KIC 8462852 Faded Throughout the Kepler Mission
... as bright as KIC 8462852 with V = 11.7 are badly saturated in such data sets). Data from the Kepler mission, however, provide exactly such an opportunity. The Kepler mission was designed to detect and characterize transit events with timescales of minutes to hours. To that end, Kepler processing pip ...
... as bright as KIC 8462852 with V = 11.7 are badly saturated in such data sets). Data from the Kepler mission, however, provide exactly such an opportunity. The Kepler mission was designed to detect and characterize transit events with timescales of minutes to hours. To that end, Kepler processing pip ...
DEDUCING THE LIFETIME OF SHORT GAMMA
... The result of the average star formation history of the z = 0 early-type galaxies is shown as the dotted curve in Figure 2. It peaks at a look-back time of about ∼12 Gyr and then rapidly declines at low redshift. The average SFH for the z = 0 late-type galaxies, computed by subtracting (2) from (1), ...
... The result of the average star formation history of the z = 0 early-type galaxies is shown as the dotted curve in Figure 2. It peaks at a look-back time of about ∼12 Gyr and then rapidly declines at low redshift. The average SFH for the z = 0 late-type galaxies, computed by subtracting (2) from (1), ...
Article PDF - IOPscience
... surface brightness. It is not correlated with linear size. Gas fraction varies with luminosity and surface brightness at the same rate, indicating evolution at Ðxed size. Dim galaxies are clearly less evolved than bright ones, having consumed only D1 of their gas. This 2 reservoirs. These resolves t ...
... surface brightness. It is not correlated with linear size. Gas fraction varies with luminosity and surface brightness at the same rate, indicating evolution at Ðxed size. Dim galaxies are clearly less evolved than bright ones, having consumed only D1 of their gas. This 2 reservoirs. These resolves t ...
Stellar Structure and Evolution
... intrinsic interest of the topic, the value of such a course is that it provides an illustration (within the syllabus in Aarhus, almost the first illustration) of the application of physics to “the real world” outside the laboratory. I am grateful to the students who have followed the course over the ...
... intrinsic interest of the topic, the value of such a course is that it provides an illustration (within the syllabus in Aarhus, almost the first illustration) of the application of physics to “the real world” outside the laboratory. I am grateful to the students who have followed the course over the ...
Carnegie Observatories Astrophysics Series, Vol. 4:
... silicates have multiple narrow features in their 10 µm spectra, while amorphous silicate material has a broad profile. The interstellar 9.7 µm feature is seen in absorption on a number of sightlines. The observed profiles are broad and relatively featureless, indicative of amorphous silicate materia ...
... silicates have multiple narrow features in their 10 µm spectra, while amorphous silicate material has a broad profile. The interstellar 9.7 µm feature is seen in absorption on a number of sightlines. The observed profiles are broad and relatively featureless, indicative of amorphous silicate materia ...
DYING STARS AND THE BIRTH OF THE ELEMENTS
... something happens to compress them (such as a collision with another cloud, for example), then they can collapse. Obeying the Ideal Gas Law, the clouds heat up as they shrink, and the density, pressure, and temperature are highest at the center. Eventually, the temperature and pressure in the collap ...
... something happens to compress them (such as a collision with another cloud, for example), then they can collapse. Obeying the Ideal Gas Law, the clouds heat up as they shrink, and the density, pressure, and temperature are highest at the center. Eventually, the temperature and pressure in the collap ...
Gamma-Ray Bursts
... star explodes in a supernova explosion. The core collapses into a neutron star, and the rest of the star explodes in a supernova explosion. The core collapses into a white dwarf, and the rest of the star explodes to form a planetary nebula. The core collapses into a neutron star, and the rest of the ...
... star explodes in a supernova explosion. The core collapses into a neutron star, and the rest of the star explodes in a supernova explosion. The core collapses into a white dwarf, and the rest of the star explodes to form a planetary nebula. The core collapses into a neutron star, and the rest of the ...
High ions towards white dwarfs: circumstellar line shifts and stellar
... In principal, the three possible sources of absorption features in DA white dwarf UV spectra should be identifiable by an accurate measurement of their interstellar, photospheric and circumstellar velocities (Vism , Vphot and Vcirc ). This is especially true for nearby targets where the interstellar ...
... In principal, the three possible sources of absorption features in DA white dwarf UV spectra should be identifiable by an accurate measurement of their interstellar, photospheric and circumstellar velocities (Vism , Vphot and Vcirc ). This is especially true for nearby targets where the interstellar ...
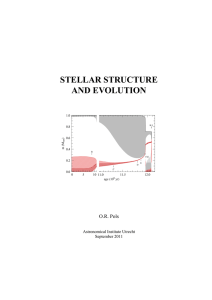
STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION
... known, a direct measurement of the radius is possible. • Spectroscopy at sufficiently high resolution yields detailed information about the physical conditions in the atmosphere. With detailed spectral-line analysis using stellar atmosphere models one can determine the photospheric properties of a s ...
... known, a direct measurement of the radius is possible. • Spectroscopy at sufficiently high resolution yields detailed information about the physical conditions in the atmosphere. With detailed spectral-line analysis using stellar atmosphere models one can determine the photospheric properties of a s ...
