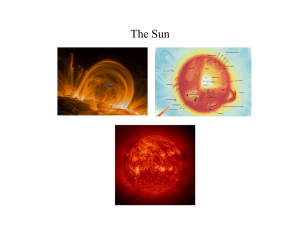
How do stars shine?
... Einstein’s famous equation means we can convert mass into energy, and c, being the speed of light, and a very big number, then squared, means a small amount of mass can make a lot of energy. It was known through spectroscopy that the Sun was made mostly of hydrogen and helium, so it was a good bet t ...
... Einstein’s famous equation means we can convert mass into energy, and c, being the speed of light, and a very big number, then squared, means a small amount of mass can make a lot of energy. It was known through spectroscopy that the Sun was made mostly of hydrogen and helium, so it was a good bet t ...
Starlight and What it Tells Us
... • Temperature is the only determinant of color • Energy per unit area is the same if temperature is the same – If two stars have the same color and distance, difference in brightness is due to difference in size – Dwarf and giant stars are literally dwarfs or giants ...
... • Temperature is the only determinant of color • Energy per unit area is the same if temperature is the same – If two stars have the same color and distance, difference in brightness is due to difference in size – Dwarf and giant stars are literally dwarfs or giants ...
How Was the Solar System Formed? Questions
... billion years ago. It started out as a spinning cloud of gas and dust. Something caused the materials to begin to clump together. Scientists think maybe it was a shockwave from a supernova. A supernova is a highly energetic explosion. It occurs at the end of a very large star's life. Its nuclear fue ...
... billion years ago. It started out as a spinning cloud of gas and dust. Something caused the materials to begin to clump together. Scientists think maybe it was a shockwave from a supernova. A supernova is a highly energetic explosion. It occurs at the end of a very large star's life. Its nuclear fue ...
1.1989 x 10 30 kg
... Spectrum analysis shows that sunspots have strong magnetic field, about 1000 times stronger than the Sun's average. Sunspots usually appear in pairs. The two sunspots of a pair have different polarities, one would be a magnetic north and the other is a magnetic south, and can be joined by magnetic ...
... Spectrum analysis shows that sunspots have strong magnetic field, about 1000 times stronger than the Sun's average. Sunspots usually appear in pairs. The two sunspots of a pair have different polarities, one would be a magnetic north and the other is a magnetic south, and can be joined by magnetic ...
Astronomy – Name: ______KEY___________________ Date
... 19. How can astronomers observe the different elements found in the sun? They study the sun’s spectrum. 20. What is a sunspot? It is an area of relatively lower temperature than the surrounding surface. 21. About how many miles is the earth from the sun? 93 M miles 22. What is meant by “space weathe ...
... 19. How can astronomers observe the different elements found in the sun? They study the sun’s spectrum. 20. What is a sunspot? It is an area of relatively lower temperature than the surrounding surface. 21. About how many miles is the earth from the sun? 93 M miles 22. What is meant by “space weathe ...
HR Diagram Activity
... Materials: Colored pencils (red, orange, yellow, blue) Procedure: 1. Review the star data chart below. Note that the sun, which is used as a standard of brightness, is given a value of 1. The brightness given for each other star shows how that star compares with the sun. 2. Using an “X” as a plot po ...
... Materials: Colored pencils (red, orange, yellow, blue) Procedure: 1. Review the star data chart below. Note that the sun, which is used as a standard of brightness, is given a value of 1. The brightness given for each other star shows how that star compares with the sun. 2. Using an “X” as a plot po ...
General Introduction 1. Luminosity, Flux and Magnitude The
... and the classical perfect gas law implies that a star’s central pressure Pc , density ρc and temperature Tc are related by Pc ∼ ...
... and the classical perfect gas law implies that a star’s central pressure Pc , density ρc and temperature Tc are related by Pc ∼ ...
The Sun and other Stars
... When stars like the Sun begin to fuse H to He they fall into the Main sequence stars. The Sun will remain a main sequence star until uses about 90% of its fuel in the core. This is the beginning of the End ...
... When stars like the Sun begin to fuse H to He they fall into the Main sequence stars. The Sun will remain a main sequence star until uses about 90% of its fuel in the core. This is the beginning of the End ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... 1. If it’s a summer day here, what season and time of day is it in Russia? Russia would be summer night 2. If it’s a winter night here, what season and time of day is it in Peru? Peru would be summer night 3. If it’s a summer night here, what season and time of day is it in Australia? Australia woul ...
... 1. If it’s a summer day here, what season and time of day is it in Russia? Russia would be summer night 2. If it’s a winter night here, what season and time of day is it in Peru? Peru would be summer night 3. If it’s a summer night here, what season and time of day is it in Australia? Australia woul ...
Star Formation
... • Interstellar gas, like the sun, is 74% hydrogen and 25% helium. • Interstellar dust, like clouds in the gas giants, are molecular carbon monoxide, ammonia, and water. • Traces of all other elements are present. ...
... • Interstellar gas, like the sun, is 74% hydrogen and 25% helium. • Interstellar dust, like clouds in the gas giants, are molecular carbon monoxide, ammonia, and water. • Traces of all other elements are present. ...
Chapter8
... Need large proton speed ( high temperature) to overcome Coulomb barrier (electrostatic repulsion between protons). T ≥ 107 0K = 10 million 0K ...
... Need large proton speed ( high temperature) to overcome Coulomb barrier (electrostatic repulsion between protons). T ≥ 107 0K = 10 million 0K ...
Solar System Review
... When the solar system began to spin faster, what shape did it become? What happened to the temperature of the solar system as it shrank? Why? What process gives the sun its energy? Explain how that process creates energy. E=mc2 can be used to calculate the energy given off by the sun. Explain what t ...
... When the solar system began to spin faster, what shape did it become? What happened to the temperature of the solar system as it shrank? Why? What process gives the sun its energy? Explain how that process creates energy. E=mc2 can be used to calculate the energy given off by the sun. Explain what t ...
Six Weeks: 3rd ALLEN Subject: Science Grade: 3 TEKS Covering
... What is the center of our Solar System? What are the planets that make up our Solar System (8) Earth and space. The student knows that there are recognizable patterns in the natural world and among the Sun, Earth, and Moon system. The student is expected to: (A) differentiate between weather and cli ...
... What is the center of our Solar System? What are the planets that make up our Solar System (8) Earth and space. The student knows that there are recognizable patterns in the natural world and among the Sun, Earth, and Moon system. The student is expected to: (A) differentiate between weather and cli ...
Stages in the Formation of Stars
... producing vast amounts of energy. _____________________________________________ 4. What two processes balance each other to make a star stable? ...
... producing vast amounts of energy. _____________________________________________ 4. What two processes balance each other to make a star stable? ...