Unit 1
... • Dust particles do not absorb light the same way that gas atoms do, but using similar methods tells us that the dust is made of silicates ...
... • Dust particles do not absorb light the same way that gas atoms do, but using similar methods tells us that the dust is made of silicates ...
Energy Production in Stars
... In the special theory of relativity Einstein demonstrated that the total mass-energy was conserved => e = mc2 Speed of light squared is a very large number => small amount of mass corresponds to a huge amount of energy The conversion of mass to energy accounts for the enormous energy output of ...
... In the special theory of relativity Einstein demonstrated that the total mass-energy was conserved => e = mc2 Speed of light squared is a very large number => small amount of mass corresponds to a huge amount of energy The conversion of mass to energy accounts for the enormous energy output of ...
How stars form slide show File
... •Nebulae are huge clouds of gas and dust that are the birth place of new stars. •The gas in a nebula is nearly all hydrogen with a small amount of helium. •When light from nearby stars hits these atoms they emit beautiful colours that give nebulae their distinctive look. ...
... •Nebulae are huge clouds of gas and dust that are the birth place of new stars. •The gas in a nebula is nearly all hydrogen with a small amount of helium. •When light from nearby stars hits these atoms they emit beautiful colours that give nebulae their distinctive look. ...
White Dwarf star. Are
... Proxima Centauri is the closest star to our solar system. It is about 4 light years away. Going the speed of light it would take us 4 years to get there. Traveling as fast as the average spaceship, it would take between 70,000 and 100,000 years to get there! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ewGsiUPeB ...
... Proxima Centauri is the closest star to our solar system. It is about 4 light years away. Going the speed of light it would take us 4 years to get there. Traveling as fast as the average spaceship, it would take between 70,000 and 100,000 years to get there! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ewGsiUPeB ...
01-Introduction
... interacting physical, chemical and radiation processes (§1.5). This provides an essential background that permits observations of the interstellar medium and molecular clouds to be placed into perspective (§2.5). This leads to the classical theory of star formation in which the opposing forces of gr ...
... interacting physical, chemical and radiation processes (§1.5). This provides an essential background that permits observations of the interstellar medium and molecular clouds to be placed into perspective (§2.5). This leads to the classical theory of star formation in which the opposing forces of gr ...
Review Quiz No. 17
... The radius in the interior of a star where fusion processes can no longer take place. The point in time of a star’s life when nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium ceases. The point in time of a star’s life when nuclear fusion processes cease alltogether. The point in a rotating star cluster beyond ...
... The radius in the interior of a star where fusion processes can no longer take place. The point in time of a star’s life when nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium ceases. The point in time of a star’s life when nuclear fusion processes cease alltogether. The point in a rotating star cluster beyond ...
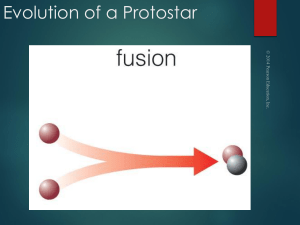
Evolution of a Protostar
... A protostar looks starlike after the surrounding gas is blown away, but its thermal energy comes from gravitational contraction, not fusion. ...
... A protostar looks starlike after the surrounding gas is blown away, but its thermal energy comes from gravitational contraction, not fusion. ...
Constellation
... pearls' surrounding an Exploding Star Two decades ago, astronomers spotted one of the brightest exploding stars in more than 400 years. This image shows the entire region around the supernova. The most prominent feature in the image is a ring with dozens of bright spots. A shock wave of material unl ...
... pearls' surrounding an Exploding Star Two decades ago, astronomers spotted one of the brightest exploding stars in more than 400 years. This image shows the entire region around the supernova. The most prominent feature in the image is a ring with dozens of bright spots. A shock wave of material unl ...
ASTR 200 : Lecture 15 Ensemble Properties of Stars
... • So, a large cloud (1000s to ~million solar masses) gets cold enough that many cores collapse into stars, giving a cluster • Each star clears gas disk away, but the cluster as a whole also blows out all the remaining interstellar gas, shutting down star formation • The stars settle onto the main se ...
