The Stars
... There are more stars in the sky than anyone can easily count, but they are not scattered evenly, and they are not all the same in brightness or color. By the end of the 5th grade, students should know that The patterns of stars in the sky stay the same, although they appear to move across the sk ...
... There are more stars in the sky than anyone can easily count, but they are not scattered evenly, and they are not all the same in brightness or color. By the end of the 5th grade, students should know that The patterns of stars in the sky stay the same, although they appear to move across the sk ...
Star Life Cycle - GSHS Mrs. Francomb
... Pumbaa: Oh. Gee. I always thought that they were balls of gas burning billions of miles away. Timon: Pumbaa, wit' you, everything's gas. ...
... Pumbaa: Oh. Gee. I always thought that they were balls of gas burning billions of miles away. Timon: Pumbaa, wit' you, everything's gas. ...
Facts - GreenSpirit
... The star explodes with the energy and light that outshines a galaxy of 200 billion stars. ...
... The star explodes with the energy and light that outshines a galaxy of 200 billion stars. ...
KMS Universe Test Study Guide
... 6) Why does the sun have such a great apparent magnitude, when it has only an average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Beca ...
... 6) Why does the sun have such a great apparent magnitude, when it has only an average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Beca ...
What is a Star
... If brightness and surface temperature are considered, stars can be plotted on a graph called the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram, a graph of great utility for the understanding of the life cycle of the stars. Birth of a star Stellar evolution begins with the gravitational collapse of part of a nebula cl ...
... If brightness and surface temperature are considered, stars can be plotted on a graph called the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram, a graph of great utility for the understanding of the life cycle of the stars. Birth of a star Stellar evolution begins with the gravitational collapse of part of a nebula cl ...
Stars - Madison County Schools
... nebula • Gravity may cause the nebula to contract • Matter in the gas cloud will begin to condense into a dense region called a protostar • The protostar continues to condense, it heats up. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass and nuclear fusion begins. • Begins the main sequence phase of the star ...
... nebula • Gravity may cause the nebula to contract • Matter in the gas cloud will begin to condense into a dense region called a protostar • The protostar continues to condense, it heats up. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass and nuclear fusion begins. • Begins the main sequence phase of the star ...
PowerPoint file - Northwest Creation Network
... Thus the ‘generally accepted’ theory of stellar formation may be one of a hundred unsupported dogmas which constitute a large part of present-day astrophysics.” ...
... Thus the ‘generally accepted’ theory of stellar formation may be one of a hundred unsupported dogmas which constitute a large part of present-day astrophysics.” ...
Jeopardy 2015
... gravitationally collapse, fragments,It heats up and spins faster. When the core temperature reaches 100 mill K, nuclear fusion begins (H into He). When outward pressure equals inward pressure the star enters the main sequence. ...
... gravitationally collapse, fragments,It heats up and spins faster. When the core temperature reaches 100 mill K, nuclear fusion begins (H into He). When outward pressure equals inward pressure the star enters the main sequence. ...
Chapter 25 - OG
... Every chemical element produces a unique pattern of dark lines ~ just like a finger print. ** Can also tell energy level Low energy: newer stars emit radio & infrared waves. Higher energy: exploding stars emit ultraviolet & x-rays. ...
... Every chemical element produces a unique pattern of dark lines ~ just like a finger print. ** Can also tell energy level Low energy: newer stars emit radio & infrared waves. Higher energy: exploding stars emit ultraviolet & x-rays. ...
Starry Night¨ Times - October 2008
... glowing hydrogen that stream across space for trillions of miles. Astronomers call M42 a stellar nursery; when you look at this giant gas cloud you are seeing what our own solar system might have looked like billions of years ago. The nebula's reddish coloration (visible only in photographs) betrays ...
