Management of the Natural Environment 2
... Pyramid of biomass- shows the dry mass at each trophic level ...
... Pyramid of biomass- shows the dry mass at each trophic level ...
Slide 1
... • Who eats what? Herbivores, Omnivores and Carnivores • Trophic levels and energy- more energy at the bottom (plants) than top (predators) • Role of decomposers • Be able to read a food web/chain and identify trophic levels ...
... • Who eats what? Herbivores, Omnivores and Carnivores • Trophic levels and energy- more energy at the bottom (plants) than top (predators) • Role of decomposers • Be able to read a food web/chain and identify trophic levels ...
Biome Bingo Term on Bingo Card Description / definition / concept 1
... Organisms that feed on meet to obtain energy Break down dead or decaying organisms An organism that makes its own food through the process of photosynthesis An organism that cannot make its own food and needs to eat plants or animals Lakes, ponds, and rivers are this type of biome A salt water biome ...
... Organisms that feed on meet to obtain energy Break down dead or decaying organisms An organism that makes its own food through the process of photosynthesis An organism that cannot make its own food and needs to eat plants or animals Lakes, ponds, and rivers are this type of biome A salt water biome ...
Human Impact on the Environment:
... of organisms which is at risk of becoming extinct through all or a portion of its range ...
... of organisms which is at risk of becoming extinct through all or a portion of its range ...
7th Grade - Vernon Independent School District
... Pioneer Species- first species to begin growing in an area (moss & ...
... Pioneer Species- first species to begin growing in an area (moss & ...
Ecology
... Habitat – The natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism. Eg. Marine habitat Niche – the relational position of species in an ecosystem to each other and how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and ...
... Habitat – The natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism. Eg. Marine habitat Niche – the relational position of species in an ecosystem to each other and how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and ...
STUDY GUIDE #1 ECOSYSTEMS: HIERARCHY, CYCLES
... 17. What organisms go through the process of photosynthesis? 18. What does photosynthesis remove from the atmosphere? 19. What does photosynthesis release as a byproduct into the atmosphere? ...
... 17. What organisms go through the process of photosynthesis? 18. What does photosynthesis remove from the atmosphere? 19. What does photosynthesis release as a byproduct into the atmosphere? ...
Ecology AS 2.4 Investigate an interrelationship or pattern in an
... • Oyster on rock (predation) – structural hard shell. Life history – produces vast quantities of eggs • Whelk (carnivorous shellfish) – way to cut into shells structural Relationship between organisms and their environment The environment includes all those factors, both living (biotic) and non livi ...
... • Oyster on rock (predation) – structural hard shell. Life history – produces vast quantities of eggs • Whelk (carnivorous shellfish) – way to cut into shells structural Relationship between organisms and their environment The environment includes all those factors, both living (biotic) and non livi ...
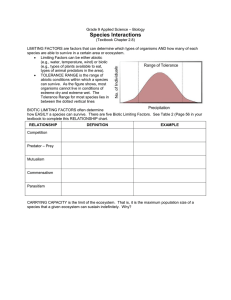
Grade 9 Applied Science – Biology
... LIMITING FACTORS are factors that can determine which types of organisms AND how many of each species are able to survive in a certain area or ecosystem. Limiting Factors can be either abiotic (e.g., water, temperature, wind) or biotic (e.g., types of plants available to eat, types of animal preda ...
... LIMITING FACTORS are factors that can determine which types of organisms AND how many of each species are able to survive in a certain area or ecosystem. Limiting Factors can be either abiotic (e.g., water, temperature, wind) or biotic (e.g., types of plants available to eat, types of animal preda ...
Document
... Benthic( bottom dwelling) animals, such as clams and worms, are often used to determine whether or not a bay is becoming polluted. Why do scientists use these kinds of animals rather than fish, crabs, or shrimp as indicators of the "health" of the bay? (check one): _____ they have body fluids that t ...
... Benthic( bottom dwelling) animals, such as clams and worms, are often used to determine whether or not a bay is becoming polluted. Why do scientists use these kinds of animals rather than fish, crabs, or shrimp as indicators of the "health" of the bay? (check one): _____ they have body fluids that t ...
Plant Ecology 101 in 5 minutes - Rutgers Environmental Stewards
... Catastrophes are infrequent but of great significance to the survival of species. The prosperity of a species may depend upon catastrophic events that control it’s competitors or provide food. Ie. fire, flood, epizootic. etc. Succession and Climax Classic plant ecology describes an orderly progressi ...
... Catastrophes are infrequent but of great significance to the survival of species. The prosperity of a species may depend upon catastrophic events that control it’s competitors or provide food. Ie. fire, flood, epizootic. etc. Succession and Climax Classic plant ecology describes an orderly progressi ...
video slide
... – Are the major types of ecological associations that occupy broad geographic regions of land or water ...
... – Are the major types of ecological associations that occupy broad geographic regions of land or water ...
Plants and Animals
... Being mutually responsible to and sharing a common set of principles with others. ...
... Being mutually responsible to and sharing a common set of principles with others. ...
Ecology Class Notes
... Biogeochemical Cycles • Phosphorus Cycle – Does not enter atmosphere. – In land, rocks, soil and ocean sediment as inorganic phosphate. – Will dissolve in water. Video ...
... Biogeochemical Cycles • Phosphorus Cycle – Does not enter atmosphere. – In land, rocks, soil and ocean sediment as inorganic phosphate. – Will dissolve in water. Video ...
EndofUnitTestReviewA.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Why might an organic farmer add manure to a field? Animal manure, which contains nitrogen compounds, can be used as a natural plant fertilizer. The manure is broken down by decomposers in the soil to release ammonia, which can be used directly by some plants as a source of nitrogen. The ammonia can ...
... Why might an organic farmer add manure to a field? Animal manure, which contains nitrogen compounds, can be used as a natural plant fertilizer. The manure is broken down by decomposers in the soil to release ammonia, which can be used directly by some plants as a source of nitrogen. The ammonia can ...
S-8-9-2_Species Interactions Quiz
... Directions: Write the name of each type of species interaction next to the example provided. Use the terms in the box below. Each term will be used one time. ...
... Directions: Write the name of each type of species interaction next to the example provided. Use the terms in the box below. Each term will be used one time. ...
chapter 37 - Aurora City Schools
... organisms that live close enough to each other for potential interaction. Ecosystem – all the organisms in a given area, along with the nonliving (abiotic) factors with which they interact. Species – A group of organisms which can interbreed with each other and able to produce a fertile offspring. H ...
... organisms that live close enough to each other for potential interaction. Ecosystem – all the organisms in a given area, along with the nonliving (abiotic) factors with which they interact. Species – A group of organisms which can interbreed with each other and able to produce a fertile offspring. H ...