Spectroscopic Variability of Supergiant Star HD14134, B3Ia
... Fig. 4 and Fig. 5. It has been revealed that the variability of radial velocity, equivalent widths, depths and half-widths of Hβ line, as well as HeIλ5875.72Å and averaged CII (λ6578.05Å, λ6582.88Å) lines indicate repeating features. The changes of the radial velocities and spectral parameters of ...
... Fig. 4 and Fig. 5. It has been revealed that the variability of radial velocity, equivalent widths, depths and half-widths of Hβ line, as well as HeIλ5875.72Å and averaged CII (λ6578.05Å, λ6582.88Å) lines indicate repeating features. The changes of the radial velocities and spectral parameters of ...
Blocking Starlight Much Closer to Home 2: This Year`s
... For Charon, with no atmosphere (and our occultation method is very sensitive), the starlight disappears abruptly. If the star is brighter than the occulting object, the occultation is quite noticeable; if the star is fainter, then just a percentage is subtracted from the total. For Pluto (and, earli ...
... For Charon, with no atmosphere (and our occultation method is very sensitive), the starlight disappears abruptly. If the star is brighter than the occulting object, the occultation is quite noticeable; if the star is fainter, then just a percentage is subtracted from the total. For Pluto (and, earli ...
The Evryscope: the first full-sky gigapixel-scale telescope Nicholas Law
... dwarfs rapidly enough to see transits Friday, August 21, 15 ...
... dwarfs rapidly enough to see transits Friday, August 21, 15 ...
Article PDF - IOPscience
... investigate the effects of the presence of terrestrial-mass planet(s) in the Kuiper belt or in the scattered disk, as proposed by Morbidelli & Valsecchi (1997) and Brunini & Melita (2002). In x 4, we propose a new model for the origin of 2000 CR105 in which the Kozai-like perturbations raised by a m ...
... investigate the effects of the presence of terrestrial-mass planet(s) in the Kuiper belt or in the scattered disk, as proposed by Morbidelli & Valsecchi (1997) and Brunini & Melita (2002). In x 4, we propose a new model for the origin of 2000 CR105 in which the Kozai-like perturbations raised by a m ...
An asymmetry detected in the disk of κ CMa⋆ with the AMBER/VLTI
... Brazil and plotted in Fig. 5. This profile is strongly asymmetric with a V/R double peak of ∼1.3. This V/R > 1 is usually interpreted in terms of a viscous disk similar to accretion disks where the gas and angular momentum are diffused outward by magnetohydrodynamic viscosity (Lee et al. 1991). Cons ...
... Brazil and plotted in Fig. 5. This profile is strongly asymmetric with a V/R double peak of ∼1.3. This V/R > 1 is usually interpreted in terms of a viscous disk similar to accretion disks where the gas and angular momentum are diffused outward by magnetohydrodynamic viscosity (Lee et al. 1991). Cons ...
Chemical Evolution of Galactic Systems
... This thesis explores the chemical signatures of galaxy formation and evolution using a software package designed specifically for this investigation. We describe the development of this multi-zone chemical evolution code, which simulates the spacetime evolution of stars, gas and a vast array of chem ...
... This thesis explores the chemical signatures of galaxy formation and evolution using a software package designed specifically for this investigation. We describe the development of this multi-zone chemical evolution code, which simulates the spacetime evolution of stars, gas and a vast array of chem ...
In Pursuit of the Least Luminous Galaxies
... extrapolation of the known population to predict a total number of ∼100–500 dwarf satellites [14, 15]. Uniform: because the very least luminous MW dwarfs (MV ∼ −2) can currently only be found within 50 kpc, it is presently unclear whether dwarfs can form with such intrinsically low luminosities, or ...
... extrapolation of the known population to predict a total number of ∼100–500 dwarf satellites [14, 15]. Uniform: because the very least luminous MW dwarfs (MV ∼ −2) can currently only be found within 50 kpc, it is presently unclear whether dwarfs can form with such intrinsically low luminosities, or ...
12 Introduction to Cepheid Variable Stars Exercise
... If you know the distance to the bulb and measure its apparent brightness then you can calculate the wattage of the bulb. Likewise, if you know the wattage of the bulb and measure the observed brightness you can calculate the distance to the bulb. This can be applied to stars, if you determine the ap ...
... If you know the distance to the bulb and measure its apparent brightness then you can calculate the wattage of the bulb. Likewise, if you know the wattage of the bulb and measure the observed brightness you can calculate the distance to the bulb. This can be applied to stars, if you determine the ap ...
File 10 VBS 17 Recreation Rotation Overview
... Point to the S group and lead them to say: “SAY the NAME.” o Say: “Today, our A group is going to play Moon Rock Toss.” Point to the T group and lead them to say: “TELL the RULES.” o Dump the moon rocks on the floor and explain that conferees will use the tongs to pick up one moon rock and try to to ...
