What evidence exists to support the Theory that an Asteroid Impact
... Biomass is renewable/does not increase surface carbon levels. Biomass still releases carbon dioxide ...
... Biomass is renewable/does not increase surface carbon levels. Biomass still releases carbon dioxide ...
What is a Star? - Yale Astronomy
... 1. gravity (dominant force on large scales in universe) 2. electromagnetism (underlies gas pressure) 3. strong nuclear force (binds nucleons n,p together) 4. weak nuclear force (responsible for radioactive decay of nuclei) ...
... 1. gravity (dominant force on large scales in universe) 2. electromagnetism (underlies gas pressure) 3. strong nuclear force (binds nucleons n,p together) 4. weak nuclear force (responsible for radioactive decay of nuclei) ...
Astronomy and Space Science
... – the distance the of the light source from the observer (inverse square law) • E.g., if a 6th magnitude star located 100 pc from the Earth were moved to 10 pc from us, it would appear 100 times brighter, and become a 1st magnitude star. • To compare the luminosity between different stars, the absol ...
... – the distance the of the light source from the observer (inverse square law) • E.g., if a 6th magnitude star located 100 pc from the Earth were moved to 10 pc from us, it would appear 100 times brighter, and become a 1st magnitude star. • To compare the luminosity between different stars, the absol ...
Document
... How to measure the distance to a galaxy using RR Lyrae variable stars: 1. Find the RR Lyrae by magnitude curve 2. Measure its apparent magnitude. 3. They all have about the same absolute magnitude (0 < M < 1) 4. Use M = m - 5 log10(d/10) to find d ...
... How to measure the distance to a galaxy using RR Lyrae variable stars: 1. Find the RR Lyrae by magnitude curve 2. Measure its apparent magnitude. 3. They all have about the same absolute magnitude (0 < M < 1) 4. Use M = m - 5 log10(d/10) to find d ...
Chapter 4 Galactic Chemical Evolution
... The material we find around us in the Universe today contains significant quantities of heavy elements, although these are still only minor contributors to the total mass of baryonic matter (most is hydrogen). These heavy elements have been synthesised in nuclear reactions in stars, a process known ...
... The material we find around us in the Universe today contains significant quantities of heavy elements, although these are still only minor contributors to the total mass of baryonic matter (most is hydrogen). These heavy elements have been synthesised in nuclear reactions in stars, a process known ...
The evolution of helium rich subdwarf B stars
... • Subdwarf B stars form the dominant population of faint blue blue stars (mB ~ 16) in our galaxy and giant elliptical galaxies • They are 0.5 MSun core helium-burning stars • Progenitors of White Dwarfs • Evolution has been the subject of much debate although evolution is though to play an important ...
... • Subdwarf B stars form the dominant population of faint blue blue stars (mB ~ 16) in our galaxy and giant elliptical galaxies • They are 0.5 MSun core helium-burning stars • Progenitors of White Dwarfs • Evolution has been the subject of much debate although evolution is though to play an important ...
Sirius Astronomer - Orange County Astronomers
... Supernovae are brilliant explosions at the end of the life of massive stars. They give off so much light, that they can outshine all the light of all the other stars in a galaxy. The forces within them are powerful enough to form new elements (in fact, almost all of the elements with a mass greater ...
... Supernovae are brilliant explosions at the end of the life of massive stars. They give off so much light, that they can outshine all the light of all the other stars in a galaxy. The forces within them are powerful enough to form new elements (in fact, almost all of the elements with a mass greater ...
Expected Coalescence Rates of NS/NS Binaries for Ground Based
... NS : fraction of massive binaries that remain bounded after the second supernova P( ): probability for a newly formed NS/NS to coalesce in a timescale 0 : minimum coalescence time * : mean timescale required for the newly formed massive system to evolve into two NSs ...
... NS : fraction of massive binaries that remain bounded after the second supernova P( ): probability for a newly formed NS/NS to coalesce in a timescale 0 : minimum coalescence time * : mean timescale required for the newly formed massive system to evolve into two NSs ...
Charting The Universe - University of Windsor
... • Ancient Calendars: for religious festivals and agriculture. (Geocentric model) • There are 88 constellations. (Most are seen in Windsor at some part of the year.) • Still useful for depicting regions of the sky. • Note: the stars are not close to each other…they just appear to be! ...
... • Ancient Calendars: for religious festivals and agriculture. (Geocentric model) • There are 88 constellations. (Most are seen in Windsor at some part of the year.) • Still useful for depicting regions of the sky. • Note: the stars are not close to each other…they just appear to be! ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412 - Queen's University Belfast
... As they are not time dependent, we must iterate with the calculation of changing chemical composition to determine short steps in the lifetime of stars. The crucial changing parameter is the H/He content of the stellar core (and afterwards, He burning will become important – to be explored in next l ...
... As they are not time dependent, we must iterate with the calculation of changing chemical composition to determine short steps in the lifetime of stars. The crucial changing parameter is the H/He content of the stellar core (and afterwards, He burning will become important – to be explored in next l ...
r - QUB Astrophysics Research Centre
... As they are not time dependent, we must iterate with the calculation of changing chemical composition to determine short steps in the lifetime of stars. The crucial changing parameter is the H/He content of the stellar core (and afterwards, He burning will become important – to be explored in next l ...
... As they are not time dependent, we must iterate with the calculation of changing chemical composition to determine short steps in the lifetime of stars. The crucial changing parameter is the H/He content of the stellar core (and afterwards, He burning will become important – to be explored in next l ...
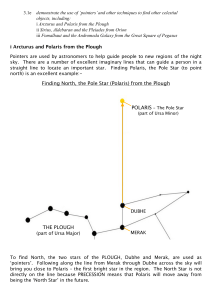
3.1e Finding Polaris and Sirius
... Star hopping is used to find the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). If you live where you have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Squar ...
... Star hopping is used to find the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). If you live where you have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Squar ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.