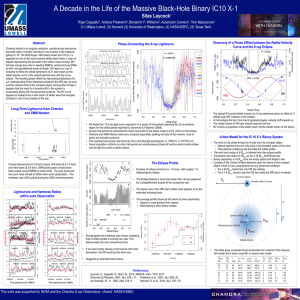
A Decade in the Life of the Massive Black-Hole Binary... Silas Laycock !
... galaxy IC 10. The Wolf Rayet + BH binary known as IC10 X-1 is regarded as one of the most massive stellar black holes; a class of objects representing the pinnacle of the stellar mass function. BH binaries occupy key roles in seeding SMBHs, producing long GRBs at birth, and gravitational waves at de ...
... galaxy IC 10. The Wolf Rayet + BH binary known as IC10 X-1 is regarded as one of the most massive stellar black holes; a class of objects representing the pinnacle of the stellar mass function. BH binaries occupy key roles in seeding SMBHs, producing long GRBs at birth, and gravitational waves at de ...
Oct 06, 2001
... 16) How does the Sun produce the energy that heats our planet? A) The gases inside the Sun are burning and producing large amounts of energy. B) Hydrogen is combined into helium, giving off large amounts of energy. C) Gas inside the Sun heats up when compressed, giving off large amounts of energy. D ...
... 16) How does the Sun produce the energy that heats our planet? A) The gases inside the Sun are burning and producing large amounts of energy. B) Hydrogen is combined into helium, giving off large amounts of energy. C) Gas inside the Sun heats up when compressed, giving off large amounts of energy. D ...
The Milky Way
... Orbits of stars in the Milky Way • The orbit of a star is determined by the total mass lying inside the orbit • By measuring the speed of the star’s orbit and its distance from the center, we can figure out the total mass lying inside the orbit of the star ...
... Orbits of stars in the Milky Way • The orbit of a star is determined by the total mass lying inside the orbit • By measuring the speed of the star’s orbit and its distance from the center, we can figure out the total mass lying inside the orbit of the star ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Mullard Space Science Laboratory
... phase transition might occur in the dense interiors of neutron stars [1,2]. At temperatures T ~ 0 - 40 MeV, there are two possibilities for phase transitions (see the QGP diagram showing quantum chromodynamics (QCD) phases in Figure 1). As density increases, hadronic matter first converts into QGP, ...
... phase transition might occur in the dense interiors of neutron stars [1,2]. At temperatures T ~ 0 - 40 MeV, there are two possibilities for phase transitions (see the QGP diagram showing quantum chromodynamics (QCD) phases in Figure 1). As density increases, hadronic matter first converts into QGP, ...
Astronomy Study Guide
... Composition—73% hydrogen, 25% helium, 2% other Brightness— apparent brightness—very bright absolute brightness—average brightness ...
... Composition—73% hydrogen, 25% helium, 2% other Brightness— apparent brightness—very bright absolute brightness—average brightness ...
public_lector_10
... The black hole itself is invisible, but we can measure its gravitational effect on nearby stars. Turbulence in the earth’s atmosphere blurs out any details smaller than about 0.5 arcsec (0.25 mm at 100 m). To see stars close enough to the black hole (0.1 arcsec), adaptive optics are needed to corre ...
... The black hole itself is invisible, but we can measure its gravitational effect on nearby stars. Turbulence in the earth’s atmosphere blurs out any details smaller than about 0.5 arcsec (0.25 mm at 100 m). To see stars close enough to the black hole (0.1 arcsec), adaptive optics are needed to corre ...
stargazing - davis.k12.ut.us
... heroines and beasts of their time and culture. Since those ancient times, people have continued to make up stories, develop religious practices and grow crops based on groups of stars. Groups of stars are called constellations, patterns of stars in the sky that have been identified and named. Some c ...
... heroines and beasts of their time and culture. Since those ancient times, people have continued to make up stories, develop religious practices and grow crops based on groups of stars. Groups of stars are called constellations, patterns of stars in the sky that have been identified and named. Some c ...
Iron does not burn.
... in the ground state. The electron moving around the proton can have a spin in the same direction as the proton's spin (i.e., parallel) or spin in the direct opposite direction as the proton's spin (i.e., anti-parallel). The energy state of an electron spinning anti-parallel is slightly lower than th ...
... in the ground state. The electron moving around the proton can have a spin in the same direction as the proton's spin (i.e., parallel) or spin in the direct opposite direction as the proton's spin (i.e., anti-parallel). The energy state of an electron spinning anti-parallel is slightly lower than th ...
two dozen compact sources and a massive disk
... • Massive stars tend to be at center (Kirk & Myers 2011) • Primordial or dynamical evolution? ~1 free-fall time • Correlation between mass of most massive star and number of cluster members (Testi+ 1999) • Do low and high mass stars form at same time? If we can examine clusters at an earlier stage o ...
