
Constituents of the Milky Way
... Measuring Ages of Individual Stars For individual stars that aren’t in clusters (like the Sun), we can’t use the cluster turnoff method to measure an age. For instance, a lone G star might be young, or it might be 10 billion years old. How do we measure its age? The universe contained only hydrogen ...
... Measuring Ages of Individual Stars For individual stars that aren’t in clusters (like the Sun), we can’t use the cluster turnoff method to measure an age. For instance, a lone G star might be young, or it might be 10 billion years old. How do we measure its age? The universe contained only hydrogen ...
Asteroseismology of white dwarf stars provides important constraints
... its importance to both asteroseismology and our understanding of convection across the DAV instability strip. R808 was discovered to be a pulsating DA white dwarf in 1976 (McGraw & Robinson 1976). It is a large amplitude, multiperiodic pulsator with an extremely nonlinear light curve (Figure 1), mak ...
... its importance to both asteroseismology and our understanding of convection across the DAV instability strip. R808 was discovered to be a pulsating DA white dwarf in 1976 (McGraw & Robinson 1976). It is a large amplitude, multiperiodic pulsator with an extremely nonlinear light curve (Figure 1), mak ...
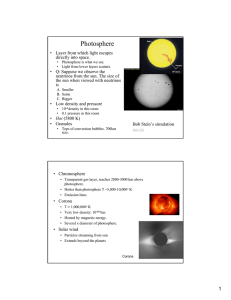
Photosphere
... Photosphere • Layer from which light escapes directly into space. • Photosphere is what we see. • Light from lower layers scatters. ...
... Photosphere • Layer from which light escapes directly into space. • Photosphere is what we see. • Light from lower layers scatters. ...
Document
... Even nearby we are uncertain! The Cyg OB2 Cluster Distance = 1.7 kpc 60 massive stars identified. ...
... Even nearby we are uncertain! The Cyg OB2 Cluster Distance = 1.7 kpc 60 massive stars identified. ...
DSST® ASTRONOMY EXAM INFORMATION
... Below is a list of reference publications that were either used as a reference to create the exam, or were used as textbooks in college courses of the same or similar title at the time the test was developed. You may reference either the current edition of these titles or textbooks currently used at ...
... Below is a list of reference publications that were either used as a reference to create the exam, or were used as textbooks in college courses of the same or similar title at the time the test was developed. You may reference either the current edition of these titles or textbooks currently used at ...
First Exam - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... 26. You look up in the night sky and see the planet Jupiter, the planet Mars, and the Moon very close together. You know that they are located in or close to one of the following. Which is it? (a) the ecliptic ∗ (b) the celestial equator (c) the zenith (d) the north celestial pole (e) the constellat ...
... 26. You look up in the night sky and see the planet Jupiter, the planet Mars, and the Moon very close together. You know that they are located in or close to one of the following. Which is it? (a) the ecliptic ∗ (b) the celestial equator (c) the zenith (d) the north celestial pole (e) the constellat ...
Part 2 - MGNet
... – Material falls straight onto white dwarf’s surface – Nuclear fusion from accreted material on surface of white dwarf causes small “novas”. ...
... – Material falls straight onto white dwarf’s surface – Nuclear fusion from accreted material on surface of white dwarf causes small “novas”. ...
L7 - QUB Astrophysics Research Centre
... Opacity Concept of opacity introduced when deriving the equation of radiation transport, and discussed extensively in the Level 3 Stellar Atmospheres course. Opacity is the resistance of material to the flow of radiation through it. In most stellar interiors it is determined by all the processes wh ...
... Opacity Concept of opacity introduced when deriving the equation of radiation transport, and discussed extensively in the Level 3 Stellar Atmospheres course. Opacity is the resistance of material to the flow of radiation through it. In most stellar interiors it is determined by all the processes wh ...
Cooling of Compact Stars
... The Astrophysical Journal V 749 N1 Chris L. Fryer et al. 2012 ApJ 749 91 ...
... The Astrophysical Journal V 749 N1 Chris L. Fryer et al. 2012 ApJ 749 91 ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 3 Stars, Galaxies, and the
... Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe ...
... Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe ...
Exploring the Universe
... spend 90% of their life. i. A diagonal band running from the bright, hot stars on the upper left to the dim, cool stars on the lower right ii. Example: The Sun lies in the main sequence iii. The sun is a yellow star (medium sized) that does fusion of hydrogen ...
... spend 90% of their life. i. A diagonal band running from the bright, hot stars on the upper left to the dim, cool stars on the lower right ii. Example: The Sun lies in the main sequence iii. The sun is a yellow star (medium sized) that does fusion of hydrogen ...