... Point to the S group and lead them to say: “SAY the NAME.” o Say: “Today, our A group is going to play Moon Rock Toss.” Point to the T group and lead them to say: “TELL the RULES.” o Dump the moon rocks on the floor and explain that conferees will use the tongs to pick up one moon rock and try to to ...
Z - STScI
... 56Ni explosively created from Si burning after corecollapse Direct probe of the explosion How Is it related to progenitor mass ? ...
... 56Ni explosively created from Si burning after corecollapse Direct probe of the explosion How Is it related to progenitor mass ? ...
Cold dark matter heats up
... even so, such simulations were expensive, taking 70 hours on state-ofthe-art 3-MHz facilities. Such calculations would now take a few minutes on a mobile telephone. The growth of computing power and parallel capabilities meant that, by the 1990s, simulations became sufficiently powerful to make deta ...
... even so, such simulations were expensive, taking 70 hours on state-ofthe-art 3-MHz facilities. Such calculations would now take a few minutes on a mobile telephone. The growth of computing power and parallel capabilities meant that, by the 1990s, simulations became sufficiently powerful to make deta ...
GAIA A Stereoscopic Census of our Galaxy
... stars V ≤ 15 ( ~30 million stars) bright star treatment for astrometric accuracy monitoring of Basic Angle (astrometric accuracy) simulations astrometric and spectro-photometric payload national facility with final end-of-mission database ...
... stars V ≤ 15 ( ~30 million stars) bright star treatment for astrometric accuracy monitoring of Basic Angle (astrometric accuracy) simulations astrometric and spectro-photometric payload national facility with final end-of-mission database ...
Black Holes
... and electrons reach the ultimate limit at which they can be packed together. But what happens when even these forces are overwhelmed in the collapse of stars more massive than three solar masses? The result is a black hole, an object so dense that light cannot escape its gravitational pull. Einstein ...
... and electrons reach the ultimate limit at which they can be packed together. But what happens when even these forces are overwhelmed in the collapse of stars more massive than three solar masses? The result is a black hole, an object so dense that light cannot escape its gravitational pull. Einstein ...
Gas Accretion is Dominated by Warm Ionized Gas in Milky Way
... suggests that heating dominates over cooling for this component. On the other hand, if we repeat the same calculation for the cold mode gas, the cooling time is shorter than the compression time at all radii, leading to net cooling and condensation of the densest parts of the inflowing streams, espe ...
... suggests that heating dominates over cooling for this component. On the other hand, if we repeat the same calculation for the cold mode gas, the cooling time is shorter than the compression time at all radii, leading to net cooling and condensation of the densest parts of the inflowing streams, espe ...
Super-solar Metal Abundances in Two Galaxies at ζ ∼ 3.57
... al. 1997). Among the many detected lines, the interesting Zn iiλ2026 line in G1 at z = 3.5673 is detected with high confidence (Figure 2) thanks to the high signal-to-noise in the spectrum. The H i column density of G0 is relatively low (NH I = 1019.62 cm−2 ), for which the ionization correction cou ...
... al. 1997). Among the many detected lines, the interesting Zn iiλ2026 line in G1 at z = 3.5673 is detected with high confidence (Figure 2) thanks to the high signal-to-noise in the spectrum. The H i column density of G0 is relatively low (NH I = 1019.62 cm−2 ), for which the ionization correction cou ...
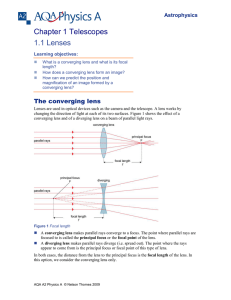
Chapter 1 Telescopes 1.1 Lenses
... This is why many more stars are seen using a telescope than using the unaided eye. The greater the diameter of the objective of a telescope, the greater the number of stars that can be seen. Planets and other astronomical objects in the solar system are magnified using a telescope (unlike stars whic ...
... This is why many more stars are seen using a telescope than using the unaided eye. The greater the diameter of the objective of a telescope, the greater the number of stars that can be seen. Planets and other astronomical objects in the solar system are magnified using a telescope (unlike stars whic ...
Lecture notes 18: Galaxies and galaxy clusters
... http://www.seds.org/ spider/ngc/ngc.cgi?n2841) number 30%. The former are presumed to be caused by quasistatic density waves, while the latter are caused by stochastic, self-propagating star formation. Both processes are probably active in most spiral galaxies. Elliptical Galaxies In contradiction t ...
... http://www.seds.org/ spider/ngc/ngc.cgi?n2841) number 30%. The former are presumed to be caused by quasistatic density waves, while the latter are caused by stochastic, self-propagating star formation. Both processes are probably active in most spiral galaxies. Elliptical Galaxies In contradiction t ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.