Lesson Planner Beyond our solar system.indd
... The Universe comprises billions of billions of stars, many of which are orbited by groups of planets in the same way that Earth and seven other planets orbit a star (the Sun). These systems of stars and planets group together to form galaxies. Our galaxy, which contains at least 100 billion stars, i ...
... The Universe comprises billions of billions of stars, many of which are orbited by groups of planets in the same way that Earth and seven other planets orbit a star (the Sun). These systems of stars and planets group together to form galaxies. Our galaxy, which contains at least 100 billion stars, i ...
31 October: Supernovae and Neutron Stars
... Formation of a neutron star from stellar core • As core collapses, matter becomes compressed • Electrons and protons forced together e+p > n + nu (neutronization) • Core of the becomes a neutron fluid • Neutronization produces a burst of neutrinos • Neutron fluid in core becomes degenerate and rigi ...
... Formation of a neutron star from stellar core • As core collapses, matter becomes compressed • Electrons and protons forced together e+p > n + nu (neutronization) • Core of the becomes a neutron fluid • Neutronization produces a burst of neutrinos • Neutron fluid in core becomes degenerate and rigi ...
AGN Workshop
... Compton thick sources---still guessing Reflection component---still uncertain Does obscuration depend on luminosity or Eddington ratio? Future surveys will figure this out? Are these intrinsically different from unobscured sources? What is clustering of Ryan/Dan’s objects compared to Adam/Alison/Nik ...
... Compton thick sources---still guessing Reflection component---still uncertain Does obscuration depend on luminosity or Eddington ratio? Future surveys will figure this out? Are these intrinsically different from unobscured sources? What is clustering of Ryan/Dan’s objects compared to Adam/Alison/Nik ...
Major Themes of “ The First Stars ”
... major implications for observable features of galaxies by JWST. 4. A new synthesis of theory is being developed to take advantage of this wealth of data, and connect it explicitly to high-z, as a perfect partner and complement to JWST. In the JWST era, we can test and extend these models to uncover ...
... major implications for observable features of galaxies by JWST. 4. A new synthesis of theory is being developed to take advantage of this wealth of data, and connect it explicitly to high-z, as a perfect partner and complement to JWST. In the JWST era, we can test and extend these models to uncover ...
Document
... • Can’t see black hole itself, but can see matter falling into a hole. • Gravitational forces stretch and rip matter: heats up. • Very hot objects emit in Xrays (interior of Sun) • Cygnus X-1. http://www.owlnet.rice.edu/~spac250/steve/ident.html ...
... • Can’t see black hole itself, but can see matter falling into a hole. • Gravitational forces stretch and rip matter: heats up. • Very hot objects emit in Xrays (interior of Sun) • Cygnus X-1. http://www.owlnet.rice.edu/~spac250/steve/ident.html ...
Black Holes and Neutron Stars
... • Can’t see black hole itself, but can see matter falling into a hole. • Gravitational forces stretch and rip matter: heats up. • Very hot objects emit in Xrays (interior of Sun) • Cygnus X-1. http://www.owlnet.rice.edu/~spac250/steve/ident.html ...
... • Can’t see black hole itself, but can see matter falling into a hole. • Gravitational forces stretch and rip matter: heats up. • Very hot objects emit in Xrays (interior of Sun) • Cygnus X-1. http://www.owlnet.rice.edu/~spac250/steve/ident.html ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy - University of Texas Astronomy
... The flux of a star is the power in the light from that star that would hit a 1 m2 area facing the star. To measure a star’s flux, we use a telescope to collect light from the star, measure the power in the light we collect, and the divide the power by the collecting area of the telescope. (A bigger ...
... The flux of a star is the power in the light from that star that would hit a 1 m2 area facing the star. To measure a star’s flux, we use a telescope to collect light from the star, measure the power in the light we collect, and the divide the power by the collecting area of the telescope. (A bigger ...
Beyond the Solar System Homework for Geology 8
... 49. Degenerate matter is highly condensed material, where even the electrons of atoms are pushed in, towards the center or nucleus of the atoms. 50. Pulsars are a type of neutron star that spins rapidly and emits pulsating radio waves. 51. A star’s color is based upon the temperature of the star’s s ...
... 49. Degenerate matter is highly condensed material, where even the electrons of atoms are pushed in, towards the center or nucleus of the atoms. 50. Pulsars are a type of neutron star that spins rapidly and emits pulsating radio waves. 51. A star’s color is based upon the temperature of the star’s s ...
The amazing lives of two stars
... than 1 percent -- is transformed into energy, according to Albert Einstein's famous equation E=mc2. It is this radiation that makes its way through the star eventually to escape, bathing its surroundings in heat and light. PHASE I: A vast compression wave moves through a galaxy. Spiral shaped, the w ...
... than 1 percent -- is transformed into energy, according to Albert Einstein's famous equation E=mc2. It is this radiation that makes its way through the star eventually to escape, bathing its surroundings in heat and light. PHASE I: A vast compression wave moves through a galaxy. Spiral shaped, the w ...