Section 4 Formation of the Universe Chapter 19
... The Beginning and End of Stars • The Beginning A star enters the first stage of its life cycle as a ball of gas and dust. Gravity pulls the gas and dust together, and hydrogen changes to helium in a processes called nuclear fusion. • The End Stars usually lose material slowly, but sometimes they can ...
... The Beginning and End of Stars • The Beginning A star enters the first stage of its life cycle as a ball of gas and dust. Gravity pulls the gas and dust together, and hydrogen changes to helium in a processes called nuclear fusion. • The End Stars usually lose material slowly, but sometimes they can ...
Paper
... Because of the dimness of the star, the evidence presented by Hajduk e al. that Sakurai’s Object has started to heat up again is indirect (Asplund, 2005). The observation conducted by scientists and astronomers suggest that there is a new area inside the old planetary nebula, which requires a stella ...
... Because of the dimness of the star, the evidence presented by Hajduk e al. that Sakurai’s Object has started to heat up again is indirect (Asplund, 2005). The observation conducted by scientists and astronomers suggest that there is a new area inside the old planetary nebula, which requires a stella ...
Bildungskonzepte von Galaxien - uni
... Potentials changing slowly Eccentricity is invariant Potentials changing rapidly Eccentricity increase with mass concentration Thus Angular momentum conserved Slow potential change: eccentricity is conserved, height above galactic plane Fast changing potential: more eccentric orbits, ...
... Potentials changing slowly Eccentricity is invariant Potentials changing rapidly Eccentricity increase with mass concentration Thus Angular momentum conserved Slow potential change: eccentricity is conserved, height above galactic plane Fast changing potential: more eccentric orbits, ...
Make Your Own Star Bracelet
... (pick up the metallic bead) "Pick up the metallic bead and thread it onto the cord. When some stars grow old, they blow off their outer layers of gas, leaving a small core that shines out radio waves as the stars rotate very fast. Astronomers did no know about these stars until they became using rad ...
... (pick up the metallic bead) "Pick up the metallic bead and thread it onto the cord. When some stars grow old, they blow off their outer layers of gas, leaving a small core that shines out radio waves as the stars rotate very fast. Astronomers did no know about these stars until they became using rad ...
Stars: Their Life and Afterlife
... fluorescence, form “planetary nebulae.” These nebulae have nothing to do with planets – they were first observed in the 1800’s and resembled Jupiter-like planets when viewed with the telescopes available then. These nebulae expand at a rate of ~10 – 30 km/s, and after 50,000 years or so have spread ...
... fluorescence, form “planetary nebulae.” These nebulae have nothing to do with planets – they were first observed in the 1800’s and resembled Jupiter-like planets when viewed with the telescopes available then. These nebulae expand at a rate of ~10 – 30 km/s, and after 50,000 years or so have spread ...
March 2011
... The image above was taken by the Hubble Space telescope and shows the Eagle Nebula (within M16) in the constellation of Serpens Caput. The nebula has been driven into pillar like structures by the powerful radiation from large young stars just out of the image to the upper right. As the gas and dust ...
... The image above was taken by the Hubble Space telescope and shows the Eagle Nebula (within M16) in the constellation of Serpens Caput. The nebula has been driven into pillar like structures by the powerful radiation from large young stars just out of the image to the upper right. As the gas and dust ...
Vibrational instability of Population III very massive mainsequence
... velocity and mass loss occurs. In addition, due to the shock dissipation, the amplitude cannot increase significantly above the value at which the shell is formed. Baraffe et al. (2001) performed linear stability analysis of Population III very massive stars and estimated mass loss due to the vibrat ...
... velocity and mass loss occurs. In addition, due to the shock dissipation, the amplitude cannot increase significantly above the value at which the shell is formed. Baraffe et al. (2001) performed linear stability analysis of Population III very massive stars and estimated mass loss due to the vibrat ...
The IR Universe
... Spitzer has found optically invisible galaxies so distant that we see them as they were only 3 billion years after the Big Bang. These galaxies are obscured by silicate dust, suggesting that planets could have formed even at this early time in the history of the Universe. ...
... Spitzer has found optically invisible galaxies so distant that we see them as they were only 3 billion years after the Big Bang. These galaxies are obscured by silicate dust, suggesting that planets could have formed even at this early time in the history of the Universe. ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.


![arXiv:1505.07406v1 [hep-ph] 27 May 2015](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007750137_1-1343a5635a0dda57ac4b2d01226e2ce5-300x300.png)



















