The Milky Way
... In a binary system, each star controls a finite region of space, bounded by the Roche Lobes (or Roche surfaces). ...
... In a binary system, each star controls a finite region of space, bounded by the Roche Lobes (or Roche surfaces). ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... massive they collapse into an object called a black hole • Light can not escape a black holes gravity because it is so massive • They are only detected through x-rays that can determine a black hole through materials from stars filtering ...
... massive they collapse into an object called a black hole • Light can not escape a black holes gravity because it is so massive • They are only detected through x-rays that can determine a black hole through materials from stars filtering ...
Earth has formed in our solar system
... because of cooling • Hence location is important for planetary composition (planets closer to the sun should be more refractory) • Interaction of large body at final stages could change composition considerably ...
... because of cooling • Hence location is important for planetary composition (planets closer to the sun should be more refractory) • Interaction of large body at final stages could change composition considerably ...
Nature template
... the probability distribution of systems with no stars having initial masses greater than 130 M versus the mass of the upper mass cutoff. The simulation uses 60,000 systems, each with test points having a mass distribution that follows a single power law initial mass function truncated at the cutoff ...
... the probability distribution of systems with no stars having initial masses greater than 130 M versus the mass of the upper mass cutoff. The simulation uses 60,000 systems, each with test points having a mass distribution that follows a single power law initial mass function truncated at the cutoff ...
WHERE DO WE SEARCH FOR LIFE IN THE UNIVERSE?
... Sun avoids spiral arms Sun has nearly circular orbit around galaxy Sun has a “synchronized” rotation with spiral arm ...
... Sun avoids spiral arms Sun has nearly circular orbit around galaxy Sun has a “synchronized” rotation with spiral arm ...
大爆炸---宇宙的起源
... hydrogen to fuse, the core of the star begins to collapse until the central temperature rises to ~100×106 K. At this point helium nuclei are fusing together at a rate high enough to rival the rate at which their product, beryllium-8, decays back into two helium nuclei. This means that there are alwa ...
... hydrogen to fuse, the core of the star begins to collapse until the central temperature rises to ~100×106 K. At this point helium nuclei are fusing together at a rate high enough to rival the rate at which their product, beryllium-8, decays back into two helium nuclei. This means that there are alwa ...
PowerPoint - Earth Science with Mrs. Wilson
... In the night sky, a band of stars can be seen across the sky as a blurry image. When you see this, you are looking into the part of the galaxy with more stars. ...
... In the night sky, a band of stars can be seen across the sky as a blurry image. When you see this, you are looking into the part of the galaxy with more stars. ...
Chapter 13: The Death of Stars
... In a binary system, each star controls a finite region of space, bounded by the Roche Lobes (or Roche surfaces). ...
... In a binary system, each star controls a finite region of space, bounded by the Roche Lobes (or Roche surfaces). ...
RFS_315_answers
... mass of a star the shorter it’s lifetime as it’s fuel is used much faster. Algol B is a dying K giant star but at only .81 solar masses, it is the LESS massive of the two. The dim companion has lost a great deal of mass to it’s closely orbiting partner. 15. Polaris is a variable star – what type of ...
... mass of a star the shorter it’s lifetime as it’s fuel is used much faster. Algol B is a dying K giant star but at only .81 solar masses, it is the LESS massive of the two. The dim companion has lost a great deal of mass to it’s closely orbiting partner. 15. Polaris is a variable star – what type of ...
Stars - Robert M. Hazen
... Stars have a history – a beginning and an end 1. Stars (and planets) begin as clouds of dust and gas, called nebulae. 2. Stars radiate heat and light, which come from the energy of nuclear fusion reactions. 3. Planets form like stars, but they are too small to begin nuclear fusion reactions. ...
... Stars have a history – a beginning and an end 1. Stars (and planets) begin as clouds of dust and gas, called nebulae. 2. Stars radiate heat and light, which come from the energy of nuclear fusion reactions. 3. Planets form like stars, but they are too small to begin nuclear fusion reactions. ...
ASTR 1020 – Spring 2017 – Prof. Magnani Answer Key – Homework 5
... molecules or ions), one of the colliding partners loses some kinetic energy and the other picks it up. However, the gain in energy could be kinetic or it could go into exciting one of the electrons of this particle to a higher energy state (there are other excitation channels, but we will ignore the ...
... molecules or ions), one of the colliding partners loses some kinetic energy and the other picks it up. However, the gain in energy could be kinetic or it could go into exciting one of the electrons of this particle to a higher energy state (there are other excitation channels, but we will ignore the ...
