Chapter 13 – Behavior of Spectral Lines
... – When H- opacity dominates, the line and the continuous absorption coefficients are both proportional to the electron pressure – Hence the ratio line/continuous opacity is independent of pressure When most of the atoms of an element are in the same or a lower state of ionization, lines are sensitiv ...
... – When H- opacity dominates, the line and the continuous absorption coefficients are both proportional to the electron pressure – Hence the ratio line/continuous opacity is independent of pressure When most of the atoms of an element are in the same or a lower state of ionization, lines are sensitiv ...
Constraining tidal dissipation in F-type main
... star and the planet, respectively, and nobs is the present mean orbital motion of the system corresponding to the orbital period Porb = 2.99433 days. As we shall see (cf. Sect. 3), the mean motion n varies by a factor of ≈4−5 during the evolution of the system, but we shall neglect this change becau ...
... star and the planet, respectively, and nobs is the present mean orbital motion of the system corresponding to the orbital period Porb = 2.99433 days. As we shall see (cf. Sect. 3), the mean motion n varies by a factor of ≈4−5 during the evolution of the system, but we shall neglect this change becau ...
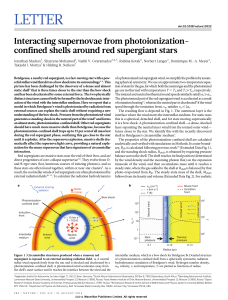
Red supergiants around the obscured open cluster Stephenson 2
... Scutum Complex represents a giant star formation region triggered by the dynamical excitation of the Galactic Bar, whose tip is believed to intersect the Scutum-Crux Arm close to this region (see discussion in D07; Garzón et al. 1997). The possibility of a hierarchical star-forming structure extend ...
... Scutum Complex represents a giant star formation region triggered by the dynamical excitation of the Galactic Bar, whose tip is believed to intersect the Scutum-Crux Arm close to this region (see discussion in D07; Garzón et al. 1997). The possibility of a hierarchical star-forming structure extend ...
On the Origin of Early-Type Galaxies and the - N
... (Governato, Tozzi, & Cavaliere 1996 ; Ghigna et al. 1998). If instead the merging event occurs outside a larger potential well, the halo is subsequently able to accrete new cold gas, and the galaxy may have sufficient time to form a new gaseous/stellar disk (Baugh et al. 1996b). If the newly created ...
... (Governato, Tozzi, & Cavaliere 1996 ; Ghigna et al. 1998). If instead the merging event occurs outside a larger potential well, the halo is subsequently able to accrete new cold gas, and the galaxy may have sufficient time to form a new gaseous/stellar disk (Baugh et al. 1996b). If the newly created ...
The APEX-CHAMP+ view of the Orion Molecular Cloud 1 core
... energetic photons from hot, massive stars in the nearby Orion Nebula’s central Trapezium cluster, active high- and intermediate-mass star formation, and a past energetic event that excites the KL nebula. Radiative transfer modeling of the various isotopologic CO lines implies typical H2 densities in ...
... energetic photons from hot, massive stars in the nearby Orion Nebula’s central Trapezium cluster, active high- and intermediate-mass star formation, and a past energetic event that excites the KL nebula. Radiative transfer modeling of the various isotopologic CO lines implies typical H2 densities in ...
Magnitude-range brightness variations of overactive K giants
... 2012). In a recent investigation of the previous three solar cycles, Fröhlich (2013) showed that the long-term solar variability requires a global solar temperature change, likely originating from the changing strength of its magnetic activity. The solar effective temperature appears lower during l ...
... 2012). In a recent investigation of the previous three solar cycles, Fröhlich (2013) showed that the long-term solar variability requires a global solar temperature change, likely originating from the changing strength of its magnetic activity. The solar effective temperature appears lower during l ...
Clumpy wind accretion in supergiant neutron star high mass X
... bulk of the wind mass. The colloquial term “wind clumps” refers to these dense shells. The space between the shells is filled by low density gas, which is usually termed “intra-clump” medium. Besides the dense cool shells and the tenuous intra-clump medium, there is a third type of structure. These ...
... bulk of the wind mass. The colloquial term “wind clumps” refers to these dense shells. The space between the shells is filled by low density gas, which is usually termed “intra-clump” medium. Besides the dense cool shells and the tenuous intra-clump medium, there is a third type of structure. These ...
The drop in the cosmic star formation rate below redshift 2 is caused
... reduced for haloes with Mhalo & 1012 M⊙ (Booth & Schaye, 2009). The AGN simulation reproduces the observed mass density in black holes at z = 0 and the black hole scaling relations (Booth & Schaye, 2009) and their evolution (Booth & Schaye, 2010) as well as the observed optical and X-ray properties, ...
