A Stellar Astronomy Toolbox 9
... If we think back to Galileo’s law, all objects fall at the same rate regardless of their mass, then there should be no reason that air molecules shouldn’t fall to the ground at the same rate that a book would fall. But we know that this is not the case. The atmosphere of the Earth is not lying on th ...
... If we think back to Galileo’s law, all objects fall at the same rate regardless of their mass, then there should be no reason that air molecules shouldn’t fall to the ground at the same rate that a book would fall. But we know that this is not the case. The atmosphere of the Earth is not lying on th ...
PDF version
... to the sun, and it's the smallest of the eight. Venus is the second-closest to the sun, and it's the hottest planet because of its gaseous atmosphere. Sunlight gets trapped and heats up Venus. Earth, the third planet from the sun, is the one we live on. Mars, the red planet, is fourth from the sun, ...
... to the sun, and it's the smallest of the eight. Venus is the second-closest to the sun, and it's the hottest planet because of its gaseous atmosphere. Sunlight gets trapped and heats up Venus. Earth, the third planet from the sun, is the one we live on. Mars, the red planet, is fourth from the sun, ...
Answer to question 1 - Northwestern University
... expands and “over shoots the point where the internal heat (and light) pressure will hold up the envelope. •The result is that the envelope then comes falling down, • Over shoots inward • Then starts over ...
... expands and “over shoots the point where the internal heat (and light) pressure will hold up the envelope. •The result is that the envelope then comes falling down, • Over shoots inward • Then starts over ...
42 SCIENTIFIC AMERICAN OCTOBER 2006 TEN
... scales. Particle physics, nuclear physics, nickel and iron. Observationally, howfluid dynamics and general relativity are complicated enough on their own, but a supernova simulation must consider all of them at once. ...
... scales. Particle physics, nuclear physics, nickel and iron. Observationally, howfluid dynamics and general relativity are complicated enough on their own, but a supernova simulation must consider all of them at once. ...
File - 5th Grade Science Almost done!!!!!!!!!
... • The first thing the students do when they enter the room is write down the homework (see next slide) in stone-silence. • After about 20 to 30 seconds of silence I tell the students “Please begin the warm up.” • Please go through the ppt with the students. Students will have to write items in blue ...
... • The first thing the students do when they enter the room is write down the homework (see next slide) in stone-silence. • After about 20 to 30 seconds of silence I tell the students “Please begin the warm up.” • Please go through the ppt with the students. Students will have to write items in blue ...
Stellar Spectral Classes
... the appearance of the two stars as seen with the unaided eye by an observer on the Earth. similarity................................................................................................. ...
... the appearance of the two stars as seen with the unaided eye by an observer on the Earth. similarity................................................................................................. ...
"Dark Matter in the Milky Way - how to find it using Gaia and other
... We combined these approaches to analyse RAVE survey data 1. For a given DM halo - demand potential fits known constraints. This Φ will have some vertical disc density profile at the Sun 2. Fit f(J) to (binned) kinematics of RAVE giants, which predicts a different disc density profile. 3. Iterate unt ...
... We combined these approaches to analyse RAVE survey data 1. For a given DM halo - demand potential fits known constraints. This Φ will have some vertical disc density profile at the Sun 2. Fit f(J) to (binned) kinematics of RAVE giants, which predicts a different disc density profile. 3. Iterate unt ...
Hitomi Observation of the Highly Obscured High-Mass X-ray
... of continuum and line components significantly decreased in this ten years while the equivalent widths increased. Unabsorbed luminosity in 2 to 10 keV is 5.8×1035 ergs/s, which is far below the Eddington limit of 1.8×1038 ergs/s for a neutron star of 1.4 M⊙ and hence permits moderate accretion. The ...
... of continuum and line components significantly decreased in this ten years while the equivalent widths increased. Unabsorbed luminosity in 2 to 10 keV is 5.8×1035 ergs/s, which is far below the Eddington limit of 1.8×1038 ergs/s for a neutron star of 1.4 M⊙ and hence permits moderate accretion. The ...
The impact of black holes on the Universe
... • Assume disc radiates as a black body (¾T4 per unit area & time) so luminous power is PL=¾T4(4¼r±r) • Now equate PL to total power = 4Pm= (2GM/r2)(dm/dt)±r • Choose dm/dt to give characteristic BH growth time 100 Myr and solve for T and L ...
... • Assume disc radiates as a black body (¾T4 per unit area & time) so luminous power is PL=¾T4(4¼r±r) • Now equate PL to total power = 4Pm= (2GM/r2)(dm/dt)±r • Choose dm/dt to give characteristic BH growth time 100 Myr and solve for T and L ...