Homework #3 10 points Question #1 (2 pts) The brightest star in the
... found several white dwarfs that all exploded as thermonuclear supernovae. The number of white dwarfs in the region B is such that in both regions, A and B, exactly the same amounts of carbon and oxygen are produced. In which region, A or B, will there be more iron produced? In a core collapse supern ...
... found several white dwarfs that all exploded as thermonuclear supernovae. The number of white dwarfs in the region B is such that in both regions, A and B, exactly the same amounts of carbon and oxygen are produced. In which region, A or B, will there be more iron produced? In a core collapse supern ...
Lecture 13 - Main Sequence Stars
... • We have been focusing on the properties of stars on the main sequence, but the chemical composition of stars change with time as the star burns hydrogen into helium. • This causes the other properties to change with time and we can track these changes via motion of the star in the HR diagram. ...
... • We have been focusing on the properties of stars on the main sequence, but the chemical composition of stars change with time as the star burns hydrogen into helium. • This causes the other properties to change with time and we can track these changes via motion of the star in the HR diagram. ...
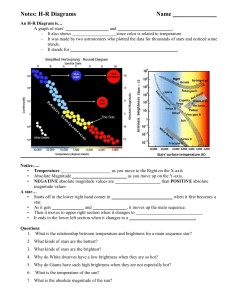
H-R Diagram Notes
... • Temperature ______________________ as you move to the Right on the X-axis • Absolute Magnitude ________________________ as you move up on the Y-axis. • NEGATIVE absolute magnitude values are ____________________ than POSITIVE absolute magnitude values A star… • Starts off in the lower right hand c ...
... • Temperature ______________________ as you move to the Right on the X-axis • Absolute Magnitude ________________________ as you move up on the Y-axis. • NEGATIVE absolute magnitude values are ____________________ than POSITIVE absolute magnitude values A star… • Starts off in the lower right hand c ...
4.1 – 4.3 - s3.amazonaws.com
... –large clouds of gas and dust floating in space –They are most common in spiral and irregular galaxies –horse head nebula is one of the most widely known nebulae ...
... –large clouds of gas and dust floating in space –They are most common in spiral and irregular galaxies –horse head nebula is one of the most widely known nebulae ...
Chapter 19 Notes Stars Stars are bright balls of gas that are trillions
... i. While many stars become white dwarves as they get older, very massive stars can become strange objects like pulsars, supernovas, black holes and neutron stars. ii. Supernovas 1. Massive stars use their hydrogen much faster than stars like the sun do. 2. At the end of their lives they may explode ...
... i. While many stars become white dwarves as they get older, very massive stars can become strange objects like pulsars, supernovas, black holes and neutron stars. ii. Supernovas 1. Massive stars use their hydrogen much faster than stars like the sun do. 2. At the end of their lives they may explode ...
powerpoint version
... Now have a mass-luminosity diagram for Main Sequence stars. This tells us that the heavier they are, the greater is their energy output rate i.e. Luminosity (mass mass mass mass) but Total energy available mass Therefore, low mass stars live longer. ...
... Now have a mass-luminosity diagram for Main Sequence stars. This tells us that the heavier they are, the greater is their energy output rate i.e. Luminosity (mass mass mass mass) but Total energy available mass Therefore, low mass stars live longer. ...
Red Giants - Uplift North Hills Prep
... as gravity caused the collapse Stars are formed by a cloud of gas and dust that collapsed inward and began to spin. These clouds are called nebula. About 30 million years after the cloud collapsed, its center has reached 15 million kelvin and has become a protostar. As stars continue to go through n ...
... as gravity caused the collapse Stars are formed by a cloud of gas and dust that collapsed inward and began to spin. These clouds are called nebula. About 30 million years after the cloud collapsed, its center has reached 15 million kelvin and has become a protostar. As stars continue to go through n ...
What is a Star? - Lisle CUSD 202
... are called protostars. Sometimes these dense areas block starlight from shining through, they look like dark spots The Nebula to the left is called the horsehead nebula, it can be found in Orion ...
... are called protostars. Sometimes these dense areas block starlight from shining through, they look like dark spots The Nebula to the left is called the horsehead nebula, it can be found in Orion ...
Slide 1
... as gravity caused the collapse Stars are formed by a cloud of gas and dust that collapsed inward and began to spin. These clouds are called nebula. About 30 million years after the cloud collapsed, its center has reached 15 million kelvin and has become a protostar. As stars continue to go through n ...
... as gravity caused the collapse Stars are formed by a cloud of gas and dust that collapsed inward and began to spin. These clouds are called nebula. About 30 million years after the cloud collapsed, its center has reached 15 million kelvin and has become a protostar. As stars continue to go through n ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.