... reduced for haloes with Mhalo & 1012 M⊙ (Booth & Schaye, 2009). The AGN simulation reproduces the observed mass density in black holes at z = 0 and the black hole scaling relations (Booth & Schaye, 2009) and their evolution (Booth & Schaye, 2010) as well as the observed optical and X-ray properties, ...
transparencies - Rencontres du Vietnam
... 2 different Monte-Carlo have been computed to estimate our detection efficiency: _ simulated microlensing effect on true light curve _ fake images that pass all the photometric chain with simulated microlensed star ► they are in excellent agreement for the bright star sample. ...
... 2 different Monte-Carlo have been computed to estimate our detection efficiency: _ simulated microlensing effect on true light curve _ fake images that pass all the photometric chain with simulated microlensed star ► they are in excellent agreement for the bright star sample. ...
Explosion and Systematics for Core
... only predictions that are made are for black hole mass and number. Furthermore, in order to estimate wether a model explodes or collapses to a black hole ad hoc assumptions on the neutrino heating were made. Therefore, predictions of the initial-final remnant mass function and of explosive nucleosyn ...
... only predictions that are made are for black hole mass and number. Furthermore, in order to estimate wether a model explodes or collapses to a black hole ad hoc assumptions on the neutrino heating were made. Therefore, predictions of the initial-final remnant mass function and of explosive nucleosyn ...
Galactic spiral structure - Proceedings of the Royal Society A
... gravitational parameter for an orbit about a mass M (e.g. Arnold 1989; Goldstein 1980). For a Keplerian orbit, the eccentricity vector is a constant of the motion. Stellar orbits are not strictly elliptical, but the orbit will approximate an ellipse at each part of its motion, and the eccentricity v ...
... gravitational parameter for an orbit about a mass M (e.g. Arnold 1989; Goldstein 1980). For a Keplerian orbit, the eccentricity vector is a constant of the motion. Stellar orbits are not strictly elliptical, but the orbit will approximate an ellipse at each part of its motion, and the eccentricity v ...
THE FUTURE IS NOW: THE FORMATION OF SINGLE LOW
... The Ohio State University, Department of Astronomy, Columbus, OH 43210; [email protected], [email protected], [email protected] Received 2007 June 21; accepted 2007 August 2 ...
... The Ohio State University, Department of Astronomy, Columbus, OH 43210; [email protected], [email protected], [email protected] Received 2007 June 21; accepted 2007 August 2 ...
SPIRou Science Case
... searching for biomarkers in their atmospheres is among the main objectives of this new century’s astronomy, motivating ambitious space missions (JWST/NASA, TESS/ NASA, CHEOPS/ESA, PLATO/ESA) The majority of the exoplanets now known were discovered thanks to RV studies measuring Doppler shifts induce ...
... searching for biomarkers in their atmospheres is among the main objectives of this new century’s astronomy, motivating ambitious space missions (JWST/NASA, TESS/ NASA, CHEOPS/ESA, PLATO/ESA) The majority of the exoplanets now known were discovered thanks to RV studies measuring Doppler shifts induce ...
a changing cosmos - Whittier Union High School District
... It is in the darkness before dawn on July 4, 1054 A.D. Chinese astronomers are greatly excited by the appearance of a “guest star”—a new star in the sky, never seen before. As the Earth spins, half a day later on July 5, it is predawn in Navajo lands of what is now northern Arizona. The Anasazi, the ...
... It is in the darkness before dawn on July 4, 1054 A.D. Chinese astronomers are greatly excited by the appearance of a “guest star”—a new star in the sky, never seen before. As the Earth spins, half a day later on July 5, it is predawn in Navajo lands of what is now northern Arizona. The Anasazi, the ...
Betelgeuse – Challenging our Understanding for more than 2000
... Upwelling material is driven by photospheric convecVon, giant fountaining or prominences, radiaVve pressure on molecules, etc. Some of this material returns to the star at high velocity. There are large ...
... Upwelling material is driven by photospheric convecVon, giant fountaining or prominences, radiaVve pressure on molecules, etc. Some of this material returns to the star at high velocity. There are large ...
Surface temperature distribution and absorption features in Isolated
... e and νe . Neutrinos play an important role in supernova explosions, since they carry away a great amount of the released energy. The collapse ends when the star central density reaches n0 , this event gives rise to a shock wave which propagates about 100-200 km before it stops, having lost energy t ...
... e and νe . Neutrinos play an important role in supernova explosions, since they carry away a great amount of the released energy. The collapse ends when the star central density reaches n0 , this event gives rise to a shock wave which propagates about 100-200 km before it stops, having lost energy t ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.