... glowing hydrogen that stream across space for trillions of miles. Astronomers call M42 a stellar nursery; when you look at this giant gas cloud you are seeing what our own solar system might have looked like billions of years ago. The nebula's reddish coloration (visible only in photographs) betrays ...
here
... A7: It’s called a brown dwarf. Brown dwarfs do not reach high enough temperatures to burn hydrogen in their cores, instead they gain most of the energy that they radiate away by slow contraction, which liberates gravitational potential energy. However, they do burn deuterium in early phases. ...
... A7: It’s called a brown dwarf. Brown dwarfs do not reach high enough temperatures to burn hydrogen in their cores, instead they gain most of the energy that they radiate away by slow contraction, which liberates gravitational potential energy. However, they do burn deuterium in early phases. ...
STAR FORMATION (Ch. 19) - University of Texas Astronomy Home
... protostar, so glow mainly in the IR. All are seen associated with molecular clouds and their fragments. Can’t see the photosphere of the star itself, just the heated dust around them. Protostars—stars for which the dust has cleared enough for a direct view of their photospheres; they appear above th ...
... protostar, so glow mainly in the IR. All are seen associated with molecular clouds and their fragments. Can’t see the photosphere of the star itself, just the heated dust around them. Protostars—stars for which the dust has cleared enough for a direct view of their photospheres; they appear above th ...
What MSU Astronomers Will Do with the SOAR
... The History of our own Galaxy Star-by-star Archeology • Growth of galaxies by accretion • Chemical evolution • All elements heavier than H and He were formed by nuclear reactions in ...
... The History of our own Galaxy Star-by-star Archeology • Growth of galaxies by accretion • Chemical evolution • All elements heavier than H and He were formed by nuclear reactions in ...
4. Massive Stars and HII Regions
... if rare in numbers, have a profound impact on their environment. They are the fundamental producers of heavy elements, generate huge amounts of high energy radiation, trigger star formation. Their lifetime on the main sequence is rather short: ...
... if rare in numbers, have a profound impact on their environment. They are the fundamental producers of heavy elements, generate huge amounts of high energy radiation, trigger star formation. Their lifetime on the main sequence is rather short: ...
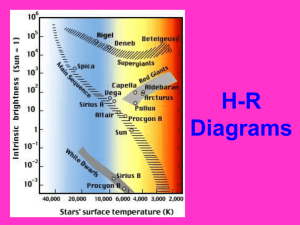
H-R Diagrams
... • Then it moves to upper right section when it changes to Giants/Supergiants. • It ends in the lower left section when it changes to a white dwarf ...
... • Then it moves to upper right section when it changes to Giants/Supergiants. • It ends in the lower left section when it changes to a white dwarf ...
LT 9: I can describe how a protostar becomes a star.
... – They are neutron stars formed in supernovas – They produce radio pulses because they rotate very rapidly ...
... – They are neutron stars formed in supernovas – They produce radio pulses because they rotate very rapidly ...
Stars and Sun
... The Sun is the closet star to Earth. Stars appear to move across the sky at night due to the rotation of Earth on its axis. Star patterns in the night sky change seasonally due to its revolution. ...
... The Sun is the closet star to Earth. Stars appear to move across the sky at night due to the rotation of Earth on its axis. Star patterns in the night sky change seasonally due to its revolution. ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What is the speed of light ? 186,000 MILES/SECOND What is the EMS and what are at its extremes ? RADIO WAVES ...
... What is the speed of light ? 186,000 MILES/SECOND What is the EMS and what are at its extremes ? RADIO WAVES ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... Heat and pressure begin to build until __________ __________ begins to take place. Inside the core, _____________ atoms smash together and are fused into heavier _____________ atoms. This process generates an enormous amount of ______________ and the star ignites becoming a _________ ______________ ...
... Heat and pressure begin to build until __________ __________ begins to take place. Inside the core, _____________ atoms smash together and are fused into heavier _____________ atoms. This process generates an enormous amount of ______________ and the star ignites becoming a _________ ______________ ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.