Thermo-regulation - Learning Central
... Homeostasis and maintenance of body temperature Homeostasis means 'staying the same'. The internal environment of a healthy body remains the same under conditions of outside environmental changes. Homeostasis is maintained by adaptive mechanisms in the body regulated by the nervous and endocrine sys ...
... Homeostasis and maintenance of body temperature Homeostasis means 'staying the same'. The internal environment of a healthy body remains the same under conditions of outside environmental changes. Homeostasis is maintained by adaptive mechanisms in the body regulated by the nervous and endocrine sys ...
CH3080_reportsample_formaterrors
... container (aluminum, copper, etc.) that holds a liquid (water, acetone, etc.) under pressure, the inner surface of the tube is lined with a porous material that acts as a wick. When heat is applied to the outer area of the tube, the liquid inside the tube boils and vaporizes into a gas that moves th ...
... container (aluminum, copper, etc.) that holds a liquid (water, acetone, etc.) under pressure, the inner surface of the tube is lined with a porous material that acts as a wick. When heat is applied to the outer area of the tube, the liquid inside the tube boils and vaporizes into a gas that moves th ...
ert254-chapter 4
... In cold climates their efficiency drops considerably when temperatures are below the freezing point. In such cases, geothermal (ground-source) HP that use the ground as the heat source can be used. Such heat pumps are more expensive to install, but they are also more efficient. Air conditioners are ...
... In cold climates their efficiency drops considerably when temperatures are below the freezing point. In such cases, geothermal (ground-source) HP that use the ground as the heat source can be used. Such heat pumps are more expensive to install, but they are also more efficient. Air conditioners are ...
ME 2322 – Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 14 Complete
... 20. (10 pt) Both the energy and mass balance must be satisfied for all thermodynamic systems. 21. (10 pt) When an initially empty rigid tank is filled from a constant fluid property source, the final specific internal energy of the fluid in the tank must equal the specific enthalpy of the source. 22 ...
... 20. (10 pt) Both the energy and mass balance must be satisfied for all thermodynamic systems. 21. (10 pt) When an initially empty rigid tank is filled from a constant fluid property source, the final specific internal energy of the fluid in the tank must equal the specific enthalpy of the source. 22 ...
BUOYANCY-DRIVEN TURBULENT CONVECTION IN A BUNDLE
... heated cylinders, where each cylinder releases an equal, uniform heat flux distribution q 00 and a Boussinesq approximation is introduced to represent buoyancy effects. Periodic boundary conditions are enforced along the cross flow directions y and z as well as the streamwise direction x on all comp ...
... heated cylinders, where each cylinder releases an equal, uniform heat flux distribution q 00 and a Boussinesq approximation is introduced to represent buoyancy effects. Periodic boundary conditions are enforced along the cross flow directions y and z as well as the streamwise direction x on all comp ...
Sceince Principles of Science II CCSC Curriculum Map
... Explain why metal feels colder than felt, even though both are at room temperature. Explain why ice melts faster on metal than felt, even though both are at room temperature. Explain what heat conductivity means and give examples of things that have high and low heat conductivity. Define conduction, ...
... Explain why metal feels colder than felt, even though both are at room temperature. Explain why ice melts faster on metal than felt, even though both are at room temperature. Explain what heat conductivity means and give examples of things that have high and low heat conductivity. Define conduction, ...
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY
... 11. How many joules of heat are lost by 3580 kg granite as it cools from 41.2°C to -12.9°C? 12. How much heat is absorbed by a 2000 kg granite boulder as energy from the sun causes its temperature to change from 10°C to 29°C? 13. How much heat is released to the surroundings when 200 g of water at 9 ...
... 11. How many joules of heat are lost by 3580 kg granite as it cools from 41.2°C to -12.9°C? 12. How much heat is absorbed by a 2000 kg granite boulder as energy from the sun causes its temperature to change from 10°C to 29°C? 13. How much heat is released to the surroundings when 200 g of water at 9 ...
2.2) Conduction - Concord Consortium
... many common insulating materials have an R-value of 3 to 5 per inch, in standard American units. Fiberglass in a 5 ½” wood frame wall adds up to about R-20. Insulation in ceilings and roofs, where there’s more room for insulation, is commonly R-30 to R-40. Windows typically have the lowest R-value i ...
