Solar X-ray and UV radiation at Earth`s surface 4–3.5 billion years ago
... that has the same age now as the Sun had 4–3.5 Ga. Atmospheric extinction was calculated using the Beer-Lambert law, assuming several density profiles for the atmosphere of the Archean Earth. We found that almost all radiation with a wavelength shorter than 200 nm is attenuated effectively, even by ...
... that has the same age now as the Sun had 4–3.5 Ga. Atmospheric extinction was calculated using the Beer-Lambert law, assuming several density profiles for the atmosphere of the Archean Earth. We found that almost all radiation with a wavelength shorter than 200 nm is attenuated effectively, even by ...
National Institute of Standards and Technology, Boulder
... 4. Calculate partial derivatives of the range with respect to each of the parameters of interest; 5. Construct the covariance matrix each day (for up to 8 years) 6. Invert and calculate the worst-case uncertainties 7. Divide by 3 to get “modified worst-case uncertainties” ...
... 4. Calculate partial derivatives of the range with respect to each of the parameters of interest; 5. Construct the covariance matrix each day (for up to 8 years) 6. Invert and calculate the worst-case uncertainties 7. Divide by 3 to get “modified worst-case uncertainties” ...
3. Measuring Distances and Magnitudes
... Telescope) have improved parallax accuracy to 0.001” within a few years. Prior to 1990, less than 10,000 stellar parallaxes had been measured (and only 500 known well), but there are about 1012 stars in our Galaxy. Space observations made by the European Space Agency with the Hipparcos mission (1989 ...
... Telescope) have improved parallax accuracy to 0.001” within a few years. Prior to 1990, less than 10,000 stellar parallaxes had been measured (and only 500 known well), but there are about 1012 stars in our Galaxy. Space observations made by the European Space Agency with the Hipparcos mission (1989 ...
Voyage of Discovery - MESSENGER Education
... and Neptune—are large planets located further out in the Solar System than the inner planets. They have no solid surface on which to stand, and the apparent visible surfaces are just the top layers of clouds in their atmospheres. The Jovian planets are gas giants—large rapidly rotating objects made ...
... and Neptune—are large planets located further out in the Solar System than the inner planets. They have no solid surface on which to stand, and the apparent visible surfaces are just the top layers of clouds in their atmospheres. The Jovian planets are gas giants—large rapidly rotating objects made ...
Aye LADEE - Robert Ferguson Observatory
... a maximum altitude, they sink back into the setting sun as The crescent moon joins the three planets and the stars they once again come between Earth and the sun, completing of Gemini in early August (see figure) for another lovely what we call one synodic period. Mercury, closest to the planetary c ...
... a maximum altitude, they sink back into the setting sun as The crescent moon joins the three planets and the stars they once again come between Earth and the sun, completing of Gemini in early August (see figure) for another lovely what we call one synodic period. Mercury, closest to the planetary c ...
Physics Honors • Calculate the range, average/mean, percent, and
... Describe the effect of different frequencies of electromagnetic waves on the Earth and living organisms (e.g., radio, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, gamma, cosmic rays) Identify information that the electromagnetic spectrum provides about the stars and the universe (e.g., chemical composition, ...
... Describe the effect of different frequencies of electromagnetic waves on the Earth and living organisms (e.g., radio, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, gamma, cosmic rays) Identify information that the electromagnetic spectrum provides about the stars and the universe (e.g., chemical composition, ...
Accretion
... Accretion disks: structure equations One can solve the a system of structure equations for accretion disks around compact object assuming (1) steady state, (2) neglecting gas infall (no protostellar envelope in this case although gas inflow may occur as gas comes from the donor star in a binary sys ...
... Accretion disks: structure equations One can solve the a system of structure equations for accretion disks around compact object assuming (1) steady state, (2) neglecting gas infall (no protostellar envelope in this case although gas inflow may occur as gas comes from the donor star in a binary sys ...
LOCV calculation for Beta-stable matter at finite temperature
... density as we increase the temperature and the maximum value of yP is pushed to the lower baryon density by an increase in the temperature. This shows that at high temperatures the beta-stable matter with higher proton abundance tends to lower its baryon density. This effect is much larger in case ...
... density as we increase the temperature and the maximum value of yP is pushed to the lower baryon density by an increase in the temperature. This shows that at high temperatures the beta-stable matter with higher proton abundance tends to lower its baryon density. This effect is much larger in case ...