Dark Matter in the Milky Way - how to find it using Gaia and other
... We combined these approaches to analyse RAVE survey data 1. For a given DM halo - demand potential fits known constraints. This ứ will have some vertical disc density profile at the Sun 2. Fit f(J) to (binned) kinematics of RAVE giants, which predicts a different disc density profile. 3. Itera ...
... We combined these approaches to analyse RAVE survey data 1. For a given DM halo - demand potential fits known constraints. This ứ will have some vertical disc density profile at the Sun 2. Fit f(J) to (binned) kinematics of RAVE giants, which predicts a different disc density profile. 3. Itera ...
10 Stellar Evolution - Journigan-wiki
... Small-Mass Stars Small-mass stars live for billions of years. They are thrifty with their fuel. As their hydrogen becomes diminished, they begin to convert helium into yet heavier elements. ...
... Small-Mass Stars Small-mass stars live for billions of years. They are thrifty with their fuel. As their hydrogen becomes diminished, they begin to convert helium into yet heavier elements. ...
Star Name __Direction ___ Degrees
... 21. Name three stars that are second magnitude or brighter. Give their location in direction and degrees above the horizon on the celestial sphere. Star Name __Direction Example: Polaris North ___________ ____________ ...
... 21. Name three stars that are second magnitude or brighter. Give their location in direction and degrees above the horizon on the celestial sphere. Star Name __Direction Example: Polaris North ___________ ____________ ...
$doc.title
... • An important distinction is that this gas unaffiliated with galaxies samples the low-density regions, which are still in a linear regime ...
... • An important distinction is that this gas unaffiliated with galaxies samples the low-density regions, which are still in a linear regime ...
Lesson Plan - ScienceA2Z.com
... 1. Spiral galaxies are disk-shaped assemblages with curving, dusty arms. 2. Spiral galaxies are named for the (usually two-armed) spiral structures that extend from the bulge into the disk. 3. The spiral arms are sites of ongoing star formation and are brighter than the surrounding disk because of ...
... 1. Spiral galaxies are disk-shaped assemblages with curving, dusty arms. 2. Spiral galaxies are named for the (usually two-armed) spiral structures that extend from the bulge into the disk. 3. The spiral arms are sites of ongoing star formation and are brighter than the surrounding disk because of ...
What is Epsilon Aurigae?
... • Very massive?, could it form planets? • Low mass? , could it form planets? •Is there a central object(s)? • Disk Morphology? Disk, “donut”, ring, gaps? Thick, thin? etc.. ...
... • Very massive?, could it form planets? • Low mass? , could it form planets? •Is there a central object(s)? • Disk Morphology? Disk, “donut”, ring, gaps? Thick, thin? etc.. ...
pptx
... because carbon nuclei have an energy level at exactly the right place otherwise carbon would be a rare element and we would not exist! ...
... because carbon nuclei have an energy level at exactly the right place otherwise carbon would be a rare element and we would not exist! ...
Week 6
... The bright star in the top left corner of Orion, Betelgeuse, has a radius 936 times that of the Sun and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What is the luminosity of this star? If Betelgeuse is 640 ly from Earth, what is the brightness of the light from Betelgeuse that reaches Earth? ...
... The bright star in the top left corner of Orion, Betelgeuse, has a radius 936 times that of the Sun and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What is the luminosity of this star? If Betelgeuse is 640 ly from Earth, what is the brightness of the light from Betelgeuse that reaches Earth? ...
Elements from Stardust
... they can join together in a process called nuclear fusion. • In nuclear fusion, atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus, releasing huge amounts of energy in the process. • Inside stars, nuclear fusion combines smaller nuclei into larger nuclei, thus creating heavier elements. ...
... they can join together in a process called nuclear fusion. • In nuclear fusion, atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus, releasing huge amounts of energy in the process. • Inside stars, nuclear fusion combines smaller nuclei into larger nuclei, thus creating heavier elements. ...
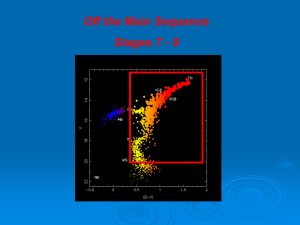
Common Stages 7 to 9
... While on the main sequence, the star is burning hydrogen. It’s luminosity is determined by the stars mass. The most intense fusion is occurring at the center regions of the core (highest pressure and temperature). ...
... While on the main sequence, the star is burning hydrogen. It’s luminosity is determined by the stars mass. The most intense fusion is occurring at the center regions of the core (highest pressure and temperature). ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.