... many common insulating materials have an R-value of 3 to 5 per inch, in standard American units. Fiberglass in a 5 ½” wood frame wall adds up to about R-20. Insulation in ceilings and roofs, where there’s more room for insulation, is commonly R-30 to R-40. Windows typically have the lowest R-value i ...
contents - UET Mechanical 09
... No bulky compressor units Precise temperature stability Tolerances of better than +/- 0.1°C Accurate and reproducible ramp and dwell times Cooling/heating mode options Fully reversible with switch in polarity Localized Cooling Spot cooling for components or medical applications Perfect f ...
... No bulky compressor units Precise temperature stability Tolerances of better than +/- 0.1°C Accurate and reproducible ramp and dwell times Cooling/heating mode options Fully reversible with switch in polarity Localized Cooling Spot cooling for components or medical applications Perfect f ...
GeoT*SOL® Exploiting the Earth`s Sustainable Energy Supply
... It’s your choice: heat sources and system types GeoT*SOL® basic supports the following heat pump configurations: Brine/Water – Brine/water heat pumps with geothermal probes extract heat stored in lower ground layers. This requires one or more holes drilled vertically into the ground. Near-surface h ...
... It’s your choice: heat sources and system types GeoT*SOL® basic supports the following heat pump configurations: Brine/Water – Brine/water heat pumps with geothermal probes extract heat stored in lower ground layers. This requires one or more holes drilled vertically into the ground. Near-surface h ...
Heat and its Transfer Study Guide
... It is a sunny day outside. The sun’s rays warm the Earth. The sun is a star made up of hot, glowing gases. It is the main source of heat and light on Earth. Energy from the sun is called solar energy and is transmitted by waves of radiation. Heat is a kind of energy that moves from one place to anot ...
... It is a sunny day outside. The sun’s rays warm the Earth. The sun is a star made up of hot, glowing gases. It is the main source of heat and light on Earth. Energy from the sun is called solar energy and is transmitted by waves of radiation. Heat is a kind of energy that moves from one place to anot ...
ATMOSPHERE AND WEATHER local energy budgets
... During the day, the ground heats the air by radiation, conduction (contact) and convection. The ground radiates energy and as the air receives more radiation than it emits, the air is warmed. Air close to the ground is also warmed through conduction. Air movement at the surface is slower due to fr ...
... During the day, the ground heats the air by radiation, conduction (contact) and convection. The ground radiates energy and as the air receives more radiation than it emits, the air is warmed. Air close to the ground is also warmed through conduction. Air movement at the surface is slower due to fr ...
Thermal and Fluid Mechanics Lab مختبر ميكانيكا الموائع والحراريه
... - Provide full technical exercises and calculation procedure. - Full training programme on running the equipment and maintenance. - Manufacturer must be from either USA, UK, Europe or Japan The apparatus is used to study the fluid friction head losses which occur when an incompressible fluid flows t ...
... - Provide full technical exercises and calculation procedure. - Full training programme on running the equipment and maintenance. - Manufacturer must be from either USA, UK, Europe or Japan The apparatus is used to study the fluid friction head losses which occur when an incompressible fluid flows t ...
Customer Application Brief General Industrial Filtration in Process
... maintain its efficiency and operation at controlled temperatures. The hot process water is pumped to a heat exchanger, where it transfers the absorbed heat to the cooling water side. The cool process water is then pumped back to the process equipment to absorb more heat. On the cooling water side, w ...
... maintain its efficiency and operation at controlled temperatures. The hot process water is pumped to a heat exchanger, where it transfers the absorbed heat to the cooling water side. The cool process water is then pumped back to the process equipment to absorb more heat. On the cooling water side, w ...
Bacon¹s inductive method, example of heat.
... moreover, the sharpest frosts are normally observed at the full moon. 2. The sun’s rays do not give off heat in the middle region of the air 3. Comets (if we may regard them as a kind of meteor) are not found to have a regular or obvious effect in increasing seasonal temperatures . . . 4. There is s ...
... moreover, the sharpest frosts are normally observed at the full moon. 2. The sun’s rays do not give off heat in the middle region of the air 3. Comets (if we may regard them as a kind of meteor) are not found to have a regular or obvious effect in increasing seasonal temperatures . . . 4. There is s ...