... • So, a large cloud (1000s to ~million solar masses) gets cold enough that many cores collapse into stars, giving a cluster • Each star clears gas disk away, but the cluster as a whole also blows out all the remaining interstellar gas, shutting down star formation • The stars settle onto the main se ...
Parallax
... Astronomers measure the apparent shift in its position when viewed from two different angles Light Year ...
... Astronomers measure the apparent shift in its position when viewed from two different angles Light Year ...
protostars and pre-main
... • Gas falling onto the protostar heats the surface and radiates directly. This additional luminosity is called accretion luminosity Lacc ...
... • Gas falling onto the protostar heats the surface and radiates directly. This additional luminosity is called accretion luminosity Lacc ...
Unit 1
... • Low-mass stars create carbon and oxygen in their cores at the end of their lifespan, thanks to the higher temperatures and pressures present in a red giant star • High-mass stars produce heavier elements like silicon, magnesium, etc., by nuclear fusion in their cores – Temperatures are much higher ...
... • Low-mass stars create carbon and oxygen in their cores at the end of their lifespan, thanks to the higher temperatures and pressures present in a red giant star • High-mass stars produce heavier elements like silicon, magnesium, etc., by nuclear fusion in their cores – Temperatures are much higher ...
Objects Beyond our Solar System
... it would have a mass of millions of kilograms. These stars are very small, just a few km across but they still have a mass that is as great as the sun. The gravity of these stars are incredible; if you dropped a marshmallow onto the surface of a neutron star it would have as much energy as a nuc ...
... it would have a mass of millions of kilograms. These stars are very small, just a few km across but they still have a mass that is as great as the sun. The gravity of these stars are incredible; if you dropped a marshmallow onto the surface of a neutron star it would have as much energy as a nuc ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... A supermassive black hole (SMBH) is the largest type of black hole, on the order of hundreds of thousands to billions of solar masses. Most—and possibly all—galaxies are inferred to contain a supermassive black hole at their centers. In the case of the Milky Way, the SMBH is believed to correspond w ...
... A supermassive black hole (SMBH) is the largest type of black hole, on the order of hundreds of thousands to billions of solar masses. Most—and possibly all—galaxies are inferred to contain a supermassive black hole at their centers. In the case of the Milky Way, the SMBH is believed to correspond w ...
Name ______KEY Date Core ______ Study Guide Galaxies and the
... When did the Big Bang happen and what has happened since? The big bang theory is theorized to have happened 14 billion years ago when the universe suddenly began to expand from one merged mass of matter or substance. At that time, all matter was dense and hot and the universe developed in less than ...
... When did the Big Bang happen and what has happened since? The big bang theory is theorized to have happened 14 billion years ago when the universe suddenly began to expand from one merged mass of matter or substance. At that time, all matter was dense and hot and the universe developed in less than ...
The Stars
... The Stars Stars vary greatly in size, brightness, temperature, and colour. Here are some of the things we have learned about the properties of stars. Measuring distance Just as with the kilometre, the AU is not very useful when we start to study stuff outside of our Solar System. A much larger unit ...
... The Stars Stars vary greatly in size, brightness, temperature, and colour. Here are some of the things we have learned about the properties of stars. Measuring distance Just as with the kilometre, the AU is not very useful when we start to study stuff outside of our Solar System. A much larger unit ...
Class 2 Solar System Characteristics Formation Exosolar Planets
... This indicates that one or more supernovae occurred near the Sun while it was forming. Spitzer reveals infrared radiation coming from dust particles heated by the supernova's shock wave. ...
... This indicates that one or more supernovae occurred near the Sun while it was forming. Spitzer reveals infrared radiation coming from dust particles heated by the supernova's shock wave. ...
the lab handout here
... How does the temperature and luminosity of the Sun compare to that of the other stars on the Main Sequence? ________________________________________________________ ...
... How does the temperature and luminosity of the Sun compare to that of the other stars on the Main Sequence? ________________________________________________________ ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.