� Why do we need to define the property of temperature independently of heat? Why doesn’t the temperature of a material simply quantify the amount of heat transferred to it? o� Looking again at the reversible process definition of entropy: ...
... •� Why do we need to define the property of temperature independently of heat? Why doesn’t the temperature of a material simply quantify the amount of heat transferred to it? o� Looking again at the reversible process definition of entropy: ...
Heat pipe
A heat pipe is a heat-transfer device that combines the principles of both thermal conductivity and phase transition to efficiently manage the transfer of heat between two solid interfaces.At the hot interface of a heat pipe a liquid in contact with a thermally conductive solid surface turns into a vapor by absorbing heat from that surface. The vapor then travels along the heat pipe to the cold interface and condenses back into a liquid - releasing the latent heat. The liquid then returns to the hot interface through either capillary action, centrifugal force, or gravity, and the cycle repeats. Due to the very high heat transfer coefficients for boiling and condensation, heat pipes are highly effective thermal conductors. The effective thermal conductivity varies with heat pipe length, and can approach 7002100000000000000♠100 kW/(m⋅K) for long heat pipes, in comparison with approximately 6999400000000000000♠0.4 kW/(m⋅K) for copper.