Page|1 - askIITians
... When a system is taken from state A to state B along the path ACB, 80 Kcal of heat flows into the system and 30 kcal of work done. a. How much heat flows into the system along path ADB if the work done is 10 kcal? b. When the system is returned from B to A along the curve path. The work done is 20 k ...
... When a system is taken from state A to state B along the path ACB, 80 Kcal of heat flows into the system and 30 kcal of work done. a. How much heat flows into the system along path ADB if the work done is 10 kcal? b. When the system is returned from B to A along the curve path. The work done is 20 k ...
Nernst`s postulate derived directly from the vanishing heat capacity
... It is worthwhile pointing out that when T is very small, so is −(∆T )S , whereas (∆yi )S need not be small. It may have a finite value which can be varied by controlling the exterior conditions, whether the temperature of the system is high or low [1,2]. In fact, this observation has been used extens ...
... It is worthwhile pointing out that when T is very small, so is −(∆T )S , whereas (∆yi )S need not be small. It may have a finite value which can be varied by controlling the exterior conditions, whether the temperature of the system is high or low [1,2]. In fact, this observation has been used extens ...
Chapter 13: The Atmosphere Learning Target Vocabulary Word
... I can identify some properties of air . . . Because air has_____________, it also has other properties, including ______________ and ___________________. I can describe how barometers can be used to measure air pressure . . . Two common kinds of barometers are __________________ barometers and _____ ...
... I can identify some properties of air . . . Because air has_____________, it also has other properties, including ______________ and ___________________. I can describe how barometers can be used to measure air pressure . . . Two common kinds of barometers are __________________ barometers and _____ ...
3-1C (a) If the lateral surfaces of the rod are insulated, the heat
... of it. Also, the temperature at any point in the wall remains constant. Therefore, the energy content of the wall does not change during steady heat conduction. However, the temperature along the wall and thus the energy content of the wall will change during transient conduction. 3-3C The temperatu ...
... of it. Also, the temperature at any point in the wall remains constant. Therefore, the energy content of the wall does not change during steady heat conduction. However, the temperature along the wall and thus the energy content of the wall will change during transient conduction. 3-3C The temperatu ...
Internal cooling system pressure, flow rate, power and
... • Enables engineers to predict, design and optimize for flow rates, pressures, temperatures and heat transfer rates in fluid systems. • Simulations with any combination of liquid, gas, two phase, slurry and mixture flows in both steady state and dynamic cases. ...
... • Enables engineers to predict, design and optimize for flow rates, pressures, temperatures and heat transfer rates in fluid systems. • Simulations with any combination of liquid, gas, two phase, slurry and mixture flows in both steady state and dynamic cases. ...
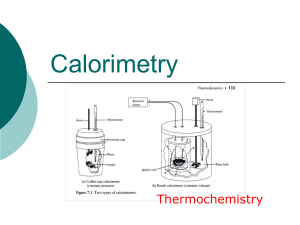
Thermochemistry - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... one another (insulation), then filled with a specific quantity of water and covered with another cup as a cover. A chemical reaction or phase change takes place inside and a thermometer is placed within to measure any change in temperature that occurs to the system. ...
... one another (insulation), then filled with a specific quantity of water and covered with another cup as a cover. A chemical reaction or phase change takes place inside and a thermometer is placed within to measure any change in temperature that occurs to the system. ...
specific heat
... Heat capacity of a body is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of the body by 1oC. The specific heat of a substance is the heat capacity per unit mass. Thus, heat capacity = mass x specific heat. The specific heat is essentially a measure of how thermally insensitive a substance i ...
... Heat capacity of a body is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of the body by 1oC. The specific heat of a substance is the heat capacity per unit mass. Thus, heat capacity = mass x specific heat. The specific heat is essentially a measure of how thermally insensitive a substance i ...
Intercooler

An intercooler is any mechanical device used to cool a fluid, including liquids or gases, between stages of a multi-stage heating process, typically a heat exchanger that removes waste heat in a gas compressor. They are used in many applications, including air compressors, air conditioners, refrigerators, and gas turbines, and are widely known in automotive use as an air-to-air or air-to-liquid cooler for forced induction (turbocharged or supercharged) internal combustion engines to improve their volumetric efficiency by increasing intake air charge density through nearly isobaric (constant pressure) cooling.