Lecture 8
... photon. No axions have so far been detected. On the other hand the detectors have so far not been sensitive enough to really expect a detection. WIMPs interact weakly with ordinary matter. In practice this means that mostly they do not interact at all, so that a WIMP will pass through the Earth easi ...
... photon. No axions have so far been detected. On the other hand the detectors have so far not been sensitive enough to really expect a detection. WIMPs interact weakly with ordinary matter. In practice this means that mostly they do not interact at all, so that a WIMP will pass through the Earth easi ...
gravitational collapse to black holes
... There has been some (weak) numerical evidence opposing the conjecture ...
... There has been some (weak) numerical evidence opposing the conjecture ...
Neutron star to strange star - Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar
... strongly interacting matter at high density and/or temperature. SQM : Equal number of up (u), down (d) and strange (s) quark. Constant effort to confirm the existence quark gluon plasma (QGP) and s quarks in ultra relativistic collisions. SQM could naturally occur in the cores of compact stars. Neut ...
... strongly interacting matter at high density and/or temperature. SQM : Equal number of up (u), down (d) and strange (s) quark. Constant effort to confirm the existence quark gluon plasma (QGP) and s quarks in ultra relativistic collisions. SQM could naturally occur in the cores of compact stars. Neut ...
198_1.pdf
... (LIC), is a very complicated phenomenon where the solar wind and interstellar plasmas, interstellar neutrals, magnetic field, and cosmic rays play prominent roles. The heliosphere provides a unique opportunity to study in detail the only accessible example of a commonplace but fundamental astrophysi ...
... (LIC), is a very complicated phenomenon where the solar wind and interstellar plasmas, interstellar neutrals, magnetic field, and cosmic rays play prominent roles. The heliosphere provides a unique opportunity to study in detail the only accessible example of a commonplace but fundamental astrophysi ...
Poster - unist
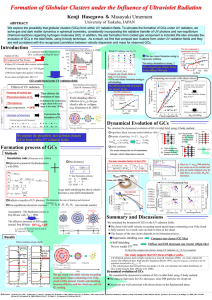
... We explore the possibility that globular clusters (GCs) form within UV radiation fields. To simulate the formation of GCs under UV radiation, we solve gas and dark matter dynamics in spherical symmetry, consistently incorporating the radiative transfer of UV photons and non-equilibrium chemical reac ...
... We explore the possibility that globular clusters (GCs) form within UV radiation fields. To simulate the formation of GCs under UV radiation, we solve gas and dark matter dynamics in spherical symmetry, consistently incorporating the radiative transfer of UV photons and non-equilibrium chemical reac ...
THE EVOLUTION OF SOLAR FLUX FROM 0.1 nm TO 160μm
... by advances in UV and X-ray telescope technology (Skumanich 1972; Zahnle & Walker 1982; Ayres 1997). The most comprehensive study is the “Sun in Time” program, which recently published multi-wavelength results from 20 years of telescopic observation of solar analogs—nearby G stars that are compositi ...
... by advances in UV and X-ray telescope technology (Skumanich 1972; Zahnle & Walker 1982; Ayres 1997). The most comprehensive study is the “Sun in Time” program, which recently published multi-wavelength results from 20 years of telescopic observation of solar analogs—nearby G stars that are compositi ...
X-ray and UV Transients
... >10 events y-1 even if the sensitivity is 102 less. • The observed signals have UV flux~host, so confusion with (even mildly) variable sources is an issue unless additional information is available • A combined UV survey+optical SN survey like PTF will be powerful to get retrospective measurements ...
... >10 events y-1 even if the sensitivity is 102 less. • The observed signals have UV flux~host, so confusion with (even mildly) variable sources is an issue unless additional information is available • A combined UV survey+optical SN survey like PTF will be powerful to get retrospective measurements ...
Lecture 2. Thermal evolution and surface emission of neutron stars
... In addition, objects have been observed with GMRT (B.C.Joshi, M. Burgay et al.). In both studies only upper limits were derived. Still, the zero result can be just due to unfavorable orientations (at long periods NSs have very narrow beams). It is necessary to increase statistics. ...
... In addition, objects have been observed with GMRT (B.C.Joshi, M. Burgay et al.). In both studies only upper limits were derived. Still, the zero result can be just due to unfavorable orientations (at long periods NSs have very narrow beams). It is necessary to increase statistics. ...