- MNASSA Page
... axy, but on the other hand it is not very can be seen lurking in the nebulosity. Star centrally placed. The inner core consists splinters dot the surface of this outstanding of stars that are very hot and large, their object like dewdrops on frosted glass. combined radiation being responsible for it ...
... axy, but on the other hand it is not very can be seen lurking in the nebulosity. Star centrally placed. The inner core consists splinters dot the surface of this outstanding of stars that are very hot and large, their object like dewdrops on frosted glass. combined radiation being responsible for it ...
EROs and submm galaxies: Expectations for FMOS in the
... Can observe targets for an entire night (or longer) ...
... Can observe targets for an entire night (or longer) ...
Astronomy Astrophysics Astrophysical parameters and orbital solution of the peculiar X-ray
... 2006b) as a sub-class of SGXBs. SFXTs spend most of their time at X-ray luminosities between LX ∼ 1032 to 1034 erg s−1 , well below the “normal” X-ray luminosity of SGXBs, with very brief excursions to outburst luminosities of up to a few times 1036 erg s−1 (e.g. Rampy et al. 2009; Sidoli et al. 200 ...
... 2006b) as a sub-class of SGXBs. SFXTs spend most of their time at X-ray luminosities between LX ∼ 1032 to 1034 erg s−1 , well below the “normal” X-ray luminosity of SGXBs, with very brief excursions to outburst luminosities of up to a few times 1036 erg s−1 (e.g. Rampy et al. 2009; Sidoli et al. 200 ...
Chemo-spectrophotometric evolution of spiral galaxies ± II. Main
... Evolution of spiral galaxies ± II the simple scaling relations for galactic discs (established in the framework of SAMs; see Section 2.2) in order to derive initial gaseous profiles. They subsequently calculate the full chemical and spectrophotometric evolution of such discs for the case of low sur ...
... Evolution of spiral galaxies ± II the simple scaling relations for galactic discs (established in the framework of SAMs; see Section 2.2) in order to derive initial gaseous profiles. They subsequently calculate the full chemical and spectrophotometric evolution of such discs for the case of low sur ...
Tracers of Discs and Winds around Intermediate and High Mass
... the original references to take account of revised distances. For sources where an accurate spectral type can be inferred we have given that. For those where only a bolometric luminosity exists (generally the most heavily embedded) we have quoted that instead. All of these sources were chosen to be ...
... the original references to take account of revised distances. For sources where an accurate spectral type can be inferred we have given that. For those where only a bolometric luminosity exists (generally the most heavily embedded) we have quoted that instead. All of these sources were chosen to be ...
Sparse aperture masking at the VLT II. Detection limits for the eight
... a debris disk, a proto-planetary disk or a planetary system. The understanding of such formation process requires the study of debris disks. These targets are substantial and particularly suitable for optical and infrared observations. Sparse Aperture masking (SAM) is a high angular resolution techn ...
... a debris disk, a proto-planetary disk or a planetary system. The understanding of such formation process requires the study of debris disks. These targets are substantial and particularly suitable for optical and infrared observations. Sparse Aperture masking (SAM) is a high angular resolution techn ...
Discovery of a bright quasar without a massive
... between the two systems about 108 years ago probably triggered both the starburst and the quasar activity13. We use the MCS deconvolution technique14–17 on our new HST images, in order to explore the vicinity of the quasar (Fig 1). These images confirm the strongly irregular shape of the companion g ...
... between the two systems about 108 years ago probably triggered both the starburst and the quasar activity13. We use the MCS deconvolution technique14–17 on our new HST images, in order to explore the vicinity of the quasar (Fig 1). These images confirm the strongly irregular shape of the companion g ...
Pair instability supernovae: Evolution, explosion, nucleosynthesis
... supernovae are exploding in the visible Universe each second, and at present there are a few of them discovered every day. The average peak luminosity of a supernova competes with that of entire galaxies. Supernovae are the main contributor of heavy elements, energy and momentum to the interstellar ...
... supernovae are exploding in the visible Universe each second, and at present there are a few of them discovered every day. The average peak luminosity of a supernova competes with that of entire galaxies. Supernovae are the main contributor of heavy elements, energy and momentum to the interstellar ...
Astrophysics for Physicists.
... Sciences as well as our Joint Astronomy and Astrophysics Programme. I must have taught this course to more than half a dozen batches. Over the years, several excellent textbooks suitable for use in one-semester courses on particle physics and solid state physics have been written. The situation with ...
... Sciences as well as our Joint Astronomy and Astrophysics Programme. I must have taught this course to more than half a dozen batches. Over the years, several excellent textbooks suitable for use in one-semester courses on particle physics and solid state physics have been written. The situation with ...
Basic Assumptions About Convection The calculation of convection
... • There exist discrete “blobs” of material inside a star that have sizes of the order of lm , where lm is the mixing length. These blobs can move distances of the order of lm before losing their identity. (This variable lm is somewhat of a fudge-factor, and many of the uncertainties will get hidden ...
... • There exist discrete “blobs” of material inside a star that have sizes of the order of lm , where lm is the mixing length. These blobs can move distances of the order of lm before losing their identity. (This variable lm is somewhat of a fudge-factor, and many of the uncertainties will get hidden ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.