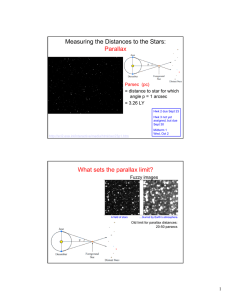
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... Hipparcos (1989-1993): 100-200 parsecs (1σ =1 milliarcsec = 1kpc) ...
... Hipparcos (1989-1993): 100-200 parsecs (1σ =1 milliarcsec = 1kpc) ...
Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars
... • What is a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram? • What is the significance of the main sequence? • What are giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs? • Why do the properties of some stars vary? ...
... • What is a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram? • What is the significance of the main sequence? • What are giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs? • Why do the properties of some stars vary? ...
Lecture17
... (from hottest to coldest). All stars have spectra lines or “gaps” in their continuous spectrum, just like the sun, but the lines differ, and depend on how hot the star is. Recently cool stellar types “L” and “T” were added, down to 700K at their surface! ...
... (from hottest to coldest). All stars have spectra lines or “gaps” in their continuous spectrum, just like the sun, but the lines differ, and depend on how hot the star is. Recently cool stellar types “L” and “T” were added, down to 700K at their surface! ...
Supernova
... • When gravitational force exceeds the electron repulsion, the core collapses immediately. – Energy in photons and neutrinos ...
... • When gravitational force exceeds the electron repulsion, the core collapses immediately. – Energy in photons and neutrinos ...
Chapter 15: The Deaths of Massive Stars
... 2. GRBs last from 0.01 second to tens of minutes, and a few GRBs are observed each day. For a short time period, some GRBs become the brightest objects in the gamma-ray sky. 3. The first observation that confirmed that GRBs are very distant and therefore very energetic was made by Beppo-SAX in 1997. ...
... 2. GRBs last from 0.01 second to tens of minutes, and a few GRBs are observed each day. For a short time period, some GRBs become the brightest objects in the gamma-ray sky. 3. The first observation that confirmed that GRBs are very distant and therefore very energetic was made by Beppo-SAX in 1997. ...
Exam 3 Solution Set - Indiana University Astronomy
... and assume ρ = 1.3 gm cm-3 The value of the mean molecular weight depends on whether the hydrogen is ionized. If not, µ = 1; if so µ = 0.5. Calculate Tc assuming one or the other, and then decide. Or, you could remember that Jupiter might have a metallic hydrogen core, which would not be ionized…. T ...
... and assume ρ = 1.3 gm cm-3 The value of the mean molecular weight depends on whether the hydrogen is ionized. If not, µ = 1; if so µ = 0.5. Calculate Tc assuming one or the other, and then decide. Or, you could remember that Jupiter might have a metallic hydrogen core, which would not be ionized…. T ...
doc - IAC
... stars, an example being the Orion Nebula. Reflection nebulae (clouds that shine by light reflected from a star), for example the Pleiades Cluster, appear blue because their light is scattered by particles of dust. Absorption, or dark, nebulae, such as the Horsehead Nebula in Orion, are clouds of coo ...
... stars, an example being the Orion Nebula. Reflection nebulae (clouds that shine by light reflected from a star), for example the Pleiades Cluster, appear blue because their light is scattered by particles of dust. Absorption, or dark, nebulae, such as the Horsehead Nebula in Orion, are clouds of coo ...
Revolutionary Times: Copernicus and Tycho Brahe
... 1. Raise or lower the movable stick to point it at each star in turn as it passes through the meridian. Differences in this ‘up-down’ sense tells you which stars are farther North or South in the sky. 2. Use a clock. If Star A passes through the meridian before Star B, then Star A is to the West of ...
... 1. Raise or lower the movable stick to point it at each star in turn as it passes through the meridian. Differences in this ‘up-down’ sense tells you which stars are farther North or South in the sky. 2. Use a clock. If Star A passes through the meridian before Star B, then Star A is to the West of ...
P1 The Earth in the Universe
... Fossils in the layers show which species lived when. Many species have become extinct. Cross-cutting features- if one type of rock cuts across another rock type, it is younger e.g. hot magma can fill cracks in existing rocks and solidify as new rock. These clues only tell us which rocks are older th ...
... Fossils in the layers show which species lived when. Many species have become extinct. Cross-cutting features- if one type of rock cuts across another rock type, it is younger e.g. hot magma can fill cracks in existing rocks and solidify as new rock. These clues only tell us which rocks are older th ...
Notes
... Degenerate carbon-oxygen core, He- and H-burning shells, thin H layer, shrouded in dust from superwind (proto-planetary nebula) Mass loss rate decreases but wind speed increases Hydrogen layer thins further from mass loss and He burning shell Star evolves at constant luminosity (~104LSun), shrinking ...
... Degenerate carbon-oxygen core, He- and H-burning shells, thin H layer, shrouded in dust from superwind (proto-planetary nebula) Mass loss rate decreases but wind speed increases Hydrogen layer thins further from mass loss and He burning shell Star evolves at constant luminosity (~104LSun), shrinking ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.