... • Massive stars tend to be at center (Kirk & Myers 2011) • Primordial or dynamical evolution? ~1 free-fall time • Correlation between mass of most massive star and number of cluster members (Testi+ 1999) • Do low and high mass stars form at same time? If we can examine clusters at an earlier stage o ...
Protogalaxies Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics eaa.iop.org S G Djorgovski
... or formation histories at work. The interplay of mass assembly and star formation fundamentally determines the galaxy morphology and the origin of disks in SPIRAL GALAXIES. In general, random merging of fragments leads to the formation of spheroidal (or, more accurately, triaxial) systems such as th ...
... or formation histories at work. The interplay of mass assembly and star formation fundamentally determines the galaxy morphology and the origin of disks in SPIRAL GALAXIES. In general, random merging of fragments leads to the formation of spheroidal (or, more accurately, triaxial) systems such as th ...
Basics of chemical evolution
... Chemical evolution • The metal abundance of the gas, and of subsequent generations of stars, should increase in time. – if there is no gas infall from the outside ...
... Chemical evolution • The metal abundance of the gas, and of subsequent generations of stars, should increase in time. – if there is no gas infall from the outside ...
Origin of Our Solar System
... All planets revolve around the Sun in a counterclockwise direction within a 7° band of the equatorial region of the Sun, and nearly all of them also turn on their individual axes in a counterclockwise direction as well. ...
... All planets revolve around the Sun in a counterclockwise direction within a 7° band of the equatorial region of the Sun, and nearly all of them also turn on their individual axes in a counterclockwise direction as well. ...
Lots of free resources!
... Accessible Astronomy Resources “The International Astronomical Union (IAU) has recognized the potential of astronomy to contribute to education and creating a better world. To fulfill this potential, however, astronomy must be accessible to everyone, regardless of background, learning styles or abil ...
... Accessible Astronomy Resources “The International Astronomical Union (IAU) has recognized the potential of astronomy to contribute to education and creating a better world. To fulfill this potential, however, astronomy must be accessible to everyone, regardless of background, learning styles or abil ...
Black holes - Red Hook Central School District
... get no more heat or light from it, but our elliptical orbit would not change. 2. We would not be “sucked in” 3. Spaceships near a black hole would merely go into orbit around it 4. Black Holes are so small it would be hard to “fall in” by accident ...
... get no more heat or light from it, but our elliptical orbit would not change. 2. We would not be “sucked in” 3. Spaceships near a black hole would merely go into orbit around it 4. Black Holes are so small it would be hard to “fall in” by accident ...
Introduc on to the Fundamental Astrophysics Course
... remainder mostly helium. • This gas appears primarily in two forms: – cold clouds of atomic or molecular hydrogen – Hot ionized hydrogen near hot young stars ...
... remainder mostly helium. • This gas appears primarily in two forms: – cold clouds of atomic or molecular hydrogen – Hot ionized hydrogen near hot young stars ...
History of the universe timeline
... from our tiny, home planet, Earth. The visible Universe contains billions of galaxies, each comprising billions of stars. Within our own Galaxy, hundreds of exoplanets have been discovered orbiting other stars. ...
... from our tiny, home planet, Earth. The visible Universe contains billions of galaxies, each comprising billions of stars. Within our own Galaxy, hundreds of exoplanets have been discovered orbiting other stars. ...
Week 3: Kepler`s Laws, Light and Matter
... types of spectra we can learn from. Emission spectrum is produced when we observe a low density warm gas cloud. In this warm gas collision are frequent to move electrons to higher energy levels and the electrons emit photons when they come down. Absorption spectrum is produced when we observe a cold ...
... types of spectra we can learn from. Emission spectrum is produced when we observe a low density warm gas cloud. In this warm gas collision are frequent to move electrons to higher energy levels and the electrons emit photons when they come down. Absorption spectrum is produced when we observe a cold ...
THE INCREDIBLE ORIGIN OF THE CHEMICAL ELEMENTS
... is used up the outward flow of radiation dies down and can no longer prevent the outer parts of the star from falling in towards the centre. The star shrinks in on itself, but in doing so it heats up further, to the point where helium nuclei can overcome their mutual repulsion arising from their cha ...
... is used up the outward flow of radiation dies down and can no longer prevent the outer parts of the star from falling in towards the centre. The star shrinks in on itself, but in doing so it heats up further, to the point where helium nuclei can overcome their mutual repulsion arising from their cha ...
Protogalaxies
... or formation histories at work. The interplay of mass assembly and star formation fundamentally determines the galaxy morphology and the origin of disks in SPIRAL GALAXIES. In general, random merging of fragments leads to the formation of spheroidal (or, more accurately, triaxial) systems such as th ...
... or formation histories at work. The interplay of mass assembly and star formation fundamentally determines the galaxy morphology and the origin of disks in SPIRAL GALAXIES. In general, random merging of fragments leads to the formation of spheroidal (or, more accurately, triaxial) systems such as th ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.